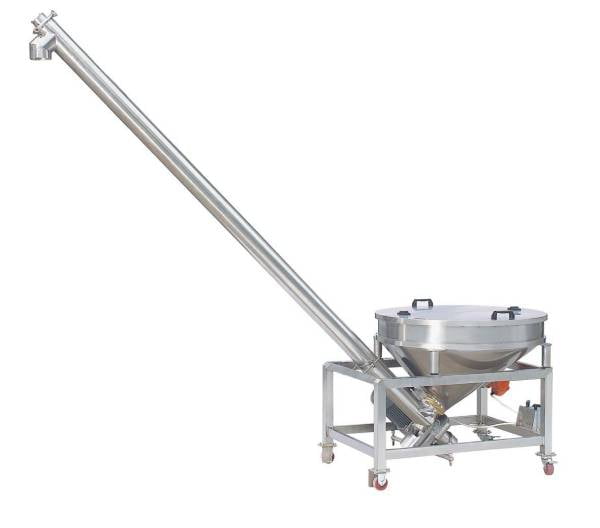
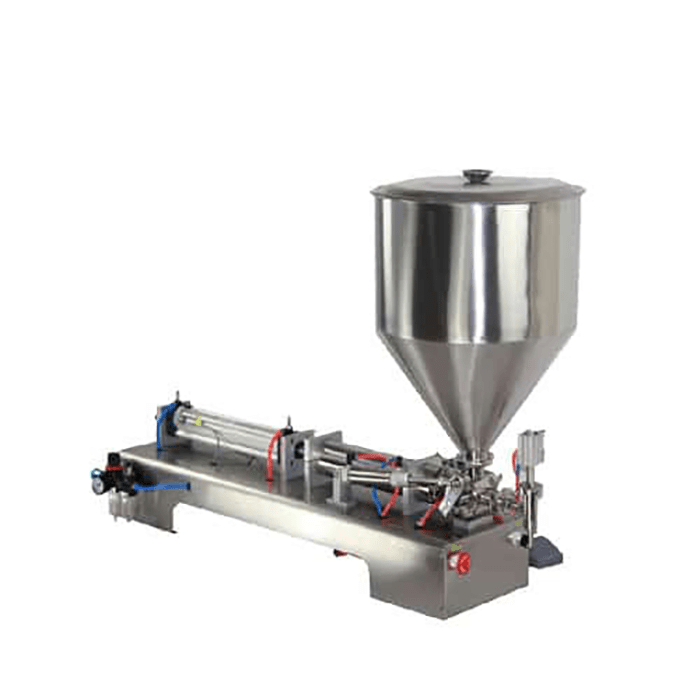
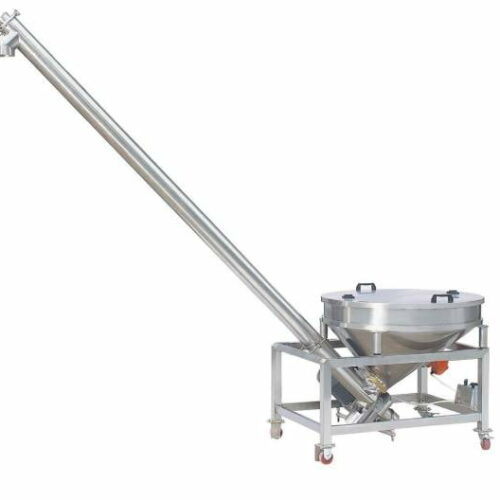
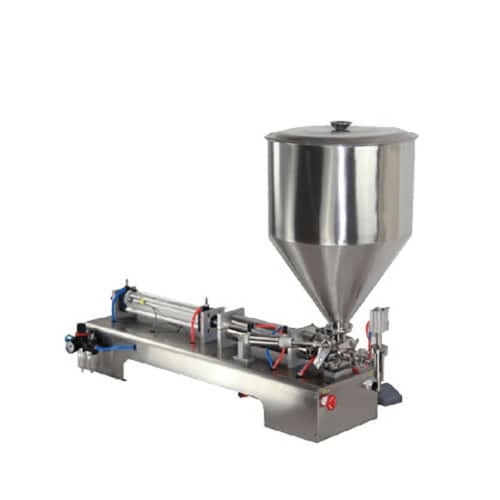
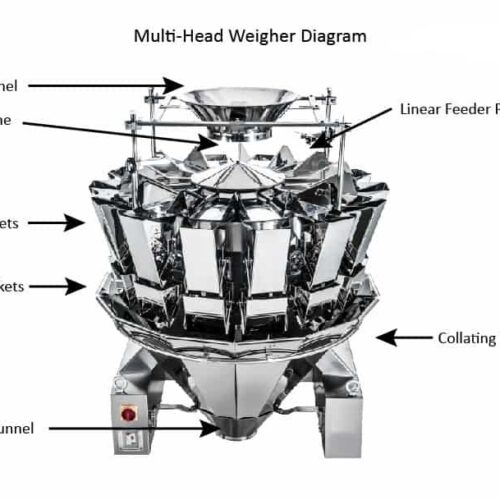
List Technical Parameters of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment is a category of machinery and devices that support primary packaging operations, enhancing efficiency, precision, and automation in the packaging process. Here are the critical technical parameters:
1. Throughput Capacity: Measured in units per minute (UPM), it reflects the speed at which the equipment can handle packaging materials or products.
2. Power Requirements: Voltage (V) and power consumption (kW) necessary for operation, considering local electrical standards.
3. Material Compatibility: Types of materials (plastics, metals, paper) that can be processed, including thickness and strength specifications.
4. Dimensions and Weight: Physical size (length, width, height) and weight of the equipment, impacting floor space and mobility.
5. Control System: Type of automation (PLC, HMI), ease of integration with other systems, and user interface features for operating the equipment.
6. Accuracy and Precision: Tolerances and repeatability of the equipment, usually specified in millimeters or microns, crucial for tasks like labeling and coding.
7. Environmental Conditions: Operating range of temperature and humidity, which affects the performance and longevity of the equipment.
8. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency, ease of access for service, and types of maintenance routines (scheduled or predictive).
9. Safety Features: Compliance with safety standards (CE, OSHA), emergency stops, guards, and alarms to protect operators.
10. Speed Adjustment: Range and method of speed control to tailor performance as per the production line requirements.
11. Connectivity: Networking capabilities (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, IoT) for data logging, remote monitoring, and integration with enterprise systems.
12. Flexibility and Adaptability: Ability to handle different product sizes and types with minimal changeover time.
These parameters collectively determine the suitability, efficiency, and operational effectiveness of auxiliary packaging equipment in various industrial contexts.
List Product features of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment refers to the supplementary machinery that enhances and supports the primary packaging operations in manufacturing and processing industries. Here are some notable features:
1. Versatility:
- Capable of handling various packaging materials such as plastic, glass, metal, and paper.
- Compatible with multiple packaging forms including bottles, pouches, cartons, and trays.
2. Automation Integration:
- Seamlessly integrates with existing automated packaging lines.
- Supports advanced automation technologies such as robotics.
3. Efficiency:
- Increases production speed and throughput.
- Reduces manual labor requirements and operational costs.
4. Precision & Accuracy:
- Ensures accurate placement and alignment of products and packaging materials.
- Minimizes waste and enhances product consistency.
5. Flexibility:
- Easily adjustable to accommodate different sizes and shapes of packaging.
- Quick changeover capabilities for various product runs.
6. Quality Control:
- Includes inspection and verification systems to ensure packaging integrity.
- Capable of detecting defects and ensuring compliance with standards.
7. User-friendly:
- Intuitive interfaces and controls for easy operation and monitoring.
- Minimal training required for operators.
8. Durability:
- Constructed with high-quality materials to withstand rigorous industrial environments.
- Long operational lifespan with minimal maintenance requirements.
9. Safety:
- Equipped with advanced safety features to protect operators.
- Complies with industry safety standards and regulations.
10. Versatile Use Cases:
- Applicable in various industries including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
- Supports processes like labeling, sealing, wrapping, coding, and palletizing.
11. Cost-Effective:
- Optimizes resource utilization and reduces downtime.
- Potential to achieve a high return on investment (ROI) through improved productivity.
Auxiliary packaging equipment streamlines packaging processes, offering enhanced operational efficiency, precision, and flexibility while ensuring high-quality and safe packaging solutions.
List Application of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment plays a crucial role in optimizing packaging operations across various industries. These machines and devices support primary packaging machinery, enhancing efficiency, quality, and flexibility. Here are key applications:
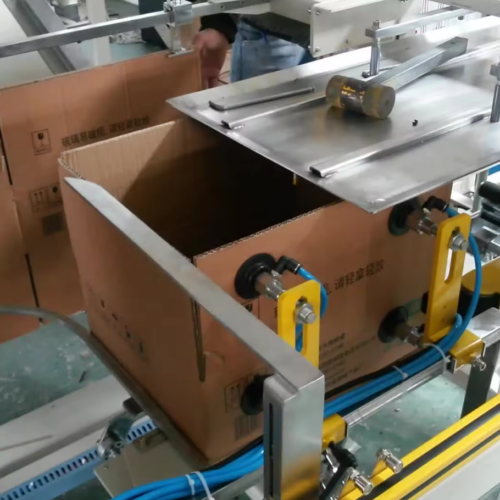
1. Carton Erectors and Sealers: These machines automate the process of forming, filling, and sealing cartons, improving throughput and consistency in packaging lines, commonly used in food, beverage, and electronics industries.
2. Labeling Machines: Essential for product identification, these machines apply labels accurately and swiftly, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and enhancing brand visibility. Used extensively in pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and logistics.
3. Conveying Systems: Conveyor belts and systems transport products through different stages of the packaging process, enabling seamless integration and reducing manual handling. Widely utilized in manufacturing and e-commerce fulfillment centers.
4. Palletizers and Depalletizers: These robotic or mechanical systems automatically stack and unstack products on pallets, increasing efficiency in warehousing and distribution activities. Industries like food processing, beverage manufacturing, and consumer goods benefit significantly.
5. Vacuum Sealers: Used to extend shelf life by removing air from packaging, maintaining product freshness. Common in food packaging, medical devices, and electronics.
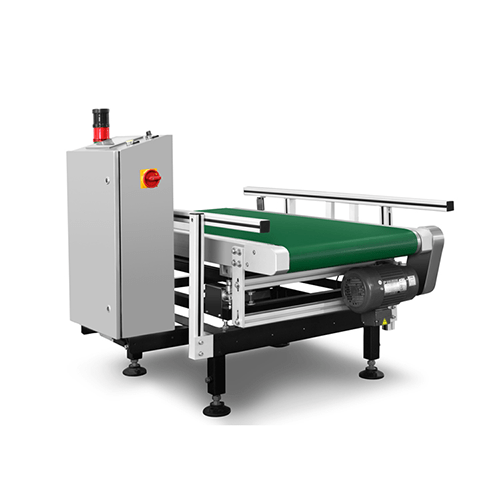
6. Checkweighers: Verify the weight of packaged goods, ensuring accurate content and compliance with labeling regulations. Critical in the food, pharmaceutical, and packaging industries.
7. Shrink Wrapping Machines: Apply a tight plastic film around products, providing tamper evidence, protection, and compactness. Popular in retail, logistics, and food sectors.
8. Stretch Wrappers: Secure products on pallets with stretch film, offering stability and protection during transportation. Used in logistics, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
9. Metal Detectors and X-ray Systems: Detect contaminants in packaged goods, ensuring safety and quality. Essential for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods industries.
10. Coding and Marking Systems: Print expiry dates, batch numbers, and barcodes on products, facilitating traceability and quality control. Utilized in almost every manufacturing and packaging sector.
These auxiliary packaging tools streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and enhance product integrity across various industries, playing a pivotal role in modern packaging solutions.
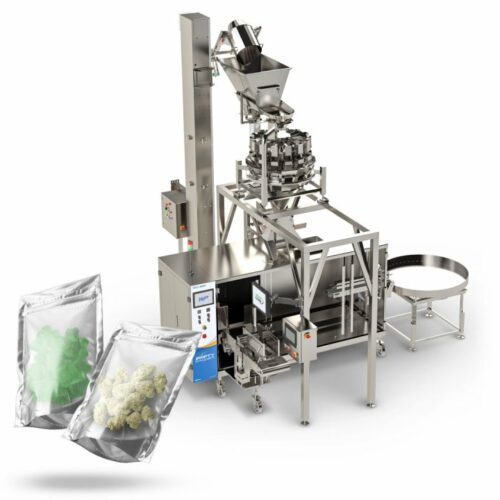
List Various Types of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment refers to machines and devices that support the main packaging process, enhancing efficiency, consistency, and workflow. Here are various types of auxiliary packaging equipment:
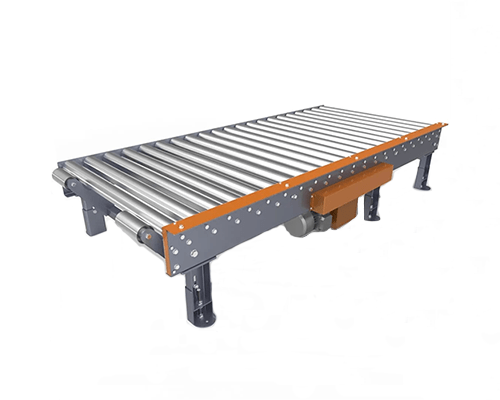
1. Conveyors: These transport materials and products between different stages of the packaging line. They can be belt, roller, or chain conveyors, depending on the type of product and packaging process.
2. Accumulators: These temporarily hold products during the packaging process, ensuring a smooth flow and mitigating the impact of any bottlenecks.
3. Carton Erectors: These machines automatically form cartons from flat boxes, preparing them for filling.
4. Case Sealers: These seal boxes or cases after they have been filled, ensuring they are secure for shipping or further handling.
5. Palletizers: These arrange products onto pallets for storage or shipping, improving handling efficiency and load stability.
6. Pallet Wrappers: These machines wrap stretch film around loaded pallets to secure products during transport.
7. Labeling Machines: These apply labels to packages, ensuring proper identification, branding, or compliance with regulations.
8. Coding and Marking Systems: These systems print essential information (e.g., manufacturing date, batch number) on packages for traceability and compliance.
9. Inspection Systems: These include metal detectors, checkweighers, and X-ray systems that ensure product quality by detecting contaminants or verifying product weight.
10. Shrink Wrappers: These machines apply heat to shrink film tightly around products, providing tamper-evident packaging and protection.
11. Tray Sealers: These seal preformed trays with a film lid, often used for food packaging to ensure freshness and extend shelf life.
12. Bagging Machines: These automate the process of filling and sealing bags, commonly used in food and pharmaceutical industries.
13. Robotic Systems: These are used for tasks like picking, placing, and stacking products, enhancing precision and speed in complex packaging lines.
14. Feeding Systems: These ensure that products are consistently fed into the packaging line, maintaining a steady flow and reducing the need for manual intervention.
By integrating these auxiliary systems, packaging operations can achieve higher efficiency, consistency, and overall productivity.
Custom Manufacturing Options for auxiliary packaging equipment
Custom manufacturing options for auxiliary packaging equipment can greatly enhance the efficiency and versatility of your production line. These options allow you to tailor equipment to your specific needs, ensuring seamless integration and maximizing productivity.
1. Material Handling Systems: Custom conveyors, hoppers, and feeders ensure smooth material flow. Options include variable speed controls, custom shapes, and specialized materials to handle everything from fragile items to bulk goods.
2. Labeling Solutions: Tailor labeling machines to accommodate various product sizes and shapes. Features can include adjustable applicator heads, multi-panel labeling, and integration with software for tracking and compliance.
3. Sealing and Closing Equipment: Custom heat sealers, glue applicators, and twist-tie machines can be designed to match your product specifications. Options like adjustable sealing temperatures, custom die cuts, and different closure mechanisms add versatility.
4. Inspection and Quality Control: Integrate customized vision systems, metal detectors, and checkweighers to ensure product quality. Configurations can include multi-camera setups, custom software algorithms, and automated rejection systems.
5. Cartoning and Case Packing: Customizable cartoners and case packers can be adapted for various product dimensions and package styles. Options like modular components, quick-change tooling, and robotic integration help cater to diverse packaging needs.
6. Palletizing and Depalletizing: Custom robotic and mechanical solutions for stacking and unsticking products on pallets can improve efficiency. Options include adjustable grippers, pattern programming, and heavy-duty construction for various weight capacities.
7. Integration and Automation: Fully integrated systems linking multiple pieces of auxiliary equipment can streamline processes. Custom control panels, software solutions, and IoT-enabled devices ensure cohesive operation and data management.
Customization not only optimizes functionality but also provides greater flexibility to adapt to future needs, ensuring scalable and sustainable packaging solutions. Partnering with a manufacturer experienced in custom designs can deliver equipment that perfectly aligns with your operational requirements.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Quality Control in Auxiliary Packaging Equipment:
1. Incoming Material Inspection: Ensure raw materials and components meet specified requirements.
2. In-Process Quality Checks: Conduct inspections during various stages of production to detect and correct flaws early.
3. Calibration and Maintenance: Regularly calibrate machinery and perform maintenance to ensure consistent performance.
4. Final Product Testing: Inspect and test finished equipment for functionality, durability, and safety standards.
5. Documentation and Traceability: Maintain detailed records of inspections, tests, and compliance with industry standards.
6. Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops and root cause analysis to continually improve processes and reduce defects.
Manufacturing Process of Auxiliary Packaging Equipment:
1. Design and Engineering: Develop detailed designs and perform simulations. Use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software for precise engineering.
2. Material Procurement: Source high-quality raw materials and components from vetted suppliers.
3. Machining and Fabrication:
– Cutting and Shaping: Utilize CNC machines, laser cutters, and other precision tools.
– Welding and Assembly: Weld and assemble components according to design specifications.
4. Sub-Assembly Production: Manufacture and test critical sub-assemblies (e.g., conveyors, sealing units).
5. Assembly: Integrate sub-assemblies into the main unit, ensuring proper alignment and connections.
6. Electrical and Software Integration: Install and configure control systems, sensors, and software.
7. Quality Testing: Conduct thorough testing, including electrical safety, operational efficiency, and performance under load.
8. Finishing: Apply protective coatings, paint, and other finishes for durability and aesthetics.
9. Final Inspection: Perform a comprehensive inspection to ensure all specifications are met and equipment is ready for delivery.
This streamlined process ensures that auxiliary packaging equipment is manufactured to the highest standards of quality and reliability.
How to use "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment complements primary packaging machines to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in packaging operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use auxiliary packaging equipment effectively:
1. Identify Needs:
- Determine which processes need auxiliary support, such as labeling, sealing, or quality inspection.
2. Select Appropriate Equipment:
- Based on your needs, choose from common auxiliary equipment like conveyors, checkweighers, case packers, palletizers, and shrink wrappers.
3. Installation:
- Place the equipment strategically within your production line to ensure smooth workflow.
- Ensure all safety measures are in place and that the equipment is securely mounted.
4. Integration:
- Connect auxiliary equipment to primary packaging machines, ensuring synchronization.
- Use appropriate interfacing technology like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for seamless communication.
5. Setup and Calibration:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines to set up and calibrate the equipment.
- Conduct test runs to ensure accurate operation.
6. Training:
- Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper use, troubleshooting, and upkeep of the equipment.
- Provide comprehensive manuals and quick guides.
7. Operation:
- Regularly monitor the equipment during operation for any anomalies.
- Use human-machine interfaces (HMIs) for real-time feedback and control adjustments.
8. Maintenance:
- Implement a routine maintenance schedule to keep the equipment running efficiently.
- Quickly address any mechanical or software issues to minimize downtime.
9. Quality Control:
- Utilize auxiliary equipment for quality checks (e.g., vision systems to inspect labels or seals).
- Ensure feedback loops are in place to address non-conformities promptly.
10. Optimization:
- Continuously assess and optimize the flow and performance of the auxiliary equipment to meet evolving production needs.
By following these steps, you can effectively incorporate auxiliary packaging equipment into your operations, enhancing productivity and ensuring consistent product quality.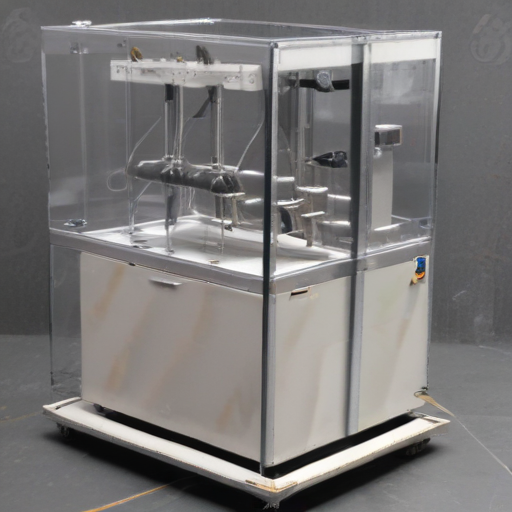
List Properties and Terms of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
Auxiliary packaging equipment refers to machines and systems that complement primary packaging processes, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, or capability in a packaging line. Here are some key properties and terms related to auxiliary packaging equipment:
Properties:
1. Enhancement of Primary Functions: These machines support main packaging equipment by performing secondary tasks such as labeling, inspection, or case packing.
2. Automation and Integration: Many auxiliary machines are designed to be seamlessly integrated into existing packaging lines, enhancing automation and reducing manual labor.
3. Versatility: Often modular, enabling customization to meet specific packaging needs and easily adaptable to different products or lines.
4. Efficiency and Speed: Designed to increase overall packaging line efficiency by speeding up processes that would otherwise be time-consuming if done manually.
5. Precision and Accuracy: Provides high levels of precision in tasks such as weighing, labeling, or quality inspection, ensuring consistency and reducing waste.
6. Space-saving Design: Often compact to fit within tight production environments without requiring significant additional space.
Terms:
1. Case Packer: Automated machinery for loading products into cases, boxes, or trays.
2. Palletizer: Equipment that stacks and organizes finished product packages onto pallets for shipment.
3. Label Applicator: Machine for affixing labels to products or packaging, ensuring accurate placement.
4. Checkweigher: Weighing machines used inline to ensure packaged products meet specified weight criteria.
5. Shrink Wrappers: Machines that apply and heat-shrink plastic film around products for protection or bundling.
6. Conveyor Systems: Mechanical handling equipment used for moving products between different stages of packaging.
7. Carton Sealer: Automated equipment that seals cartons or boxes, typically using tape or glue.
8. Vision Inspection Systems: Advanced setups incorporating cameras and sensors to inspect packaging quality, label accuracy, and product integrity.
9. Rewinder: Equipment used in film or label production lines to roll finished products onto cores for further processing or shipping.
10. De-palletizer: Machines that remove products from pallets for further processing or packaging.
Auxiliary packaging equipment is essential to modern packaging lines, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently while maintaining high standards of quality and consistency.
List The Evolution history of "auxiliary packaging equipment"
The history of auxiliary packaging equipment has evolved significantly over time to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and automation in various industries.
1. Early 1900s – Manual Handling: Packaging relied heavily on manual labor, with workers handling and assembling products individually. Simple machines like hand-cranked fillers and labelers started to appear.
2. 1950s – Mechanization: Post World War II, the advent of industrial automation brought basic mechanical packaging equipment, such as conveyers, semi-automatic fillers, and carton sealers. This period saw the introduction of auxiliary equipment like the first mechanical palletizers, which began to automate end-of-line operations.
3. 1970s – Electronics Integration: With the rise of electronics, packaging machines integrated basic electronic controls, improving precision and reducing human intervention. Auxiliary equipment evolved to include check weighers, metal detectors, and basic PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems for streamlined processes.
4. 1980s-1990s – Computerization and Robotics: The introduction of computers and robotic technologies revolutionized auxiliary packaging equipment. Automated packaging lines became more prevalent, integrating advanced sensors, vision systems, and multi-axis robots for tasks like sorting, packing, and palletizing. This era saw the development of more sophisticated check weighers, automated case packers, and robotic palletizers.
5. 2000s – Intelligent Systems: With the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) and smart manufacturing, auxiliary packaging equipment became increasingly interconnected and data-driven. Advanced SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems allowed for real-time monitoring and optimization. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) began to handle material transport, and high-precision vision systems improved quality control.
6. 2010s and Beyond – Industry 4.0: The latest evolution is marked by the integration of smart technologies like AI, machine learning, and advanced robotics. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators, enhancing safety and efficiency. Predictive maintenance, powered by data analytics, reduces downtime and enhances equipment longevity. Additionally, advancements in 3D printing are influencing prototyping and the creation of custom packaging solutions.
This progression underscores a continuous trend toward increased automation, efficiency, and integration within the packaging industry.
How to Select a Reliable auxiliary packaging equipment
Selecting reliable auxiliary packaging equipment is crucial for ensuring efficiency and quality in your packaging process. Here’s a concise guide to help:
1. Define Your Needs: Understand your specific packaging requirements, including the type of products, volume, and packaging materials. This helps in identifying suitable equipment features.
2. Research Manufacturers: Look for reputable manufacturers with a proven track record. Check online reviews, customer testimonials, and industry awards.
3. Equipment Quality: Prioritize equipment made from durable materials. High-quality construction minimizes downtime and maintenance issues.
4. Compatibility and Flexibility: Ensure the equipment is compatible with your existing systems. Flexible equipment that can handle various tasks is advantageous for future scalability.
5. Technology and Automation: Modern equipment with advanced automation can increase productivity and accuracy. Look for features like touch-screen controls, easy programmability, and integration capabilities.
6. Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient machines can significantly reduce operational costs. Check for energy ratings and eco-friendly features.
7. Maintenance and Support: Reliable equipment should come with comprehensive support and maintenance plans. Choose vendors with robust after-sales support, including training, spare parts availability, and technical assistance.
8. Cost vs. Value: Don’t just go for the cheapest option. Consider the overall value, including productivity gains, maintenance costs, and lifespan.
9. Compliance and Safety: Ensure the equipment meets all relevant industry standards and safety regulations. This protects your workforce and minimizes legal risks.
10. Trial and Demonstration: Whenever possible, request a demonstration or trial period. This allows you to assess the equipment’s performance in real-world conditions.
By meticulously evaluating these factors, you can select reliable auxiliary packaging equipment that enhances your operations and provides long-term benefits.
List "auxiliary packaging equipment" FAQ
Auxiliary Packaging Equipment FAQ
-
What is auxiliary packaging equipment?
Auxiliary packaging equipment includes machinery and tools that support the main packaging process. Examples include conveyors, palletizers, shrink wrap machines, and coding systems. -
Why is auxiliary packaging equipment important?
This equipment enhances efficiency, ensures product safety, and improves packaging consistency. It also helps streamline workflows and reduce manual labor. -
Can auxiliary packaging equipment be integrated with existing systems?
Yes, most auxiliary equipment is designed to integrate seamlessly with primary packaging systems, offering modular and customizable solutions. -
What types of auxiliary packaging equipment are available?
Key types include:- Conveyors for material transport
- Palletizers for stacking products
- Shrink wrap machines for packaging
- Labeling and coding systems for product identification
- Case packers for secondary packaging
-
How do I choose the right auxiliary equipment?
Consider factors like production speed, product type, packaging material, and existing equipment compatibility. Consulting with equipment suppliers and conducting a needs assessment can also help. -
What are the maintenance requirements for auxiliary packaging equipment?
Regular inspections, cleaning, and servicing are essential. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for preventative maintenance to ensure longevity and optimal performance. -
Are there safety considerations for using auxiliary packaging equipment?
Yes, ensure proper training for operators, use safety guards and emergency stop features, and conduct regular safety audits to comply with regulations. -
How does auxiliary packaging equipment impact production costs?
While initial investment might be high, the long-term benefits include improved efficiency, reduced labor costs, and minimized downtime, ultimately lowering overall production costs. -
Can auxiliary packaging equipment be customized?
Many manufacturers offer customizable solutions tailored to specific needs, including adjustments for size, speed, and functionality. -
Where can I purchase auxiliary packaging equipment?
You can buy auxiliary packaging equipment from specialized industrial equipment suppliers, both online and offline, who often provide installation and ongoing support services.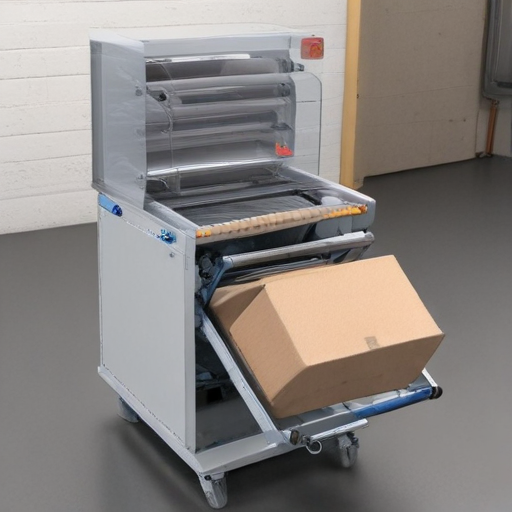
Top 10 FAQ with answer about auxiliary packaging equipment for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here is a concise FAQ on auxiliary packaging equipment for buyers sourcing from China:
-
What is auxiliary packaging equipment?
Auxiliary packaging equipment includes machines that support primary packaging processes, like conveyors, labelers, and palletizers. These machines enhance efficiency, handling, and packing operations. -
Why source auxiliary packaging equipment from China?
China offers cost-effective manufacturing, advanced technology, and a vast selection of auxiliary packaging equipment. Chinese suppliers often provide competitive prices and customization options to suit various needs. -
How to ensure quality when sourcing from China?
Verify certifications (ISO, CE), request samples, and conduct factory audits. Consider third-party inspection services to ensure the equipment meets your standards before shipment. -
What are the payment terms for ordering from Chinese suppliers?
Common terms include 30% upfront and the remaining 70% before shipping. Letter of Credit (LC) and Trade Assurance through Alibaba are also popular for added security. -
How long is the lead time for manufacturing and shipping?
Lead times vary but typically range from 30 to 60 days for manufacturing. Shipping can take an additional 2-6 weeks depending on the destination and shipping method. -
Are there warranties and after-sales services?
Most reputable suppliers offer warranties ranging from 1 to 2 years. After-sales services can include spare parts, technical support, and online troubleshooting. -
How to handle communication and language barriers?
Many Chinese suppliers have English-speaking sales teams. Use clear, simple language and confirm mutual understanding through written agreements. -
What transportation options are available for shipping equipment?
Common options include sea freight (cost-effective for bulky items), air freight (faster but expensive), and express courier services for smaller items. -
Can I customize the equipment to my specific needs?
Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization services. Provide detailed specifications and discuss feasibility and cost implications with the supplier. -
What should I look out for in supplier agreements and contracts?
Ensure they include detailed product specifications, payment terms, delivery timeline, warranty, and after-sales support clauses. Having clear terms prevents misunderstandings.
By considering these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing auxiliary packaging equipment from China.