List Technical Parameters of "capping equipment"
Capping equipment is essential in various industries for sealing containers with caps or lids. Here are the key technical parameters to consider when evaluating capping equipment:
1. Cap Type Compatibility: Screw caps, snap caps, corks, ROPP (Roll-On Pilfer Proof), etc.
2. Container Type: Bottles, jars, vials, etc. of varying shapes and sizes.
3. Closure Diameter: Specifies the range of cap sizes the machine can accommodate.
4. Torque Range: The amount of force applied to tighten the cap, measured in Newton meters (Nm).
5. Production Speed: Measured in caps per minute or hour, which can vary from a few to several thousand.
6. Automation Level: Manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic systems, impacting operational efficiency and labor requirements.
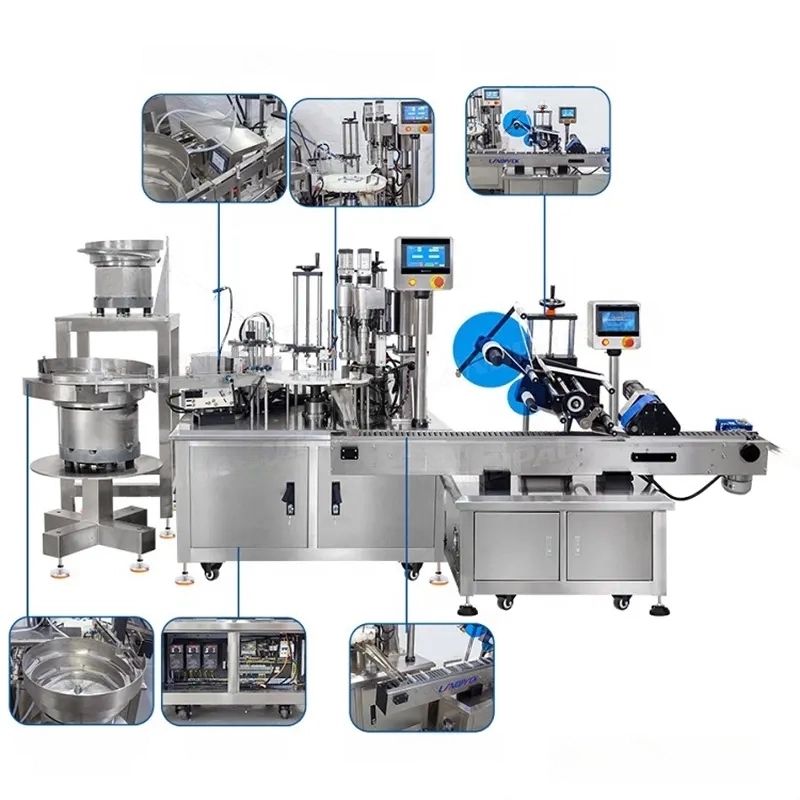
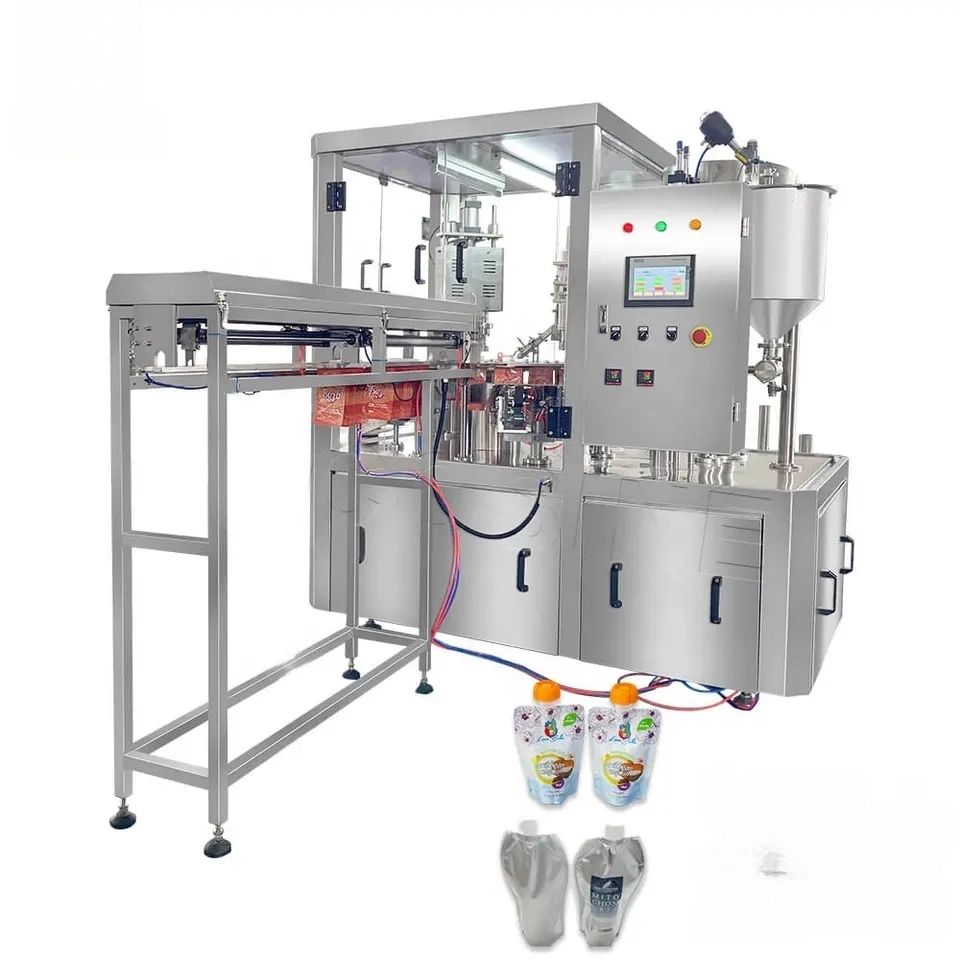
7. Cap Feeding Mechanism: Methods include vibratory bowl feeders, centrifugal feeders, or elevator systems to orient and deliver caps to the capping head.
8. Adjustability: Ability to adjust for different container heights and diameters.
9. Changeover Time: The time required to switch from one product type or size to another, affecting productivity.
10. Construction Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum, or other materials that impact durability, hygiene, and maintenance requirements.
11. Control System: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) with HMI (Human-Machine Interface) screens for ease of operation and precision.
12. Power Requirement: Electrical specifications, typically ranging from single-phase to three-phase power.
13. Air Pressure Requirement: For pneumatic systems, indicating the PSI or bar needed for optimum operation.
14. Sensor Technology: Sensors for detecting the presence of a cap, ensuring proper alignment, and confirming closure integrity.
15. Compliance Standards: Ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations like FDA, CE, or GMP for quality and safety.
16. Maintenance and Serviceability: Accessibility of parts for routine maintenance and the availability of service support.
17. Footprint: The space the equipment occupies on the production floor.
Understanding these parameters helps in selecting the most suitable capping equipment for specific production needs, ensuring efficiency, and maintaining product quality.
List Product features of "capping equipment"
Capping equipment is essential for sealing containers in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, cosmetics, and chemicals. Here are some critical features of capping equipment:
1. Versatility:
– Multi-capability: Handles various cap types such as screw, snap, and ROPP (Roll On Pilfer Proof) caps.
– Container Flexibility: Compatible with a wide range of container shapes and sizes.
2. Efficiency:
– High Throughput: Capable of sealing a high volume of containers per minute.
– Automated Operations: Minimizes manual intervention, increasing productivity.
3. Precision:
– Accurate Torque Control: Ensures consistent seal integrity without damaging caps or containers.
– Consistent Application: Provides uniform pressure and alignment.
4. Ease of Use:
– User-friendly Interface: Simplified settings and controls for easy operation.
– Quick Changeovers: Facilitates rapid adjustments for different cap or container sizes.
5. Durability:
– Robust Construction: Made with high-quality materials for long-lasting performance.
– Low Maintenance: Designed for minimal downtime and easy servicing.
6. Safety:
– Protective Features: Includes guards and emergency stop functions to protect operators.
– Compliance: Meets industry standards and regulations.
7. Customization:
– Tailored Solutions: Options to customize machinery to meet specific production needs.
– Modular Design: Expandable with additional features and upgrades.
8. Integration:
– Seamless Compatibility: Easily integrates with existing production lines and automated systems.
– Data Connectivity: Supports monitoring and data collection for quality control and traceability.
These features ensure that capping equipment is versatile, efficient, precise, easy to use, durable, safe, customizable, and integratable, making it a crucial component in modern packaging operations.
List Application of "capping equipment"
Capping equipment is utilized across diverse industries to secure caps onto containers. Here are a few notable applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry: Ensures bottles and jars (e.g., sodas, sauces) are sealed to maintain freshness and prevent contamination.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry: Used to seal medicine bottles, ensuring product integrity and tamper-evidence to maintain consumer safety.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care: Helps in capping products like lotions, shampoos, and creams, ensuring that packaging meets aesthetic and safety standards.
4. Chemical Industry: Seals containers holding chemicals, protecting against spills, contamination, and ensuring safe storage and transport.
5. Agriculture: Used for sealing pesticide, herbicide, and seed containers, ensuring that the products are securely closed and preventing leakage.
6. Household Products: Capping equipment is essential for products like detergents, cleaners, and other household items to ensure they are user-friendly and leak-proof.
7. Automotive Industry: Seals containers holding lubricants, coolants, and other automotive fluids, maintaining product quality and preventing contamination.
8. Health and Wellness: Involved in capping nutritional supplements and essential oils to maintain their potency and safety.
9. Industrial Goods: Used for sealing various industrial product containers to ensure safe and effective storage and usage.
10. Dairy Industry: Secures caps on milk bottles and other dairy product containers, ensuring they remain fresh and uncontaminated.
These applications highlight the critical role capping equipment plays in ensuring product safety, quality, and integrity across a multitude of industries.
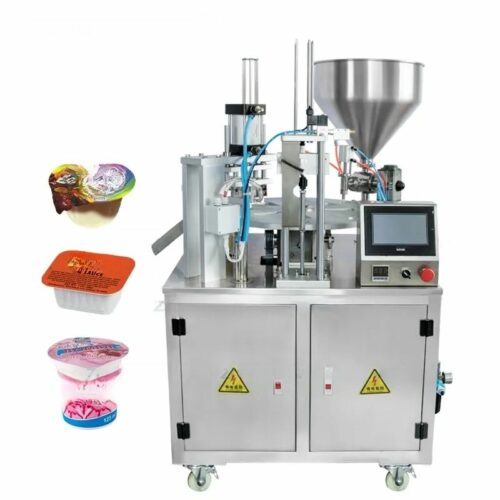
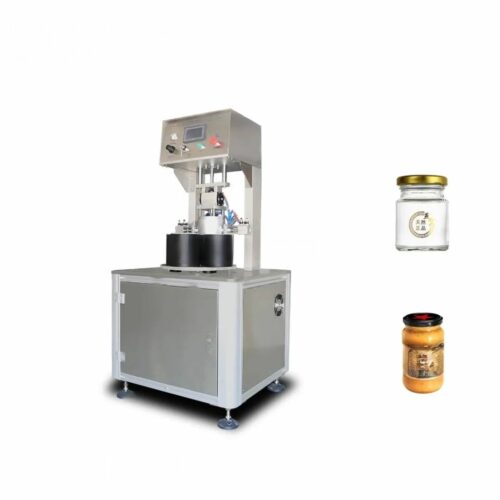
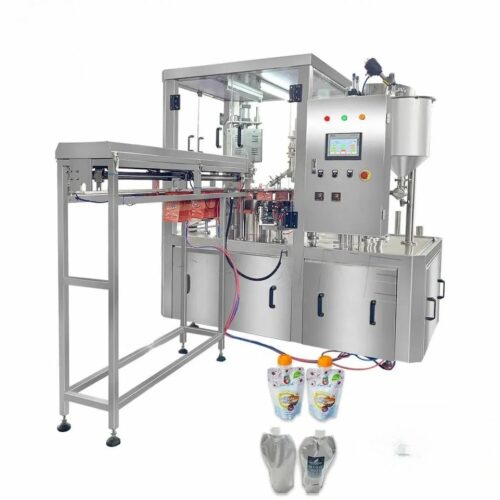
List Various Types of "capping equipment"
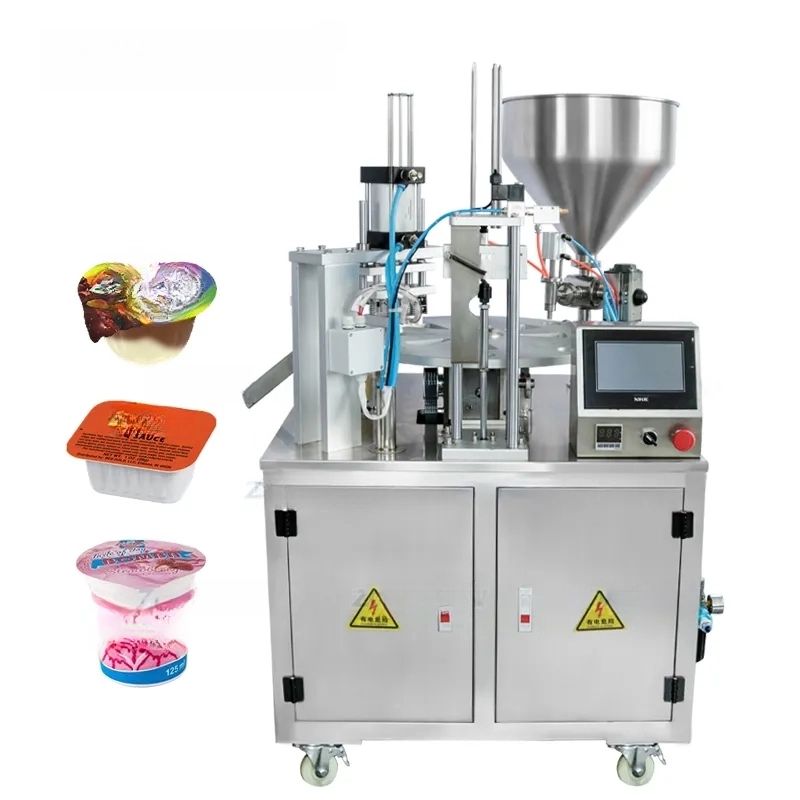
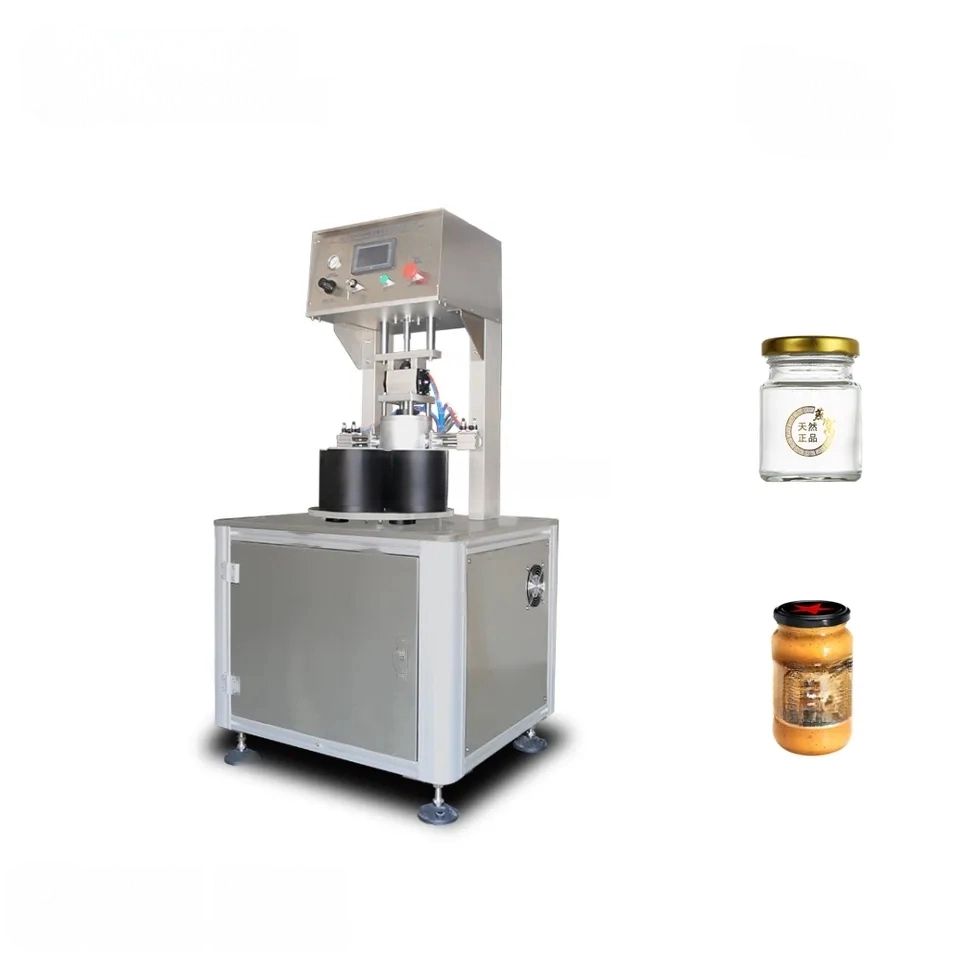
Capping equipment is vital in the packaging industry to apply and secure caps on various types of containers like bottles, jars, and vials. Here’s a concise list of various types:
1. Automatic Capping Machines:
– Chuck Cappers: Utilize a chuck to descend and tighten caps, suitable for high-speed operations.
– Spindle Cappers: Use spinning wheels to secure the cap as the container passes through, ideal for continuous production lines.
– Snap Cappers: Press caps onto containers, commonly used in cases where caps don’t need to be threaded.
– Rotary Cappers: High-speed cappers that use multiple capping heads in a rotating mechanism.
2. Semi-Automatic Capping Machines:
– Benchtop Chuck Cappers: Require manual placement of the cap; the machine tightens it.
– Portable Handheld Cappers: Mobile and versatile, fit for small-scale operations or irregularly shaped containers.
3. Manual Capping Tools:
– Cap Tighteners: Basic hand tools to manually secure caps, commonly used in low-volume production or where automation isn’t feasible.
– Capping Wrenches: Simple tools for tightening or loosening caps by hand.
– Cap Pryers: Used for removing caps, especially in small-scale operations or laboratory settings.
4. Specialized Cappers:
– Crimp Cappers: Used for sealing aluminum caps, frequently in pharmaceuticals and perfume industries.
– Corkers: Specifically designed for inserting corks into wine or similar bottles.
– ROPP (Roll-On Pilfer-Proof) Cappers: Roll aluminum closures onto bottles, offering tamper-evident protection.
Choosing the right capping equipment hinges on production scale, container type, cap design, and industry-specific requirements.
Custom Manufacturing Options for capping equipment
Custom manufacturing options for capping equipment can significantly enhance efficiency, precision, and flexibility in production lines, catering to unique business needs. Here are several aspects to consider:
1. Customization Based on Cap Types
– Screw Caps: Equipment can be tailored for specific torque settings to ensure caps are neither too tight nor too loose.
– Snap Caps: Systems can be adapted for precise alignment and pressure application.
– Corking: Machines can be modified to handle natural corks or synthetic alternatives, adjusting pressure as needed.
– ROPP Caps: Specialized rotary equipment can be customized for Roll-On Pilfer-Proof caps, ensuring secure sealing and tamper evidence.
2. Container Versatility
– Size and Shape: Machines can be designed to handle various container sizes and shapes, from small vials to large jugs.
– Materials: Customizations can accommodate different materials like glass, plastic, or metal.
3. Production Speed
- Customized capping equipment can be tailored for specific production speeds, balancing output rate with precision.
- Integration with conveyor systems can optimize flow and minimize bottlenecks.
4. Automation Levels
– Semi-Automatic: Custom semi-automatic machines allow for manual intervention, offering flexibility for small batches.
– Fully Automatic: Tailored fully automatic systems can integrate with existing production lines for continuous high-speed operation.
5. Special Features
– Multi-head Cappers: Custom configurations can include multiple capping heads for increased throughput.
– Torque Control: Precision torque control options ensure consistent application across all units.
– Vision Systems: Integrated cameras and sensors for quality control to detect and reject improperly capped containers.
6. Ergonomics and Safety
- Equipment can be designed with user-friendly interfaces and safety features, ensuring efficient and safe operation.
Conclusion
Custom manufacturing of capping equipment enables businesses to address specific operational needs, improve efficiency, and maintain high-quality standards. By working with a knowledgeable manufacturer, companies can develop tailored solutions that align perfectly with their production demands.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "capping equipment"
Quality Control in Capping Equipment Manufacturing
Material Inspection:
- Verify raw materials for compliance with specifications.
- Perform assessments for durability, consistency, and reliability.
Design Validation:
- Conduct simulations and prototypes to ensure design accuracy.
- Confirm that equipment meets regulatory and customer specifications.
Component Testing:
- Inspect individual components for defects or non-conformance.
- Use precision instruments to measure tolerances.
Assembly Checks:
- Continuous monitoring during the assembly to avoid errors.
- Implement error-proofing mechanisms (Poka-Yoke).
Functionality Tests:
- Run tests to confirm that the capping equipment performs under various conditions.
- Inspect for proper torque and seal integrity.
Operational Verification:
- Ensure functioning with various bottle types and cap sizes.
- Test for speed, efficiency, and consistency in the capping process.
Final Inspection:
- Conduct a thorough check before packaging.
- Utilize checklists to confirm that all criteria are met.
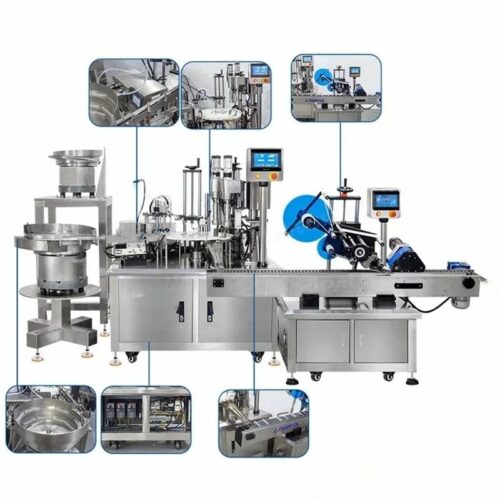
Manufacturing Process of Capping Equipment
Design Phase:
- Conceptualize based on client requirements and industry standards.
- Employ CAD software for detailed engineering.
Material Procurement:
- Source high-quality metals, plastics, and electronic components.
- Ensure supplier reliability through stringent vendor evaluations.
Fabrication:
- Use CNC machining for high-precision parts.
- Employ welding, molding, and forming techniques suitable for different components.
Assembly:
- Systematically assemble sub-components in clean environments.
- Incorporate automation for accuracy and speed.
Quality Checks:
- Implement in-line and end-of-line inspections.
- Use calibrated testing devices to measure performance metrics.
Software Integration:
- Program control systems for automated adjustments and error handling.
- Continuously update software for improvements and new features.
Testing:
- Conduct stress tests and operational tests.
- Simulate real-world operating conditions to ensure reliability.
Packaging & Dispatch:
- Securely package to avoid damage during transit.
- Include user manuals and maintenance guidelines.
Customer Support:
- Provide installation assistance and user training.
- Offer post-sales support and regular maintenance checks.
By adhering to stringent quality control measures and a meticulous manufacturing process, capping equipment can be produced to meet high standards of performance and reliability.
How to use "capping equipment"
Using capping equipment is straightforward but requires attention to detail for optimal performance. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Preparation:
– Select the Appropriate Cap: Ensure you have the right cap type and size for your containers.
– Check the Equipment: Ensure the capping machine is clean, in good working condition, and properly assembled.
2. Setup:
– Adjust Settings: Set the torque and speed settings based on the cap and container specifications.
– Load Caps: Fill the cap feeder or cap chute with the required number of caps.
– Position Containers: Place the containers on the conveyor or worktable.
3. Operation:
– Start the Machine: Turn on the capping equipment and ensure it’s ready for operation.
– Automatic Feeding: If the machine has an automatic cap feeder, caps will be fed to the capping head.
– Manual Feeding: For manual machines, place a cap onto each container.
– Capping Process: The capping head will descend to secure the cap onto the container, applying the preset torque.
4. Quality Control:
– Check Seals: Ensure each cap is properly sealed, without being too tight or too loose.
– Inspect Occasionally: Periodically check to ensure consistent quality and make adjustments if necessary.
5. Maintenance:
– Regular Cleaning: Keep the machine clean to avoid contamination.
– Lubrication and Inspection: Regularly lubricate moving parts and inspect for wear and tear.
6. Safety:
– Follow Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines.
– Wear Protective Gear: Use gloves and safety glasses as needed.
By adhering to these steps, you can effectively use capping equipment to ensure your containers are securely and efficiently capped.
List Properties and Terms of "capping equipment"
Capping equipment refers to machinery designed to seal containers, typically bottles, jars, or vials, with caps or lids. Here’s a concise overview of its properties and terms:
Properties:
1. Automation Level:
– Manual: Requires human operation.
– Semi-Automatic: Combines manual loading with automatic capping.
– Fully Automatic: Complete capping process with minimal human intervention.
2. Types of Capping Heads:
– Chuck Cappers: Use a cap chuck to place caps onto containers.
– Spindle Cappers: Employ spindles or rollers to apply caps.
– Snap Cappers: Push or snap caps onto containers.
– Pump Cappers: Specialized for pump or trigger-style caps.
3. Container Compatibility:
- Designed to handle different shapes and sizes, such as bottles, jars, and vials made of various materials (glass, plastic, metal).
4. Cap Types:
– Screw Caps: Twisted onto the container.
– Snap-On Caps: Pressed onto the container.
– Crimp Caps: Sealed by crimping around the container neck.
– ROPP Caps (Roll-On Pilfer Proof): Aluminum caps rolled onto the container.
5. Speed and Efficiency:
- Measured in caps per minute (CPM), ranging from low-speed manual machines to high-speed automatic systems.
6. Quality Control Features:
- Torque measurement for consistent application.
- Detection systems for misaligned or missing caps.
Terms:
1. Torque: The force applied by capping equipment to secure caps, crucial for ensuring they are tightly and consistently applied.
2. Conveyor System: Mechanism to move containers through various stages of the capping process.
3. Cap Elevator: Device used to feed caps into the capping machine.
4. Alignment System: Ensures caps are perfectly aligned with containers before sealing.
5. Cap Feeder: Supplies caps to the capping head.
6. Level Sensors: Monitor and manage the supply of caps.
7. Activation Mechanism: Triggers the capping head to engage with the container.
8. Changeover: Process of adjusting the capping equipment to handle different cap sizes or types.
Capping equipment plays a critical role in packaging by ensuring product safety, integrity, and consumer convenience.
List The Evolution history of "capping equipment"
Capping equipment has undergone significant evolution since its inception, driven by the demands for efficiency, consistency, and safety in packaging industries. The history can be broadly categorized into several key phases:
1. Manual Capping Era (Pre-20th Century):
Early capping involved manual techniques, using basic tools such as hand-cranked corkers or screw cap wrenches. Labor-intensive, these methods were prone to inconsistency and low throughput.
2. Mechanical Advancements (Early 20th Century):
With the industrial revolution came the first mechanical capping machines. Driven by belts and pulleys, these devices automated the capping process, increasing speed and uniformity. However, they still required significant human oversight.
3. Electromechanical Innovations (Mid-20th Century):
Electric motors replaced manual and mechanical drives, allowing for more precise control. This era saw the development of various capping styles, including screw caps, snap-on caps, and crown caps. Machines became specialized for each type, improving the efficiency and hygiene of operations.
4. Microprocessor Control (Late 20th Century):
The integration of microprocessors in the 1980s revolutionized capping equipment, enabling programmable logic controls (PLCs). This allowed for greater automation, reduced human error, and enhanced flexibility to handle different cap types and sizes.
5. Modern Automated Systems (21st Century):
Today’s capping machines are highly automated, incorporating sensors, robotics, and sophisticated software. Features like vision systems ensure accurate cap placement, while feedback loops adjust for discrepancies in real-time. Modern machines are also built for quick changeovers to accommodate various packaging needs.
6. Smart and Sustainable Solutions (Present and Future):
Current trends focus on smart technologies, including IoT integration and machine learning, to optimize performance and predictive maintenance. Sustainability is also a key focus, with machines being designed to use less energy and materials.
These innovations have transformed capping equipment from simple manual tools to sophisticated, highly efficient machines essential for modern production lines.
How to Select a Reliable capping equipment
Selecting reliable capping equipment is crucial for ensuring the quality and consistency of product packaging. Here are key factors to consider, keeping your word count constraint in mind:
1. Compatibility with Products: Ensure the capping equipment is compatible with your product type and packaging materials. Check if it can handle various cap sizes and types, such as screw caps, snap-on caps, or corks.
2. Production Speed: Match the equipment’s capping speed with your production requirements. Assess if the machine can maintain desired output without compromising on quality.
3. Ease of Use: Opt for user-friendly equipment that doesn’t require extensive training. Features like intuitive controls, easy setup, and minimal maintenance can save time and reduce operational disruptions.
4. Precision and Consistency: Look for equipment that ensures precise torque application and uniform capping. Inconsistent capping can lead to leaks and product spoilage, affecting customer satisfaction.
5. Durability and Build Quality: Invest in robust machinery crafted from high-quality materials. Durable equipment reduces downtime and long-term maintenance costs.
6. Flexibility and Scalability: Choose equipment that can be easily adjusted or upgraded to accommodate future growth or changes in packaging formats.
7. Compliance and Safety: Ensure the equipment complies with industry standards and safety regulations. Features like safety guards and emergency stop functions are essential.
8. Support and Service: Select suppliers with a solid reputation for after-sales support. Prompt technical assistance and availability of spare parts are critical for minimizing downtime.
9. Cost vs. Value: While budget constraints are important, prioritize overall value over cost. Reliable, efficient equipment might have a higher upfront cost but offers better ROI through longevity and performance.
By considering these factors, you can select capping equipment that enhances efficiency, ensures product integrity, and supports your business’s growth.
List "capping equipment" FAQ
Capping Equipment FAQ
-
What is capping equipment?
Capping equipment refers to machinery used to apply caps to bottles, jars, and containers. This equipment ensures a secure, airtight seal essential for product preservation and safety. -
What types of capping equipment are available?
There are several types of capping machines including:
– Manual Capping Machines: Operated by hand, ideal for low-volume production.
– Semi-Automatic Capping Machines: Partially automated, suitable for medium-scale production.
– Automatic Capping Machines: Fully automated systems designed for high-volume production. -
How does an automatic capping machine work?
Automatic capping machines use conveyor belts to transport containers to a capping station where caps are automatically placed and tightened. -
What types of caps can capping equipment handle?
Capping equipment can handle various cap types including screw caps, snap-on caps, corks, and push-on caps among others. -
What industries use capping equipment?
Industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and household products frequently use capping equipment. -
Can capping equipment handle different container sizes and shapes?
Yes, many capping machines are adjustable and come with customizable parts to handle various container sizes and shapes. -
What are the benefits of using capping equipment?
– Efficiency: Increases production speed.
– Consistency: Ensures uniform sealing quality.
– Safety: Reduces the risk of contamination.
– Versatility: Suitable for different cap and container types. -
How do you maintain capping equipment?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning, lubricating moving parts, inspecting for wear and tear, and ensuring all components are properly aligned. -
How do you select the right capping equipment?
Factors to consider include production volume, type of caps and containers, level of automation desired, and budget. -
Are there any specific safety measures to follow?
Yes, always adhere to the manufacturer’s safety guidelines, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and ensure regular training for operators.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about capping equipment for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure! Here are the top 10 FAQs about sourcing capping equipment from China, along with concise answers:
-
What types of capping equipment are available?
- China offers various types of capping machines including screw cappers, snap cappers, ROPP cappers, and press-on cappers to accommodate different types of closures and bottles.
-
How do I find reliable manufacturers?
- Research online directories, attend trade shows, and verify suppliers through third-party platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources. Check reviews, ask for references, and conduct factory audits if possible.
-
What is the typical lead time for delivery?
- The lead time varies by manufacturer and product complexity but generally ranges from 4 to 12 weeks. Customizations or larger orders might extend this timeframe.
-
How can I ensure the equipment’s quality?
- Request product samples before purchasing, ask for quality certifications (e.g., ISO, CE), and consider hiring local inspection agencies to verify the machinery before shipment.
-
What is the cost range for capping equipment?
- Prices can vary widely depending on machine type and specifications. Basic models might start at a few thousand dollars, while advanced or customized systems can cost significantly more.
-
Are there any hidden costs?
- Consider shipping, import duties, and potential installation/training fees. Additionally, budget for spare parts and maintenance.
-
Can the machines be customized?
- Many manufacturers offer customization options to suit specific requirements. Discuss your needs in detail with the supplier to ensure feasibility and accurate quotes.
-
What payment methods are accepted?
- Common payment methods include T/T (telegraphic transfer), L/C (letter of credit), and occasionally PayPal for smaller transactions. Negotiate payment terms where possible.
-
How do I handle after-sales service and support?
- Confirm the availability of after-sales service, including remote support, spare parts supply, and warranty terms. Some suppliers may have local partners for quicker service.
-
What are the shipping options?
- Shipping modes include sea freight (most cost-effective for large orders), air freight (faster but more expensive), and express couriers for smaller items. Work with freight forwarders to manage logistics.
By addressing these key questions, buyers can make more informed decisions and ensure a smoother sourcing process for capping equipment from China.










