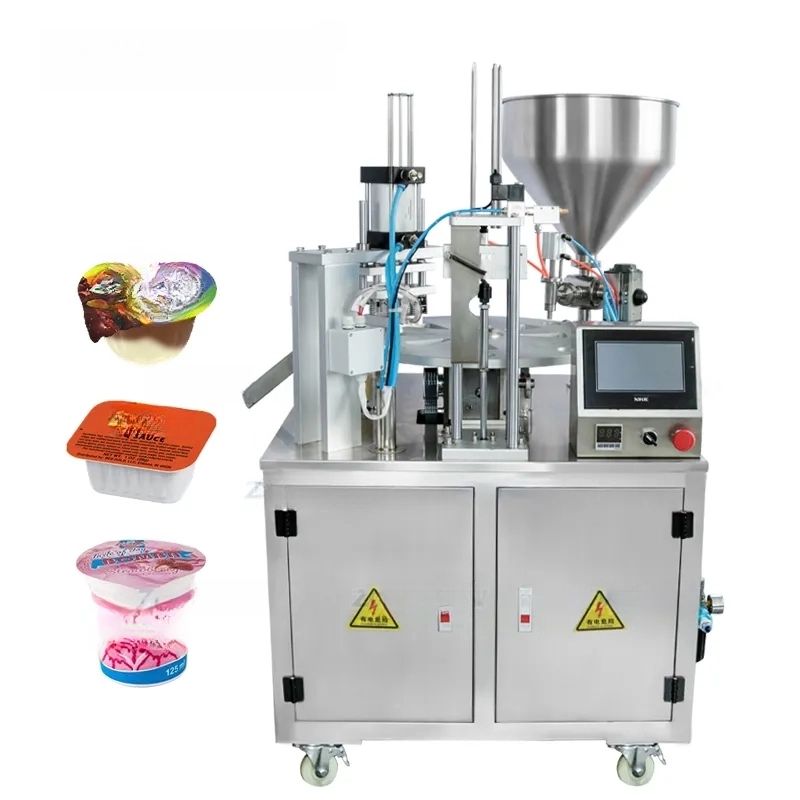
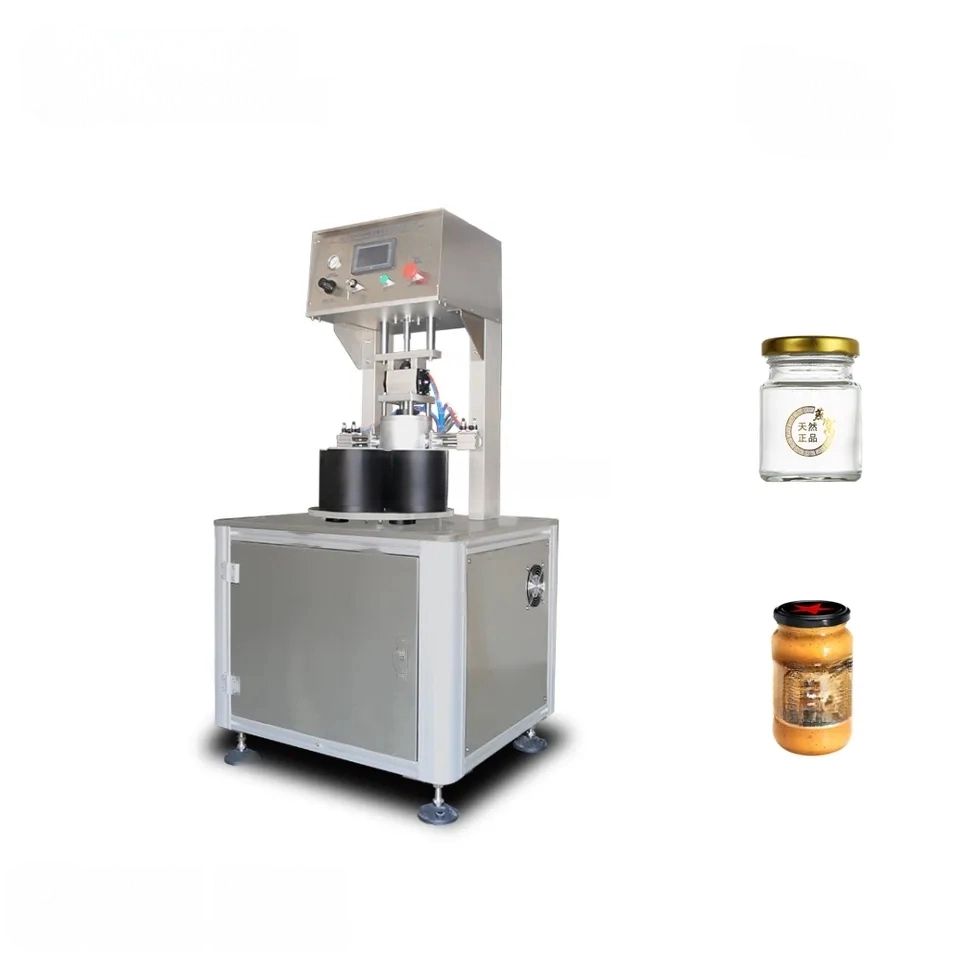
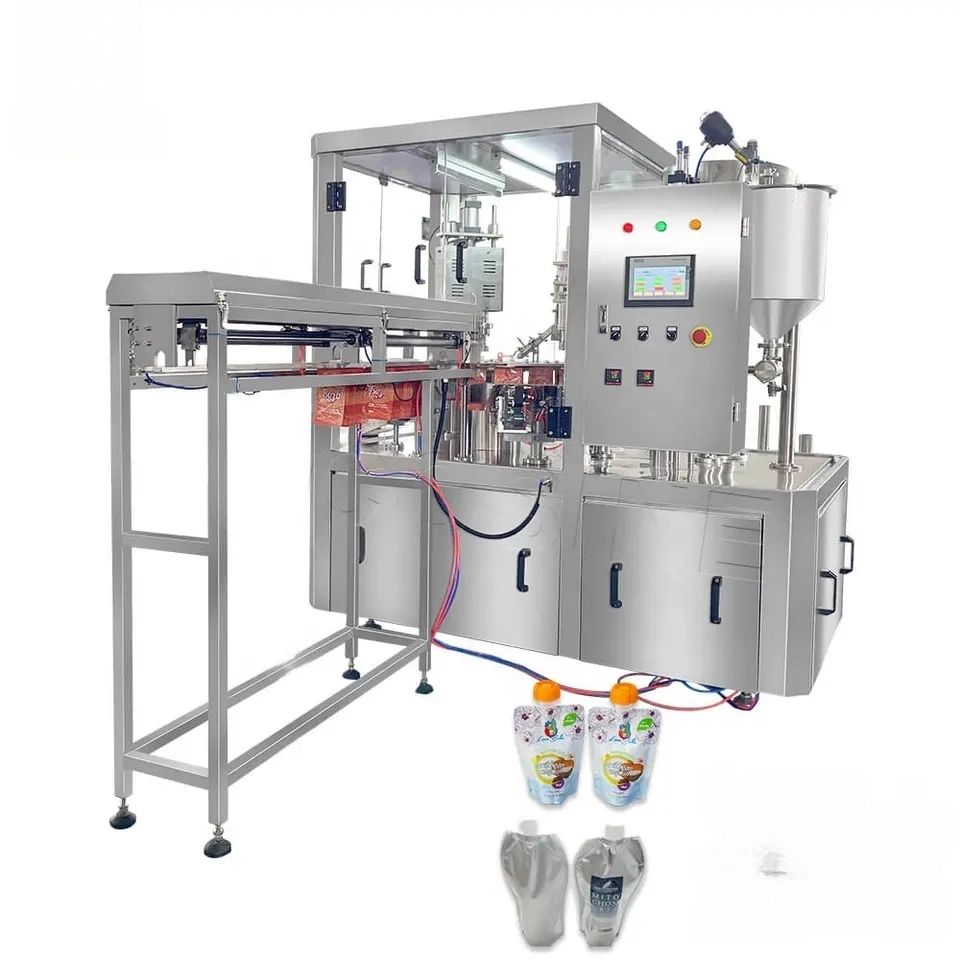
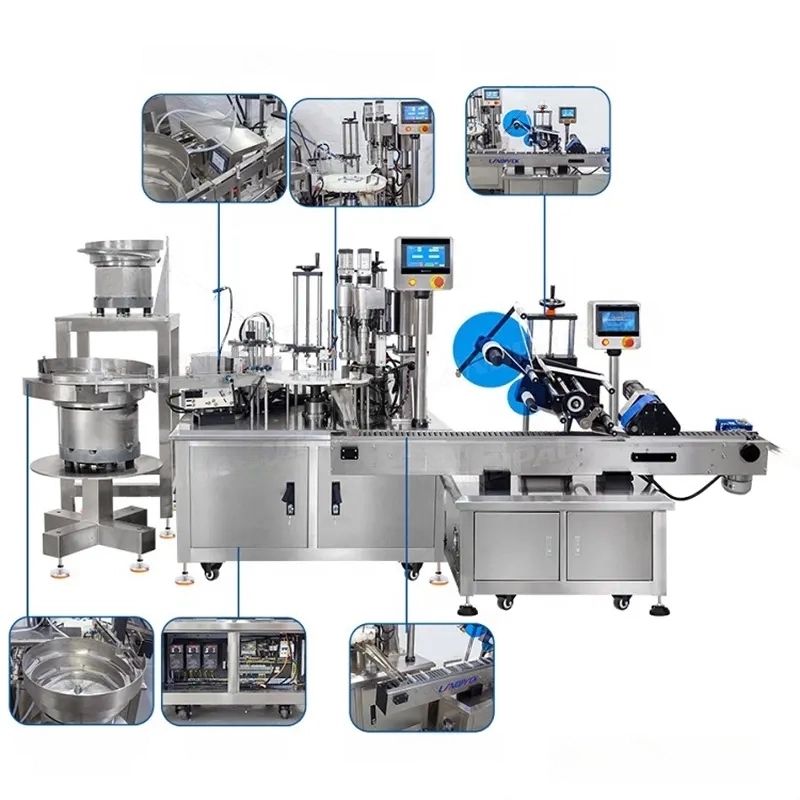
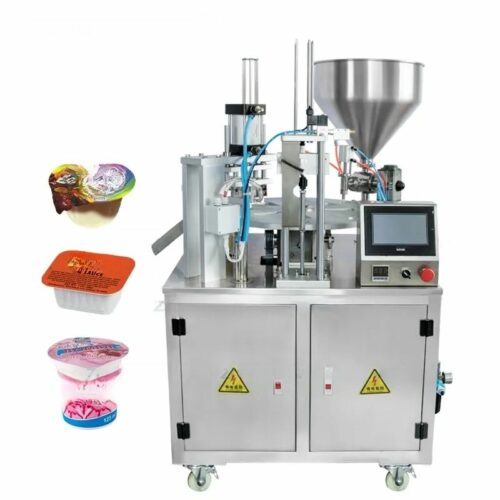
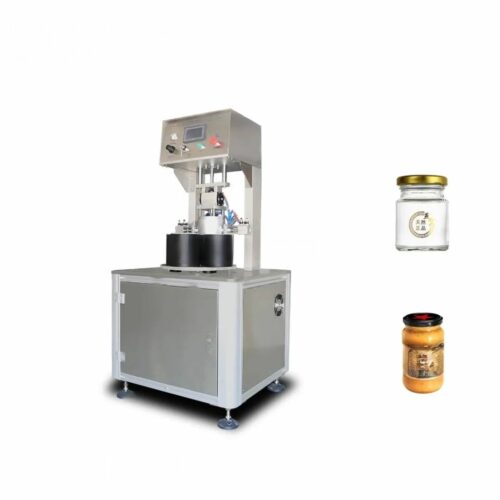
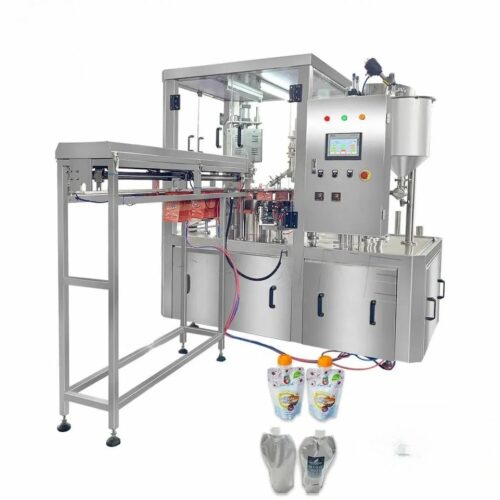
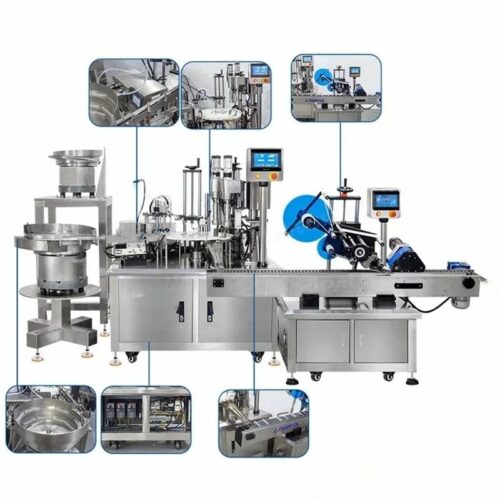
List Technical Parameters of "capping machine"
Capping machines are employed in various industries to securely apply caps to containers such as bottles, jars, and vials. Here are the key technical parameters to consider:
1. Type:
– Automatic: Designed for high-speed operations.
– Semi-Automatic: Requires some manual intervention.
– Manual: Entirely operated by hand.
2. Capping Speed:
– Output Rate: Measured in caps per minute (cpm). Varies from around 40 cpm for semi-automatic to over 200 cpm for high-end automatic machines.
3. Cap Types:
– Screw Cap: Threaded caps twisted onto the container.
– Snap Cap: Pressed onto the container.
– Crimp Cap: Crimped around the neck of the container.
– ROPP (Roll-On Pilfer-Proof) Cap: Tamper-evident caps.
4. Container Size and Shape Compatibility:
- Diameter range typically from 20mm to 120mm.
– Accommodates various container shapes: round, square, oval, etc.
5. Torque Control:
- Accurate torque application to ensure secure sealing without damaging the container or cap.
6. Power Requirements:
- Typically measured in kilowatts (kW). Commonly ranges from 0.5 kW for smaller machines to over 5 kW for industrial-scale equipment.
7. Material and Build:
– Frame: Often made of stainless steel for durability and hygiene.
– Grip and Press Mechanism: Made of robust, wear-resistant materials to withstand repetitive operations.
8. Control System:
- Modern machines use PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems for enhanced precision and flexibility.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI) for user-friendly operation.
9. Integration Capability:
- Ability to integrate with existing production lines including conveyors, labeling machines, and filling machines.
10. Compliance:
- Standards and certifications such as CE, GMP, and FDA, especially for use in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics industries.
Understanding these parameters helps ensure that the capping machine selected will meet production requirements and maintain efficiency and quality.
List Product features of "capping machine"
A capping machine is a crucial component in the packaging industry, ensuring that containers are securely sealed. Here are some notable features:
1. Versatility: Designed to handle various cap types such as screw caps, snap-on caps, and tamper-evident caps.
2. Adjustable Torque Control: Allows precise control of torque to ensure consistent cap tightness without damaging the container.
3. High Speed and Efficiency: Capable of sealing a large number of containers per minute, enhancing production throughput.
4. Automated Operation: Equipped with automated feeding and capping mechanisms for reduced manual labor and increased efficiency.
5. Container and Cap Size Adaptability: Adjustable components to accommodate different container and cap sizes.
6. User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive control panel for easy operation, programming, and troubleshooting.
7. Quality Assurance Features: Includes sensors and vision systems to detect and reject improperly sealed containers, thus ensuring high product quality.
8. Durable Construction: Made of robust materials like stainless steel to withstand heavy usage and harsh environments.
9. Easy Changeover: Quick and efficient changeover mechanisms to switch between different cap and bottle sizes with minimal downtime.
10. Safety Features: Equipped with safety guards and emergency stop buttons to protect operators.
11. Customizable Settings: Options for different capping speeds, torque levels, and other parameters to suit specific production needs.
12. Integration Capabilities: Can be seamlessly integrated with other production line equipment like filling machines and labeling systems.
13. Low Maintenance: Designed for easy cleaning and maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs.
14. Consistent Performance: Engineered to provide reliable and uniform capping results over extended periods.
15. Compact Design: Space-efficient design to fit within various production layouts without compromising performance.
These features make capping machines essential for ensuring product safety, enhancing production efficiency, and maintaining high standards in the packaging process.
List Application of "capping machine"
A capping machine is a specialized device used in various industries to seal containers, ensuring product integrity and safety. Here are some of its primary applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry: Capping machines are widely employed to seal bottles and jars containing liquids, sauces, jams, and other food products to maintain freshness and prevent contamination.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry: Ensures secure sealing of medicinal bottles and vials to preserve the efficacy of drugs and prevent tampering.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care: Used to seal containers holding lotions, shampoos, perfumes, and other cosmetic products, ensuring they remain uncontaminated and spill-proof.
4. Chemical Industry: Secures bottles of household cleaners, industrial chemicals, and other potentially hazardous substances, ensuring user safety and preventing leaks.
5. Packaging Industry: Integral part of the packaging line, providing consistent and efficient sealing of various container types, enhancing productivity and reducing manual labor.
6. Automotive Industry: Utilized for sealing containers of automotive fluids such as motor oils, brake fluids, and coolants to prevent leaks and maintain product quality.
7. Agricultural Industry: Seals containers of pesticides, fertilizers, and other agricultural chemicals, ensuring they are safe for transport and storage.
8. Dairy Industry: Used to seal milk bottles, yogurt cups, and other dairy containers, maintaining product freshness and extending shelf life.
9. Brewing Industry: Essential for capping beer bottles and other alcoholic beverages to ensure carbonation and prevent spoilage.
10. Healthcare and Laboratory: Seals specimen containers, reagent bottles, and other lab materials, ensuring sterility and preventing cross-contamination.
In summary, capping machines play a crucial role across various sectors by ensuring that containers are securely sealed, thereby maintaining product quality, safety, and extending shelf life.
List Various Types of "capping machine"
Capping machines are essential in packaging industries, sealing containers with different types of caps to ensure product safety and integrity. Various types of capping machines cater to different sealing requirements:
1. Chuck Cappers: Use a chuck, a cylindrical tool, to apply torque to caps, ensuring a precise and uniform seal. Ideal for higher torque requirements and more secure capping.
2. Spindle Cappers: Use spinning discs or spindles to tighten caps. Often used for screw caps and in high-speed production lines due to their rapid and continuous operation.
3. Snap Cappers: Compress caps onto containers, perfect for snap-on caps commonly used in beverage and dairy industries.
4. Rotary Cappers: Feature rotating heads for high-speed applications. These are multi-head machines that provide consistent and high-throughput capping.
5. Inline Cappers: Align containers sequentially and cap them in a linear process. Suitable for medium to high-speed operations and easy integration into existing production lines.
6. Pump Cappers: Designed specifically for pump caps, often used in industries like cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. These ensure precise torque application for pump mechanisms.
7. ROPP Cappers (Roll-On Pilfer-Proof): Create tamper-evident seals by rolling the edges of aluminum caps around bottle necks, commonly used in the beverage industry for wine and spirits.
8. Servo Cappers: Utilize servo motors for precise torque control and flexibility. Ideal for applications requiring varied torque settings or high adaptability.
9. Snap/Screw Combination Cappers: Can handle both snap and screw caps, offering versatility for different container types in a single machine.
Each type of capping machine is designed to meet specific sealing needs, ensuring product integrity and enhancing operational efficiency across various industries.
Custom Manufacturing Options for capping machine
Custom manufacturing options for capping machines cater to various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, cosmetics, and chemicals. By tailoring the equipment to specific needs, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, precision, and adaptability. Here are some key custom options:
1. Cap Types and Sizes:
– Versatility: Machines can be designed to handle different types of caps, such as screw caps, snap caps, press-on caps, or child-resistant caps.
– Range of Sizes: Adjustable elements can accommodate various cap and bottle sizes, meeting diverse product specifications.
2. Automation Level:
– Semi-Automatic: Ideal for small to medium production runs, offering a balance between manual intervention and automation.
– Fully Automatic: Suitable for high-volume production, these systems ensure consistent and rapid capping with minimal human supervision.
3. Integration with Existing Line:
– Modular Systems: Can be seamlessly integrated into existing production lines, enhancing or replacing current equipment without extensive modifications.
– Customization: Specific adjustments to feed, cap placement, and torque control can be made to fit existing workflows.
4. Material and Durability:
– Corrosion-Resistant Materials: For industries dealing with harsh chemicals or liquids, using stainless steel or other resistant materials is vital.
– Heavy-Duty Design: Ensures longevity and reliability in demanding environments.
5. Control and Monitoring Systems:
– Intelligent Controls: Advanced PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems enable precise control over capping processes.
– Real-Time Monitoring: Features like sensors and cameras can monitor consistency, ensuring quality control.
6. Safety and Ergonomics:
– Guarding and Safety Features: Implementation of safety guards and emergency stop functions to protect operators.
– User-Friendly Interfaces: Easy-to-navigate HMI (Human-Machine Interface) panels enhance operational ease and reduce training time.
7. Speed and Capacity:
– High-Speed Options: For large-scale production, machines can be customized to operate at higher speeds while maintaining accuracy.
– Adjustable Throughput: Flexibility to adjust speed settings based on production requirements.
Customizing capping machines ensures they meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and product quality across sectors.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "capping machine"
Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of a Capping Machine
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design & Engineering:
- Conceptualize and create detailed blueprints.
- CAD software usage for precise design.
2. Material Selection:
- Choose robust materials (stainless steel, aluminum) for durability and corrosion resistance.
3. Component Manufacturing:
- Use CNC machines for precise part fabrication.
- Include parts like cap chute, capping heads, and conveyors.
4. Assembly:
- Assemble the machine in stages, ensuring proper alignment.
- Incorporate electrical components like sensors and control panels.
5. Integration:
- Integrate capping machine with bottling line ensuring synchronization.
- Install software/PLC for automated control and monitoring.
6. Testing & Calibration:
- Test for functionality.
- Calibrate to handle different cap sizes.
7. Finishing & Packaging:
- Conduct surface treatments like polishing.
- Package components securely for delivery.
Quality Control:
1. Incoming Material Inspection:
- Verify material quality against specifications.
- Reject non-compliant materials.
2. In-Process Inspection:
- Perform dimensional checks on parts using metrology tools.
- Monitor machining processes for precision.
3. Assembly Quality Checks:
- Ensure correct assembly via checklists.
- Test electric and mechanical assemblies for functionality.
4. Performance Testing:
- Run the machine in simulated production conditions.
- Verify consistent capping torque and alignment.
5. Software Testing:
- Validate automated control systems.
- Ensure user interface is intuitive and responsive.
6. Final Inspection:
- Thoroughly inspect the complete machine.
- Perform trials with different cap types and sizes.
7. Documentation & Compliance:
- Maintain records of QC processes.
- Ensure the machine meets industry standards (e.g., ISO, GMP).
Adhering to stringent quality control and a structured manufacturing process ensures the reliability and efficiency of capping machines, leading to optimal performance in various production environments.
How to use "capping machine"
A capping machine is used to seal containers with caps. Here’s a concise guide on using one:
1. Preparation:
- Ensure the machine is clean and in proper working condition.
- Check that the correct cap type and size are loaded.
- Adjust the machine for the specific bottle height and cap type.
2. Setup:
- Turn on the machine and set required parameters (speed, torque).
- Position bottles on the conveyor belt or in the designated loading area.
3. Operation:
- Start the conveyor belt to move bottles toward the capping area.
- The machine will automatically place and secure the caps onto the bottles.
- Monitor the process for any jams or misalignments.
4. Inspection:
- Regularly check bottles to ensure caps are properly sealed.
- Make adjustments if caps are loose or improperly aligned.
5. Shutdown:
- Stop the conveyor belt after processing the last container.
- Turn off the machine and clean as necessary.
- Perform routine maintenance checks.
6. Safety:
- Always follow safety protocols.
- Wear appropriate protective gear (gloves, eye protection).
- Keep hands away from moving parts.
By following these steps, you can efficiently and safely use a capping machine in your packaging process.
List Properties and Terms of "capping machine"
A capping machine is an essential piece of equipment in various industries, primarily used to securely apply caps or lids to bottles, containers, or other types of packaging. Here are some key properties and terms associated with capping machines:
Properties:
1. Automation Level:
– Manual: Operator-dependent, suitable for small-scale operations.
– Semi-Automatic: Partial automation with manual intervention.
– Fully Automatic: Operates without manual involvement, ideal for high-volume production.
2. Speed:
- Measured in bottles per minute (BPM), speed indicates how fast the machine can cap containers.
3. Versatility:
- Ability to handle different types of caps (screw caps, press-on caps, snap-on caps, etc.) and containers (bottles, jars, etc.).
4. Accuracy:
- Precision in applying the cap securely without over-tightening or damaging the container.
5. Changeover Time:
- The time required to switch from capping one type of container or cap to another.
6. Durability:
- Built to withstand continuous operation, often made from robust materials like stainless steel.
Terms:
1. Torque:
- The force applied to tighten the cap. Torque settings must be precise to ensure proper sealing without damaging the cap or bottle.
2. Chucks:
- The component that holds and tightens the cap on the container. Different chucks are used for different cap types.
3. Cap Feeder:
- A mechanism that supplies caps to the capping machine, ensuring a continuous flow and proper alignment.
4. Plunger:
- Used in some machines to press caps onto containers, especially for snap-on or press-on caps.
5. Carousel:
- A rotating platform that moves bottles through the capping station, common in high-speed automatic machines.
6. Conveyor System:
- Transports containers to and from the capping area, ensuring seamless integration into production lines.
7. Pick-and-Place:
- A system that picks up caps and places them on bottles, commonly used in automated machines.
In summary, a capping machine’s properties like automation level, speed, versatility, and accuracy are crucial for its performance. Understanding terms such as torque, chucks, cap feeder, plunger, carousel, conveyor system, and pick-and-place is vital for optimizing its operation in various industries.
List The Evolution history of "capping machine"
The evolution of the capping machine has been a journey driven by advancements in technology and industry needs. Here is a concise overview of its history:
1. Early 20th Century: Manual Capping
- Initially, bottle sealing was done manually using simple hand tools. This process was labor-intensive and inconsistent.
2. 1920s: Semi-Automatic Capping Machines
- With the advent of assembly lines, semi-automatic capping machines emerged, combining manual and mechanical elements to improve efficiency and consistency.
3. 1930s-1940s: Rotary and Chuck Cappers
- Rotary cappers, which use a rotating motion to seal bottles, and chuck cappers, utilizing a chuck to grip and tighten caps, were developed. These machines increased speed and reliability in production lines.
4. 1950s-1960s: Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
- The incorporation of pneumatic and hydraulic systems allowed for greater precision and control, significantly enhancing the performance and adaptability of capping machines.
5. 1970s-1980s: Electronic Control Systems
- The integration of electronic control systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) revolutionized capping machines. These advancements enabled automated adjustments and improved accuracy, leading to higher production rates.
6. 1990s: Advanced Materials and Ergonomics
- With advancements in materials science, lighter and more durable components were used. Ergonomic designs improved operator safety and comfort, further streamlining the capping process.
7. 2000s: High-Speed Inline Capping Machines
- High-speed inline capping machines became standard in many industries. These machines offered unparalleled speed and could handle various cap types and sizes with minimal changeover time.
8. 2010s-Present: Smart and Adaptive Capping Technologies
- The latest capping machines are highly automated, incorporating sensors, IoT (Internet of Things) technology, and AI for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. These smart systems ensure maximum efficiency and minimal downtime.
The evolution of capping machines from manual to advanced automated systems illustrates the continuous pursuit of efficiency, precision, and innovation in manufacturing and packaging industries.
How to Select a Reliable capping machine
Selecting a reliable capping machine is crucial for ensuring efficient and consistent sealing of containers. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Production Requirements: Determine your production speed and volume. Select a machine that can handle your current and future production demands.
2. Cap Types: Ensure the machine can handle the specific types of caps you use, such as screw caps, snap-on caps, or pump caps.
3. Container Compatibility: Verify that the machine accommodates the sizes and shapes of your containers. Some machines offer adjustable features to handle various container types.
4. Automation Level: Decide between manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic machines based on your budget and labor resources. Fully automatic machines offer higher efficiency but require a bigger investment.
5. Build Quality and Materials: Look for machines made from durable materials like stainless steel, which offer longevity and resistance to corrosion.
6. Ease of Use: Choose a machine with intuitive controls and easy setup to minimize training time and operational errors.
7. Consistency and Precision: Check for machines that offer consistent torque and precision to ensure proper sealing and avoid leaks or contamination.
8. Maintenance and Support: Opt for machines with good manufacturer support and readily available spare parts. A reliable supplier with excellent customer service can save you time and resources.
9. Budget: Balance your needs with your budget. While it might be tempting to go for a cheaper option, investing in a reliable machine can save costs in the long run by reducing downtime and maintenance expenses.
10. Reviews and Recommendations: Research customer reviews and seek recommendations from industry peers. Learning from others’ experiences can provide valuable insights into machine reliability and performance.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a capping machine that enhances your production efficiency and meets your specific operational needs.
List "capping machine" FAQ
Certainly! Here is a list of commonly asked questions (FAQ) regarding capping machines:
Capping Machine FAQ
-
What is a capping machine?
A capping machine securely places caps or lids onto containers, such as bottles, jars, and vials, ensuring a tight seal to protect the product inside. -
What types of capping machines are available?
– Automatic capping machines: Fully automate the capping process.
– Semi-automatic capping machines: Require some manual intervention.
– Manual capping tools: Operated entirely by hand.
– Snap cappers: For snap-on caps.
– Screw cappers: For screw-type caps.
– ROPP (Roll-on Pilfer Proof) cappers: For caps that need to be secured tightly to prevent pilfering. -
How do I choose the right capping machine?
– Container and cap size/type: Match machine specifications with your container and cap.
– Production speed: Choose based on your required throughput.
– Budget: Factor in your investment capacity.
– Flexibility: Consider if you need the machine to handle multiple cap types and sizes. -
What materials can capping machines handle?
Most machines handle various materials including plastic, metal, and glass containers. -
What maintenance is required for a capping machine?
Regular cleaning, lubrication, inspection of moving parts, and periodic software updates for automated systems. -
Are capping machines difficult to operate?
Training is usually provided by manufacturers, but modern capping machines are generally user-friendly with digital interfaces and easy-to-follow instructions. -
Can capping machines handle different shapes and sizes of caps?
Yes, many modern machines are designed to be versatile, allowing adjustments to fit and secure different shapes and sizes. -
What industries commonly use capping machines?
Pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, cosmetics, chemicals, and household goods. -
How do I troubleshoot common issues with capping machines?
Refer to the user manual for guidance on common issues like misaligned caps, inconsistent sealing, or mechanical malfunctions. Regular maintenance often prevents many of these problems. -
Where can I buy a capping machine?
You can purchase capping machines from specialized industrial equipment suppliers, online marketplaces, or directly from the manufacturers.
These FAQs should provide a concise overview of essential information about capping machines.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about capping machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here’s a succinct FAQ list for buyers sourcing capping machines from China:
-
What types of capping machines are available?
- Various capping machines include spindle cappers, chuck cappers, snap cappers, and ropp cappers. Selection depends on your specific application and bottle type.
-
How to ensure the quality of the capping machine?
- Verify ISO certifications, request sample test results, check customer reviews, and consider third-party inspections. A trial run request can also be beneficial.
-
What is the average lead time for a capping machine?
- Typically, lead times range from 30 to 60 days. However, this can vary based on customizations and factory capacity.
-
Can the capping machine be customized to specific requirements?
- Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization based on your bottle dimensions, cap types, and production speed requirements.
-
What is the cost range for capping machines from China?
- Prices vary widely based on specifications and capabilities. Entry-level machines can start at $5,000, while high-end, fully automated systems can exceed $50,000.
-
How does shipping and logistics work?
- Most manufacturers offer FOB (Free on Board) terms. It’s best to work with a trusted freight forwarder for seamless importation. Understand Incoterms to clarify responsibility.
-
What kind of after-sales support is available?
- Reputable manufacturers typically provide remote technical support, spare parts, and sometimes on-site service. Ensure warranty terms and support details are clear.
-
Is it easy to find replacement parts?
- Common parts are usually readily available. However, it’s wise to maintain an inventory of critical components and confirm part availability with the manufacturer.
-
What are the power and voltage specifications?
- Verify that the machine’s power requirements match your country’s electrical standards (e.g., 220V, 50Hz or 110V, 60Hz). Adapters or converters may be necessary.
-
What are the payment terms?
- Standard payment terms can include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), or a combination of deposits and balance payments upon delivery.
This covers the essential aspects buyers need to consider when sourcing capping machines from China, ensuring informed and efficient procurement.










