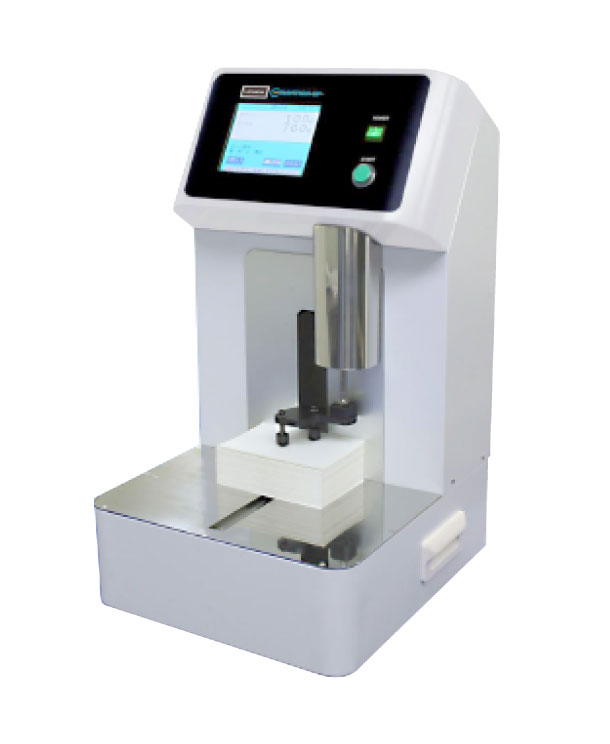
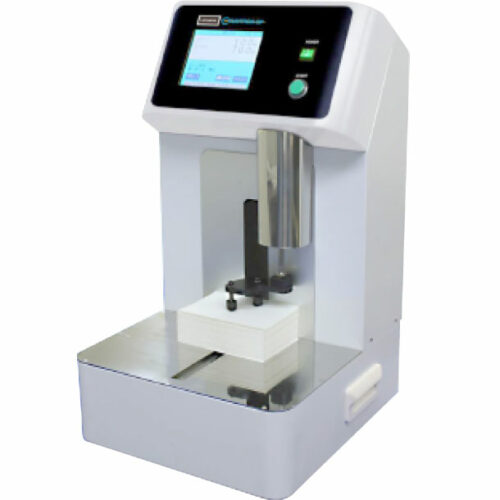
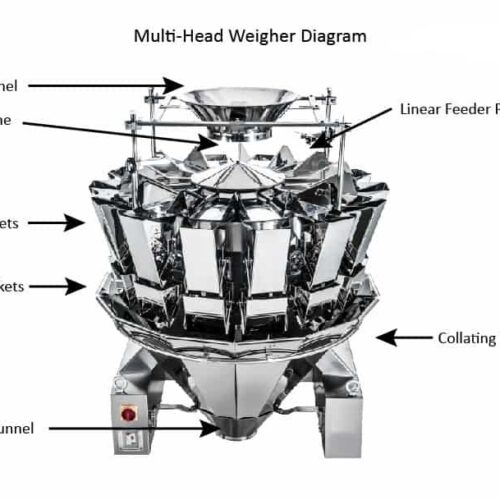
List Technical Parameters of "optical counting machine"
An "optical counting machine" is a device used for counting small items with high precision utilizing optical technologies. Here are some key technical parameters:
1. Counting Speed:
- Typically measured in items per second.
- Varies based on the machine’s design and the type of items being counted.
2. Accuracy:
- Degree of precision in counting, often expressed as a percentage.
- Factors affecting accuracy include the machine’s optical resolution and algorithm.
3. Capacity:
- Maximum number of items that can be counted in a single batch.
- Determined by the size and design of the machine’s hopper and conveyor system.
4. Item Size Range:
- Minimum and maximum dimensions (length, width, height) of items that can be accurately counted.
- Ensures compatibility with a wide range of products.
5. Optical Resolution:
- Quality and precision of the optical sensors, usually measured in micrometers.
- Higher resolution enables accurate detection of smaller items.
6. Detection Technology:
- Types of sensors used (e.g., laser, CCD cameras, infrared).
- Each type has specific advantages depending on the application’s requirements.
7. Software Capabilities:
- Algorithms for distinguishing, tracking, and counting items.
- May include features like automatic calibration, error logging, and reporting.
8. Power Requirements:
- Voltage and wattage necessary for operation.
- Determines the machine’s energy consumption and compatibility with electrical standards.
9. Interface and Connectivity:
- Types of ports and connectivity options (e.g., USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi).
- Facilitates data transfer and integration with other systems.
10. Build Material:
- Materials used in the construction of the machine (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum).
- Affects the machine’s durability and suitability for different environments.
11. Environmental Conditions:
- Operating temperature, humidity range, and dust resistance.
- Ensures reliable performance in various working environments.
These parameters collectively define the performance and applicability of an optical counting machine in various industrial and commercial settings.
List Product features of "optical counting machine"
An optical counting machine is a sophisticated device used extensively in various industries for counting items with high precision and speed. Below are some of its key features:
1. High Accuracy and Precision: Utilizes advanced optical sensors and image processing technology to ensure accurate counting, reducing errors to negligible levels.
2. High Speed: Capable of processing large quantities rapidly, making it ideal for high-volume applications such as pharmaceutical, electronics, and manufacturing industries.
3. Versatility: Can count a wide range of items regardless of their shape, size, or material, including tablets, capsules, seeds, screws, and more.
4. User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with an intuitive touch screen or control panel, allowing operators to easily set parameters, monitor the counting process, and adjust settings.
5. Automatic Feeding System: Features automated feeder and conveyor systems that ensure continuous and smooth flow of items for uninterrupted counting.
6. Data Logging and Reporting: Capable of storing counting data, generating reports, and integrating with external systems for data analysis and inventory management.
7. Compact and Robust Design: Built with durable materials and a compact footprint, making it suitable for diverse work environments, including space-constrained areas.
8. Adjustable Speed and Sensitivity: Allows customization of counting speed and sensor sensitivity to match the specific requirements of different items.
9. Multiple Counting Modes: Offers various counting modes, such as batch counting, total count, and pre-set count, providing flexibility for different operational needs.
10. Easy Maintenance and Cleaning: Designed for quick disassembly and straightforward cleaning, ensuring hygiene and reducing downtime.
11. Compatibility with Packaging Systems: Can be integrated seamlessly with packaging machines for automated counting and packing solutions.
12. Alarm Systems: Equipped with alarms to alert operators in case of jams, errors, or malfunctions, ensuring continuous and reliable operation.
These features make optical counting machines indispensable in industries where precise counting is critical for efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
List Application of "optical counting machine"
An optical counting machine utilizes advanced imaging and optical sensor technology to count objects. These devices have a variety of applications across multiple industries due to their high speed, accuracy, and efficiency. Below are some common applications:
1. Pharmaceuticals:
– Tablet and Capsule Counting: Essential for accurately distributing doses into bottles or packaging, thereby ensuring correct medication quantities.
– Quality Control: Used to verify the correct number of tablets in blister packs, reducing human error.
2. Agriculture:
– Seed Counting: Facilitates precise packaging and planting processes, improving yield predictions and resource allocation.
– Grain and Bean Counting: Ensures consistent quantity during packaging and helps in quality assessments.
3. Electronics:
– Component Counting: Used for counting tiny electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and microchips, ensuring inventory accuracy and reducing production downtime.
4. Food and Beverage:
– Confectionery: Counts candies, nuts, and other small edibles for packaging, ensuring consistent product weight and customer satisfaction.
– Bottling Lines: Ensures the correct number of bottles in each batch, optimizing packaging processes and inventory management.
5. Manufacturing:
– Fasteners and Hardware: Counts screws, bolts, nuts, and other hardware components for packaging and inventory control.
– Plastic Parts: Ensures the accurate counting of small plastic parts used in various manufacturing processes, improving assembly line efficiency.
6. Healthcare:
– Laboratory Applications: Useful in counting cells, bacteria colonies, and other microscopic entities to assist in research and diagnostics.
7. Retail and Vending:
– Product Stocking: Helps in counting items like books, toys, and other retail products for inventory management and automated restocking in vending machines.
8. Textiles:
– Fiber and Yarn Counting: Ensures the accurate count of fibers or threads in textiles, crucial for high-quality textile production.
Optical counting machines enhance operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve accuracy across various sectors. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable tools in modern industry.
List Various Types of "optical counting machine"
Optical counting machines utilize optical sensors and sophisticated algorithms to count objects quickly and accurately. Here are some common types:
1. Barcode Scanners:
These machines use laser or LED light sources to read barcodes on products and count them during processes like inventory management.
2. Photoelectric Sensors:
Employ light beams to detect and count objects as they pass through the sensor’s field. They are widely used in packaging and production lines for counting items like bottles or boxes.
3. Vision Systems:
Advanced systems featuring cameras and image-processing software. They can count objects by identifying shapes, sizes, and colors, suitable for intricate tasks such as counting pills in pharmaceuticals or parts in electronics manufacturing.
4. Laser Counters:
Use laser beams to scan and count objects. Capable of high-speed operations, these are often used in industrial environments where quick and accurate counting of materials like sheets, rods, or textiles is essential.
5. Particle Counters:
Utilize lasers or light-blockage methods to count microscopic particles in fluids or air. Commonly used in cleanroom environments and air quality monitoring.
6. Infrared Counters:
Employ infrared light to count objects, particularly effective in counting people entering or exiting an area. These counters are useful for crowd management and retail outlet analytics.
7. Fiber Optic Sensors:
Use fiber optics to transmit light, useful across long distances or in harsh environments. They count objects in sectors like manufacturing and automation where durability and flexibility are critical.
8. LiDAR Systems:
Utilize laser pulses to create high-resolution maps and count objects, typically used in autonomous vehicles and advanced manufacturing for precise placement and counting.
These different types of optical counting machines cater to diverse industries, providing accurate, efficient, and versatile solutions for a wide range of counting needs.
Custom Manufacturing Options for optical counting machine
Creating a custom optical counting machine involves several tailored design options:
1. Sensors and Cameras: Select high-resolution cameras and advanced sensors based on the size, shape, and type of items being counted to ensure accuracy. Options can range from monochrome to full-color sensors depending on the application.
2. Lighting: Customizable lighting setups such as LED, diffuse lighting, or stroboscopic lights to enhance image clarity and reduce shadows, improving counting precision.
3. Conveyor Systems: Design conveyors that accommodate the speed and volume of items. Options include adjustable speeds, anti-static belts, or specialized materials suitable for different item types.
4. Software and Algorithms: Tailor software features for specific counting needs. This can include advanced image processing algorithms, AI-based recognition, or machine learning for more complex item differentiation.
5. User Interface: Develop an intuitive user interface for easy operation and real-time monitoring. Customizable dashboards and touch screens can enhance user experience.
6. Data Integration: Ensure seamless integration with existing inventory management systems, SCADA, or IoT platforms for real-time data analytics and reporting.
7. Build and Materials: Choose materials and build options to match operational environments, whether they require waterproof, dustproof, or food-grade materials.
8. Modular Design: Implement modularity for easy upgrades and maintenance. This can include plug-and-play components or expandable counting lanes.
9. Scalability: Design machines with scalability in mind, allowing for future expansion or increased capacity as business needs grow.
Customizing an optical counting machine involves integrating the right components and software to meet specific requirements, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in counting processes.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "optical counting machine"
Quality Control of Optical Counting Machines:
1. Component Inspection: Verify that optical sensors, circuits, lenses, and mechanical parts meet quality standards.
2. Calibration: Calibrate optical sensors to ensure accurate counting.
3. Software Validation: Test software for accuracy and functionality.
4. Assembly Line Check: Inspect assembly processes for adherence to specifications.
5. Performance Testing: Conduct repeated trials to ensure reliable counting under various conditions.
6. Environmental Testing: Ensure devices can operate under different temperatures and humidity levels.
7. Final Inspection: Verify that the final product meets all design and performance requirements.
Manufacturing Process of Optical Counting Machines:
1. Design and Prototyping: Develop initial designs using CAD software. Create and test prototypes.
2. Sourcing Components: Procure high-quality optical sensors, processors, screens, and other electronic components from reputable suppliers.
3. PCB Fabrication: Manufacture the Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) that will house the electronic components.
4. Component Assembly: Place and solder components onto PCBs using surface-mount technology or through-hole technology.
5. Optical Assembly: Install lenses and optical sensors into the machine. Ensure alignment for accurate counting.
6. Software Installation: Load operational software and perform initial system checks.
7. Calibration: Calibrate sensors to ensure they detect objects accurately. Use calibration tools and software.
8. Enclosure Assembly: Encapsulate the assembled PCBs and optical systems within robust enclosures.
9. Functional Testing: Conduct rigorous tests to ensure the machine counts accurately and operates reliably.
10. Quality Assurance: Perform comprehensive quality checks, including performance in different environments and conditions.
11. Packaging: Securely package the machines for shipment, including user manuals and calibration certificates.
12. Distribution: Distribute the optical counting machines to clients or markets.
Thorough quality control and meticulous manufacturing processes ensure high performance and reliability in optical counting machines.
How to use "optical counting machine"
An optical counting machine is designed to count small objects, such as pills, seeds, or coins, accurately and efficiently using optical sensors. Here’s how to use it:
1. Setup:
– Position the Machine: Place it on a stable, flat surface.
– Power On: Plug in the machine and switch on the power.
2. Configuration:
– Settings: Adjust settings according to the object’s size and shape. This may involve setting the sensitivity of the optical sensors, which can be done via a control panel or touchscreen interface.
– Calibrate: Run a calibration cycle if required. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate counting.
3. Loading Objects:
– Hopper: Pour the objects into the input hopper, which feeds them to the counting area.
– Feed Rate: Adjust the feed rate to control the flow of objects to avoid jams and ensure accuracy.
4. Counting:
– Initiate Counting: Press the start button or initiate the count via the touchscreen.
– Monitoring: Watch the display. The machine uses optical sensors to detect and count each object as it passes through the counting area.
5. Collection:
– Output Tray: Objects are dispensed into the output tray or container once counted. Ensure the container is adequately sized to avoid overflow.
6. Final Steps:
– Review Count: Check the display for the final count. Some machines offer printout options for records.
– Shutdown: Turn off the machine if counting is complete or if it will not be used for a while.
Maintenance:
– Clean: Regularly clean the sensors and machine parts to ensure accuracy.
– Inspection: Inspect for wear and tear to prevent malfunctions.
Always refer to the user manual for specific instructions and safety guidelines. Regular maintenance ensures longevity and accuracy.
List Properties and Terms of "optical counting machine"
An optical counting machine is a device used to count objects, typically small items such as pills, seeds, or electronic components. These machines use optical technology for accuracy and speed. Below are key properties and terms associated with optical counting machines:
Properties:
1. High Accuracy: Optical sensors detect and count items with great precision, minimizing errors.
2. Speed: Capable of processing large quantities rapidly, enhancing productivity.
3. Non-Contact: Utilizes light beams, reducing the risk of mechanical wear and tear.
4. Versatility: Can be adapted to various shapes, sizes, and types of objects.
5. Automated: Reduces manual counting labor and associated human error.
6. User-Friendly Interface: Often equipped with intuitive controls for ease of operation.
7. Data Recording: Can log and store count data for further analysis or reporting.
8. Compact Design: Many models are designed to save space while still performing efficiently.
9. Integration: Can be incorporated into larger automated systems or production lines.
10. Durability: Constructed to withstand industrial environments and frequent use.
Terms:
1. Optical Sensor: A device within the machine that detects objects using light.
2. Photoelectric System: Technology based on the emission and reception of light beams to count items.
3. Resolution: The smallest detectable object that the machine can accurately count.
4. Throughput: The amount of items the machine can count per unit of time.
5. Calibration: Adjusting the machine to ensure the accuracy of counting.
6. Singulation: Process of separating items to ensure each is counted individually.
7. Batch Counting: Counting items in groups or sets rather than individually.
8. False Rejection: Occurs when the machine incorrectly identifies an object as incorrect or out of spec.
9. Real-time Monitoring: The ability to observe and adjust the counting process live as it occurs.
10. Maintenance: Regular checks and servicing to ensure optimal performance of the machine.
Optical counting machines are critical in industries where precision and efficiency are paramount, offering a reliable solution for automated counting needs.
List The Evolution history of "optical counting machine"
The evolution of optical counting machines is a captivating journey through technological progress, extending from primitive mechanical contraptions to sophisticated digital systems.
1. Early Mechanical Devices: The concept of counting started with simple mechanical devices like the abacus, dating back to at least 3000 BCE. While not optical, these devices laid the groundwork for subsequent counting technologies.
2. Photomultiplier Tubes (1950s-1960s): Early optical counting systems emerged with the invention of the photomultiplier tube. These devices were used to count particles in various fields, particularly in scientific research, by detecting light emitted from chemical reactions or radioactive samples.
3. Fluorescence Microscopy (1970s-1980s): Advances in microscopy allowed for the counting of cells and microorganisms. Fluorescence techniques used specific dyes and optical devices to enhance visibility and automate counting.
4. Digital Image Processing (1990s): The development of digital imaging revolutionized optical counting. Computers, paired with advanced software, enabled the analysis and counting of objects from digital images. This was particularly useful in medical and biological research.
5. Automated Flow Cytometry (2000s): Flow cytometry brought higher precision to optical counting by using laser technology to detect and count cells in a fluid mixture. This advanced technique became vital in medical diagnostics and research.
6. Machine Learning and AI (2010s-Present): The integration of artificial intelligence has significantly enhanced the capabilities of optical counting machines. Machine learning algorithms can now accurately analyze and count objects in complex images, revolutionizing fields such as histology, pathology, and material sciences.
Each phase in the evolution of optical counting machines reflects vast improvements in accuracy, efficiency, and application scope, supporting a wide array of industries and scientific disciplines. Technological advances promise an even more precise and automated future for optical counting.
How to Select a Reliable optical counting machine
Choosing a reliable optical counting machine is crucial for accuracy and efficiency. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Accuracy and Precision: Ensure the machine delivers high accuracy and consistently reproducible results. Check for error rates and consistency.
2. Speed: Evaluate the counting speed to meet your operational needs. Fast processing without compromising accuracy is ideal.
3. Compatibility: Ensure the machine handles various shapes, sizes, and materials of objects you’re counting. Versatility is important for diverse inventories.
4. Ease of Use: Look for user-friendly interfaces and easy-to-navigate controls. Training requirements should be minimal.
5. Quality and Durability: Opt for machines from reputable manufacturers known for quality construction and durable materials. Customer reviews and ratings can provide insights.
6. Maintenance and Support: Check for availability of technical support and ease of maintenance. A good warranty and service plan are beneficial.
7. Cost: Balance cost with features. While affordability is important, don’t compromise on essential functionalities.
8. Upgradability: Consider machines that offer software or hardware upgrades to adapt to future needs.
9. Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the machine meets industry standards and regulatory requirements relevant to your sector.
10. Trial and Demonstration: If possible, request a demo or trial period to test the machine’s performance in your operational environment.
By paying attention to these factors, you can select a reliable optical counting machine that enhances productivity and accuracy in your workflow.
List "optical counting machine" FAQ
Optical Counting Machine FAQ
-
What is an Optical Counting Machine?
An optical counting machine uses advanced imaging and sensor technology to count objects, such as pills or electronic components, by analyzing visual data. -
How does it work?
The machine captures high-resolution images or videos of items passing through an observation area. It then uses specialized algorithms to identify and count the objects based on their shape, size, and color. -
What industries benefit from optical counting machines?
Primarily used in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and manufacturing, these machines are valuable in any industry requiring precise and rapid object counting. -
What are the advantages over traditional counting methods?
Optical counting machines are faster, more accurate, and reduce human error. They also minimize product waste and ensure compliance with quality control standards. -
Can it count different shapes and sizes?
Yes, the machine’s software can be programmed to recognize a variety of shapes and sizes, making it versatile for different applications. -
How accurate is the counting process?
Typically, optical counting machines have an accuracy rate of 99% or higher, depending on the quality of the imaging system and software algorithms. -
What is the typical speed of these machines?
Speed varies by model and application, but high-end machines can count thousands of items per minute. -
What maintenance is required?
Regular cleaning of lenses and sensors, software updates, and occasional calibration checks are necessary to maintain optimal performance. -
Is it easy to integrate into existing production lines?
Yes, most optical counting machines are designed for easy integration with existing production systems and can be customized for specific needs. -
Can it be used for quality control?
Absolutely. Beyond counting, it can inspect items for defects, ensuring that only products meeting quality standards pass through.
Overall, optical counting machines offer a reliable, efficient, and versatile solution for modern counting needs across various industries.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about optical counting machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is an Optical Counting Machine?
An optical counting machine uses advanced imaging and sensor technology to accurately count small items such as screws, tablets, or electronic components. It’s widely used in pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and logistics.
-
Why Source Optical Counting Machines from China?
China offers a wide variety of optical counting machines at competitive prices. Chinese manufacturers are renowned for their advanced technology, innovation, and cost-effective solutions. -
What Certifications Should I Look for?
Look for ISO certifications, CE marking, and other relevant industry-specific certifications. These ensure the machine meets international safety and quality standards. -
How Reliable are Chinese Manufacturers?
It varies. Research the manufacturer’s reputation, check for reviews and ratings, and ideally, get recommendations from other buyers. Visiting the manufacturer’s site or third-party inspections can also help verify reliability. -
What is the Typical Lead Time?
Depending on the complexity and customization required, lead times can range from a few weeks to a few months. Always confirm lead times with the manufacturer before placing an order. -
Are Spare Parts and After-Sales Services Available?
Reputable Chinese manufacturers often provide spare parts and after-sales services. Ensure that the manufacturer offers comprehensive support, including online troubleshooting and maintenance guidance. -
Can the Machine be Customized?
Many Chinese manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific industry needs. Provide detailed requirements to the manufacturer to ensure the machine fits your specific application. -
How Do I Ensure Quality?
Request samples or demo units. Use third-party inspection services to check for compliance with international quality standards. Explicitly mention quality control terms in the sales contract. -
What Payment Terms are Common?
Common payment terms include a small percentage upfront and the remainder upon delivery. Letter of Credit (L/C) and escrow services can also be used to safeguard transactions. -
How Can I Manage Shipping and Import Regulations?
Chinese manufacturers usually have experience exporting their products. They can guide you through shipping and customs procedures. Consider working with a logistics provider specializing in international trade.
By carefully considering these FAQs, buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing optical counting machines from China.