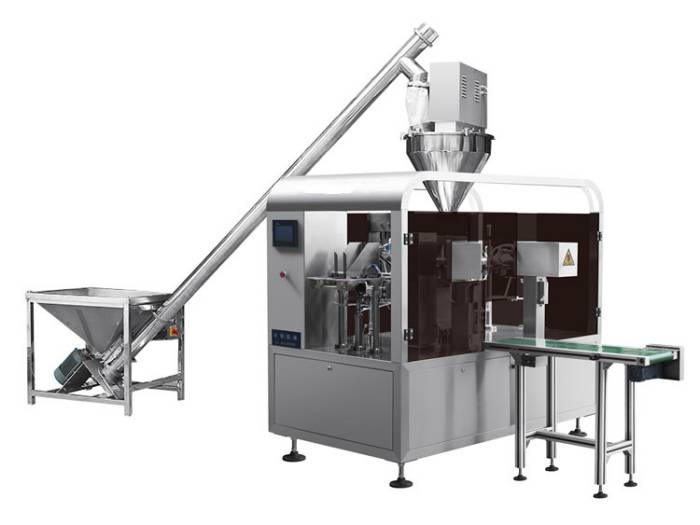
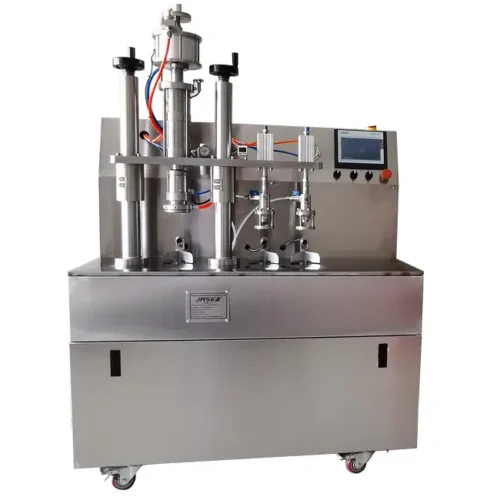
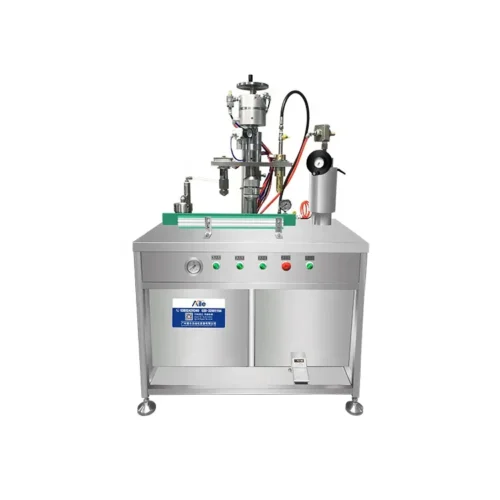
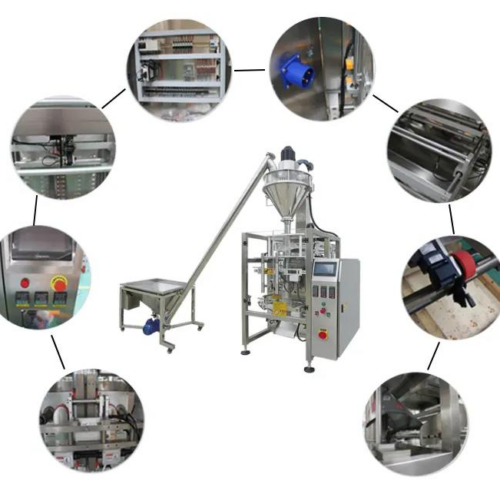
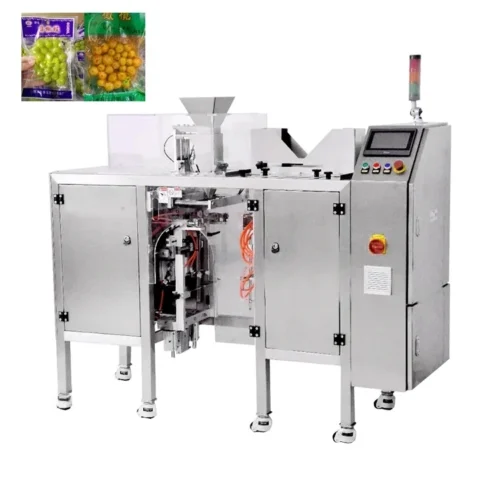
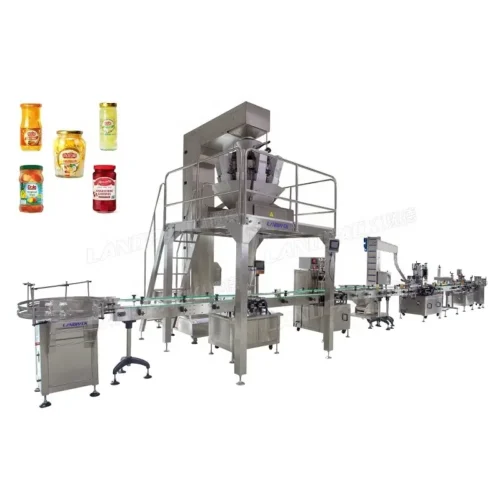
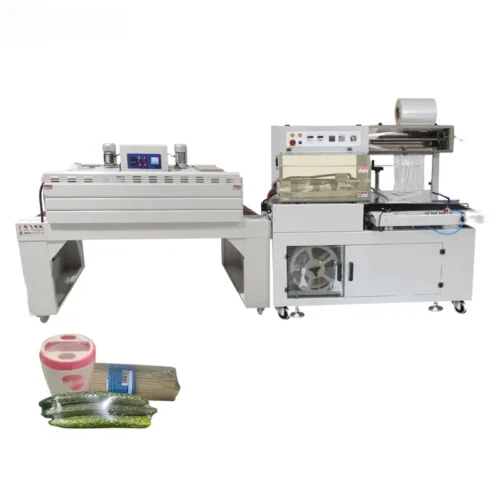
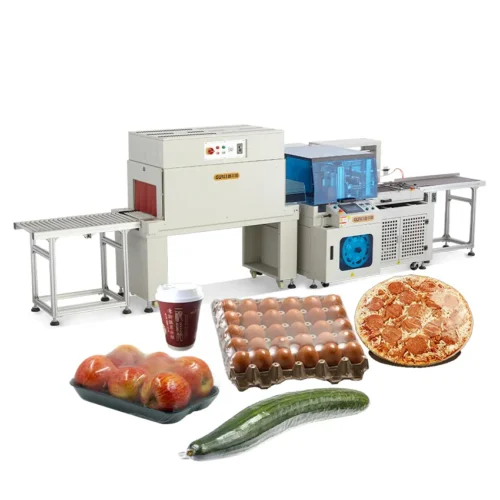
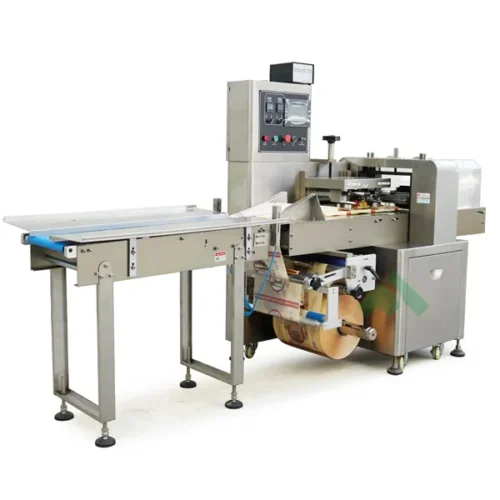
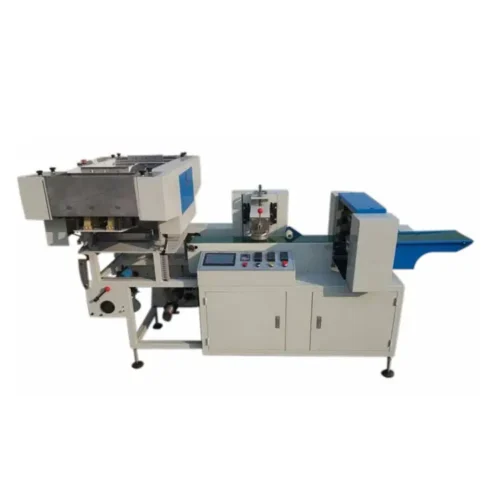
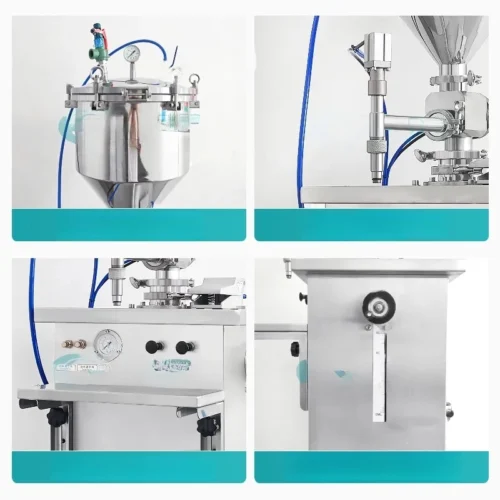
List Technical Parameters of "packaging machinery"
Certainly! Packaging machinery encompasses a wide range of equipment used to automate and streamline the packaging process. Here are the key technical parameters commonly associated with packaging machinery:
1. Machine Type: Categorizes machinery into sub-types like form-fill-seal, blister packing, cartoners, palletizers, labeling machines, etc.
2. Speed: Represents how fast the machine operates, usually measured in packs per minute (PPM) or cycles per minute (CPM).
3. Capacity: Indicates the production capability, such as the number of units packed per hour or per shift.
4. Dimensions:
– Machine Footprint: The physical space the machine occupies.
– Package Dimensions: The size range of packages the machine can handle.
5. Power Requirements: Specifies electrical requirements, typically in voltage (V) and frequency (Hz).
6. Material Compatibility: Types of packaging materials the machine can work with, such as plastics, paper, glass, or metal.
7. Load Capacity: The maximum weight the machinery can handle per package or batch.
8. Precision and Tolerance: Accuracy of measurement, cutting, sealing, etc., often expressed in millimeters or percentages.
9. Control System: Type of control interface, e.g., PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), HMI (Human-Machine Interface), etc.
10. Automation Level: Degree of automation, ranging from semi-automated to fully automated systems.
11. Durability and Build Quality: Material quality and robustness, often determined by the type of metals and composites used.
12. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and type of maintenance needed, e.g., lubrication intervals, parts replacement.
13. Safety Features: Safety mechanisms like emergency stops, guarding, and sensor systems.
14. Output Quality: Consistency and adherence to packaging standards, such as seal integrity or labeling accuracy.
15. Environmental Considerations: Energy efficiency, waste production, and compliance with environmental regulations.
16. Integration Capabilities: Ability to integrate with existing systems like ERP or MES (Manufacturing Execution System).
17. Flexibility: Ease of making adjustments for different packaging sizes and materials.
These parameters can vary significantly based on the application and specific requirements of the packaging process.
List Product features of "packaging machinery"
Packaging machinery offers an array of features designed to enhance efficiency, precision, and versatility in packaging processes. Here’s a concise yet comprehensive overview:
1. Automation: Modern packaging machinery often includes advanced automation capabilities, reducing human intervention and increasing operational efficiency.
2. Versatility: Capable of handling a wide range of products and packaging materials, from liquids to solids and delicate items to durable goods.
3. Advanced Controls: Equipped with user-friendly interfaces, touchscreens, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for precise control and easy adjustments.
4. Speed and Efficiency: High-speed operations ensure rapid and consistent packaging, catering to high-demand environments.
5. Precision: Accurate dosing, filling, and sealing mechanisms reduce waste and ensure product consistency.
6. Scalability: Modular designs allow for easy upgrades and scalability as production demands grow.
7. Safety Features: Integrated safety controls, emergency stop buttons, and protective enclosures to ensure operator safety.
8. Flexibility in Packaging Formats: Support for various packaging formats, including bottles, pouches, trays, and cartons.
9. Quality Control: Built-in inspection systems such as vision systems, checkweighers, and metal detectors ensure product quality and compliance.
10. Hygienic Design: Especially in food and pharmaceutical applications, machines are designed for easy cleaning and compliance with hygiene standards.
11. Energy Efficiency: Modern designs often focus on reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
12. Remote Monitoring: IoT-enabled features allow for real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and maintenance from remote locations.
13. Customization: Tailorable to specific industry needs, with options for custom configurations and add-ons.
14. Durability: Constructed with robust materials to withstand rigorous usage, ensuring longevity.
15. Minimized Downtime: Easy maintenance and quick-changeover capabilities reduce downtime, maximizing productivity.
These features collectively enable packaging machinery to meet diverse industrial requirements, drive productivity, and ensure high-quality output.
List Application of "packaging machinery"
Packaging machinery plays a crucial role across various industries, automating and streamlining the process of wrapping, enclosing, or protecting products for distribution, storage, and sale. Here’s a concise overview of its applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry: Ensures safety and extends the shelf life of products through processes like sealing, wrapping, and labeling. Machinery includes vacuum sealers, bottling lines, and cartoning systems.
2. Pharmaceuticals: Maintains sterility and accurate dosing, crucial for compliance with health regulations. Blister packs, strip packaging, and bottle filling machines are commonly used.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care: Enhances the aesthetic appeal and functionality of products. Machinery includes tube fillers, capping machines, and shrink packaging.
4. Consumer Electronics: Provides protection against static and mechanical damage. Examples are blister packaging, foam insertion, and thermoforming machines.
5. Automotive: Protects parts during shipping and storage. Applications include shrink-wrapping and foam-in-place packaging.
6. E-commerce & Retail: Streamlines order fulfillment with automated packaging lines for faster processing and improved accuracy. Includes box forming and sealing machines, and automated sorting systems.
7. Agriculture: Packages bulk products like seeds and grains, ensuring proper weight and protection through bag filling, sealing, and palletizing machinery.
8. Chemical Industry: Handles hazardous materials with precision and safety. Filling and sealing machines for chemicals in liquid or powder form are essential.
9. Textiles: Ensures products are neatly packed to maintain quality. Automated folding and packing lines are standard in this sector.
10. Healthcare: Accurately packages medical devices and supplies, ensuring sterility and correct part identification. Vacuum sealing and sterile packaging machines are widely used.
Packaging machinery not only enhances efficiency and quality but also reduces labor costs and waste, contributing significantly to the operational success in myriad sectors.
List Various Types of "packaging machinery"
Packaging machinery encompasses various types of equipment designed to perform specific functions in the packaging process, ensuring that products are efficiently and safely enclosed for distribution and sale. Here is a list of various types:
1. Filling Machines: Automatically fill containers with products, whether liquids, powders, or granules.
2. Sealing Machines: Securely seal packaging materials such as bags, pouches, and boxes to protect the contents.
3. Form-Fill-Seal Machines (FFS): Perform three tasks—forming the packaging, filling it with the product, and sealing it—all in one integrated process.
4. Labeling Machines: Apply labels to products, containers, or packages for identification and branding purposes.
5. Wrapping Machines: Enclose products in protective wraps; includes stretch wrappers and shrink wrappers.
6. Cartoning Machines: Form, fill, and close cartons (boxes), often used for products like food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
7. Blister Packaging Machines: Create and seal blister packs, commonly used for pills and electronic components.
8. Palletizing Machines: Automate the stacking of products onto pallets for easier transport and storage.
9. Thermoforming Machines: Heat plastic sheets until pliable to form specific shapes, often used for creating custom packaging.
10. Counting Machines: Automatically count and dispense a specific number of product units into each package.
11. Strapping Machines: Apply straps around boxes or pallets to secure items during transport.
12. Capping Machines: Secure caps onto containers, used extensively in the beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industries.
13. Vacuum Packaging Machines: Remove air from packages before sealing to extend shelf life, commonly used for perishable food items.
14. Heat-Shrink Machines: Apply heat to shrink plastic film tightly around a product for tamper resistance and damage protection.
15. Flow Wrapping Machines: Wrap products in a continuous, horizontal plastic film, often used for snack bars and small items.
These diverse types of packaging machinery cater to various industries, ensuring that products are packaged efficiently, safely, and attractively.
Custom Manufacturing Options for packaging machinery
Custom manufacturing options for packaging machinery are crucial in meeting the unique requirements of various industries. These options provide flexibility, efficiency, and tailored solutions to maximize productivity and cost-effectiveness.
1. Modular Design: Adaptable modules can be configured to meet specific production needs, allowing for easy updates and scalability as business demands grow.
2. Material Handling: Custom systems can handle diverse materials, including fragile, heavy, or oddly shaped products, ensuring safe and efficient packaging.
3. Automation Integration: Integration with existing automation systems like conveyors, robotics, and sensors enhances efficiency. Custom software solutions can also streamline operations, providing real-time monitoring and analytics.
4. Size and Speed Adjustment: Machines can be tailored to package products of varying sizes and shapes, with adjustable speeds to match production rates.
5. Multi-functional Capabilities: Combining multiple packaging functions—such as filling, sealing, labeling, and cartoning—into a single custom machine can improve efficiency and reduce floor space requirements.
6. Ergonomics and Safety Features: Customized machinery can include ergonomic designs to improve operator safety and comfort, reducing strain and enhancing productivity.
7. Compliance and Standards: Ensuring machines are built to comply with industry standards and regulations is critical. Custom options can meet specific sanitary, safety, and environmental regulations.
8. Aesthetic and Branding: Custom machinery can include specialized features for applying branding elements, ensuring consistency and enhancing market presentation.
9. Energy Efficiency: Incorporating energy-efficient technologies and components into custom packaging machines can lower operational costs and support sustainability initiatives.
These tailored solutions ensure that packaging machinery aligns perfectly with operational goals, regulatory requirements, and future growth, offering businesses a competitive edge in the market.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "packaging machinery"
Quality Control and Manufacturing Process of Packaging Machinery
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Development:
- Engineers use CAD software to create detailed designs and blueprints.
- Prototypes may be built and tested for performance and durability.
2. Material Selection:
- Engineers select high-quality materials like stainless steel or aluminum for durability and hygiene.
- Components such as motors, sensors, and control systems are sourced from trusted suppliers.
3. Fabrication:
– Cutting: Precision cutting tools such as laser cutters or CNC machines are used for accurate dimensions.
– Machining: Components are machined to exact specifications using CNC lathes and milling machines.
– Welding: High-strength welding techniques ensure robust assembly of parts.
4. Assembly:
- Components are meticulously assembled, often on specialized assembly lines.
- Custom jigs and fixtures may be used to ensure proper alignment and fit.
5. Electrical and Control Systems:
- Integration of electronic components, wiring, and control units.
- Programming of PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for automation and control.
6. Testing:
- Functional tests are conducted to verify operational efficiency.
- Safety tests ensure compliance with industry standards.
Quality Control:
1. Incoming Inspection:
- All raw materials and purchased components undergo rigorous inspection for quality and compliance.
2. In-Process Inspection:
- Continuous monitoring during manufacturing for adherence to design specs.
- Use of measuring instruments like calipers and micrometers to check dimensions.
3. Final Inspection:
- Complete machinery undergoes thorough testing in real operating conditions.
- Verification of performance, accuracy, and safety.
4. Quality Assurance Programs:
- Implementation of ISO 9001 or similar quality management systems.
- Regular audits and reviews for continuous improvement.
5. Documentation and Traceability:
- Detailed documentation of each production step.
- Traceability systems to track component history and identify potential issues quickly.
This structured approach ensures that packaging machinery meets high standards of quality, reliability, and safety, thereby providing efficient and long-lasting performance.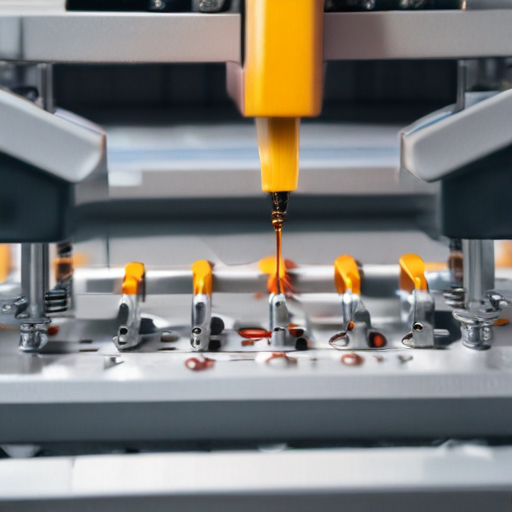
How to use "packaging machinery"
Using packaging machinery involves a series of steps designed to ensure efficient and accurate packing of products. Below is a concise guide to help you use packaging machinery effectively, adhering to a 300-word limit:
1. Read the Manual:
Always start by reading the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains essential safety guidelines, operating instructions, and maintenance tips specific to your machine.
2. Safety First:
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and ear protection. Ensure that the working area is free of obstructions and hazards.
3. Machine Setup:
– Power On: Connect the machine to the power source and switch it on.
– Load Materials: Load the packaging materials (e.g., films, boxes, labels) into the designated compartments.
– Adjust Settings: Configure the machine settings based on product specifications. This may include selecting appropriate packaging size, sealing temperature, and speed.
4. Calibrate the Machine:
Perform a test run with sample products to ensure the machine is properly calibrated. Check for issues like misalignment, incorrect sealing, or inconsistent filling.
5. Feeding Products:
Place the products onto the conveyor belt or feeding system. Ensure they are arranged correctly to avoid jams or mispacks.
6. Monitoring the Process:
Continuously monitor the packaging process. Watch for irregularities like machine stoppages, error messages, or damaged packaging. Address any issues promptly.
7. Quality Control:
Regularly check the packaged products for quality. Ensure that seals are secure, labels are correctly placed, and packages are intact.
8. Maintenance:
Follow maintenance schedules for cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting parts. This helps in preventing breakdowns and extends the machine’s lifespan.
9. Shut Down:
After completing the packaging, turn off the machine and disconnect it from the power source. Clean the machine as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
By following these steps, you can effectively use packaging machinery to enhance productivity and ensure consistent product packaging quality.
List Properties and Terms of "packaging machinery"
Packaging machinery encompasses a wide range of equipment designed for the various stages of production where products are packaged for distribution, sale, or storage. Here are some key properties and terms associated with packaging machinery:
1. Automation Level:
– Manual: Requires human intervention for each operation.
– Semi-automatic: Combines manual and automated processes.
– Automatic: Operates with minimal human input.
2. Types of Machinery:
– Fillers: Machines that measure and fill products into packaging.
– Cappers: Apply caps to bottles or containers.
– Labelers: Attach labels to packages.
– Cartoners: Form cartons and place products inside.
– Case Packers: Pack products into cases or boxes.
– Wrappers: Enclose packages with materials like plastic film.
3. Packaging Materials:
– Plastics: Widely used for flexibility and durability.
– Paper/Cardboard: Common for secondary packaging and eco-friendliness.
– Glass: Often used for liquids due to its barrier properties.
– Metals: Used for canned goods and certain pharmaceuticals.
4. Speeds and Capacities:
- Measured in units per minute (UPM) or pieces per hour (PPH).
- Higher speeds usually imply higher levels of automation.
5. Accuracy and Precision:
- Crucial for dosage and fill levels, especially in pharmaceutical and food industries.
6. Integration Capability:
- Ability to integrate with existing production lines and other machinery.
7. Compliance and Standards:
– ISO: International standards for quality and safety.
– GMP: Good Manufacturing Practices applicable in food and pharma.
– FDA: U.S. standards for food and drug safety.
8. Maintenance and Reliability:
- Regular maintenance is essential to prevent downtime.
- Reliability is critical for maintaining production schedules.
9. Safety Features:
- Guards, emergency stops, and non-contact sensors to ensure operator safety.
10. Customization Options:
- Machines can be tailored to specific product requirements and packaging styles.
Understanding these properties and terms is fundamental for selecting the appropriate packaging machinery that meets the needs of a specific production process.
List The Evolution history of "packaging machinery"
The evolution of packaging machinery is closely tied to technological advancements and changing market demands. Here’s a brief history:
1. Early Innovations (1800s):
- The Industrial Revolution spurred initial developments in packaging machinery.
- In 1843, the first patented envelope-folding machine marked the beginning of automated packaging.
- The late 1800s saw the introduction of canning and bottling machines to preserve food.
2. Early 20th Century:
- The early 1900s brought more sophistication with the development of carton-making machines.
- In 1925, the invention of the cellophane wrapper improved product visibility and preservation.
- Automated form-fill-seal (FFS) machines emerged, streamlining the process of creating, filling, and sealing packages.
3. Post-War Advances (1940s-1960s):
- World War II accelerated innovation in materials, giving rise to plastics.
- The 1940s and 50s saw increased automation and the development of vacuum packaging for prolonged shelf-life.
- In 1963, the first in-line computerized rotary motion control system was introduced, enhancing precision.
4. Digital Revolution (1970s-1990s):
- The 1970s introduced microprocessors, leading to programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in packaging lines.
- Robotics began to be integrated into packaging systems in the 1980s, improving efficiency and flexibility.
- Barcode technology emerged in the 1990s, revolutionizing inventory and supply chain management.
5. Modern Era (2000s-present):
- Focus on sustainability led to innovations in eco-friendly packaging materials and machinery.
- The 2000s saw the rise of smart packaging with QR codes and RFID tags for better tracking.
- Advanced robotics, AI, and IoT are now integral, providing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Industry 4.0 principles have led to further automation, interconnected systems, and enhanced data analytics in packaging line management.
Thus, from simple manual operations to today’s sophisticated, interconnected systems, packaging machinery has undergone significant evolution to meet changing industry needs.
How to Select a Reliable packaging machinery
Selecting a reliable packaging machinery involves several key considerations to ensure efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some important steps:
1. Specify Your Needs: Clearly define your packaging requirements, including the type of product, production speed, material compatibility, and desired automation level.
2. Research Manufacturers: Look for reputable manufacturers with a history of producing reliable machinery. Check for certifications, industry reputation, and user reviews.
3. Quality and Durability: Ensure the machinery is made from high-quality materials and has a robust construction. Durability is crucial to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
4. After-Sales Support: Choose a supplier who offers strong after-sales support, including maintenance services, spare parts availability, and technical assistance.
5. Vendor Experience: Opt for vendors with experience in your specific industry. They are more likely to understand your unique needs and provide tailored solutions.
6. Technological Features: Look for machinery with the latest technological advancements to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. Features like automation, integration capabilities, and user-friendly interfaces can be highly beneficial.
7. Cost of Ownership: Consider not only the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, and operational costs.
8. Trial and Testing: If possible, arrange for a trial run or visit existing installations to see the machinery in action. This can provide insights into performance and reliability.
9. Customization Options: Sometimes, off-the-shelf solutions may not meet all your needs. Check if the manufacturer offers customization to better align with your specific requirements.
10. Compliance and Safety: Ensure the machinery complies with industry standards and safety regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure worker safety.
By following these guidelines, you can select a reliable packaging machine that meets your operational needs and offers long-term value.
List "packaging machinery" FAQ
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about packaging machinery:
-
What types of packaging machinery are available?
Packaging machinery ranges from form-fill-seal machines, labeling machines, cartoning machines, bottling lines, blister packaging machines, shrink wrap machines, and others designed for specific packaging needs. -
How do I choose the right packaging machine for my product?
Consider product specifications, production volume, budget, available space, and desired packaging materials. Consulting with machinery suppliers who offer customization can help pinpoint your exact needs. -
What materials can packaging machinery handle?
Packaging machines can handle a variety of materials including plastic, glass, metal, paper, and biodegradable materials. The choice depends on the product and the machine’s capabilities. -
How important is machine flexibility?
Flexibility is crucial for businesses handling multiple products or packaging formats. Machines with adjustable settings can accommodate different sizes, shapes, and materials, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. -
What maintenance is required for packaging machinery?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning, lubrication, inspection for wear and tear, and replacing worn-out parts. Adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule ensures longevity and optimal performance. -
Can packaging machinery be integrated into existing production lines?
Yes, most modern packaging machinery is designed for easy integration with existing production lines. Ensure compatibility by consulting with equipment suppliers during the planning stage. -
What are the safety measures for operating packaging machinery?
Safety measures include installing guardrails, emergency stop buttons, regular training for operators, and adherence to local safety standards and regulations. -
How can I improve the efficiency of my packaging line?
Efficiency can be enhanced by choosing the right machinery, ensuring proper maintenance, training operators, and continuously monitoring and optimizing the production process. -
What is the cost of packaging machinery?
Costs vary widely based on the type, complexity, and level of automation. Prices can range from a few thousand to several hundred thousand dollars. Evaluating ROI is essential before making an investment. -
Is financing available for purchasing packaging machinery?
Many suppliers offer financing options. Leasing or financing through third-party financial services providers is also common, allowing businesses to manage cash flow more effectively.
These FAQs should provide a solid foundation for understanding packaging machinery. Each specific scenario may have unique considerations, so consulting with experts is always recommended.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about packaging machinery for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here are the top 10 FAQ about packaging machinery for buyers sourcing from China:
-
What types of packaging machinery are available?
- You can find machinery for various packaging needs, including filling, sealing, labeling, wrapping, and cartoning. Machines can be semi-automatic or fully automatic depending on your requirements.
-
How do I choose the right packaging machine?
- Assess your production volume, product type, packaging material, and desired automation level. Consult with the manufacturer for customized solutions to fit your specific needs.
-
Are Chinese packaging machines reliable and durable?
- Yes, many Chinese manufacturers produce high-quality, reliable machines. It’s essential to check certifications, client reviews, and request samples or factory visits to ensure quality.
-
What certifications should I look for?
- Look for international certifications such as CE, ISO 9001, and GMP. These indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
-
How can I ensure the machine will meet my specifications?
- Provide detailed product specifications to the manufacturer. Request a pre-shipment inspection or a Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) to verify that the machine meets your requirements.
-
What is the lead time for delivery?
- Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the machinery’s complexity and customization level. Confirm with the manufacturer early in the process.
-
Do Chinese manufacturers provide after-sales service?
- Many reputable manufacturers offer after-sales services, including installation support, training, spare parts, and remote troubleshooting. Verify these details before purchasing.
-
What is the average cost of packaging machinery from China?
- Costs vary widely based on machine type, size, and complexity. Basic models may start at a few thousand dollars, while advanced, fully-automated machines can cost upwards of $100,000.
-
How should I handle shipping and import duties?
- Work with a reliable freight forwarder experienced with importing machinery. Be aware of your country’s import duties, taxes, and regulations to avoid delays and additional costs.
-
Can I get a warranty for the packaging machine?
- Most manufacturers offer warranties ranging from 1 to 2 years. Confirm warranty details, including what parts and services are covered, before purchasing.
These answers should help you navigate the process of sourcing packaging machinery from China effectively.



















