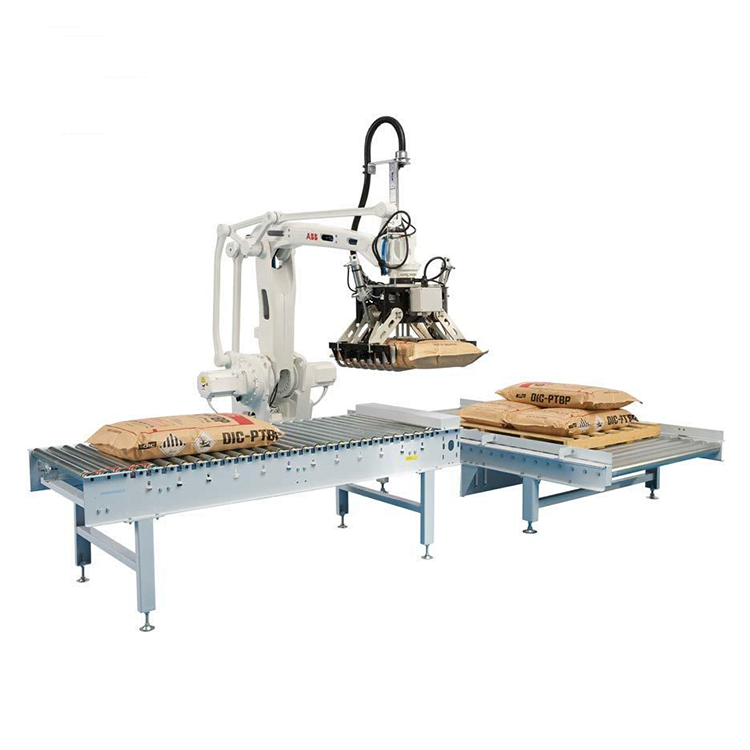
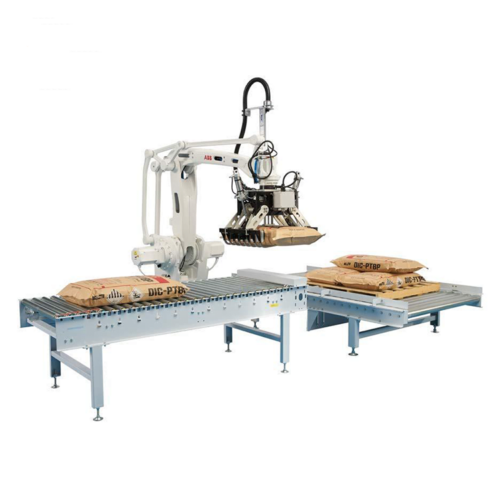
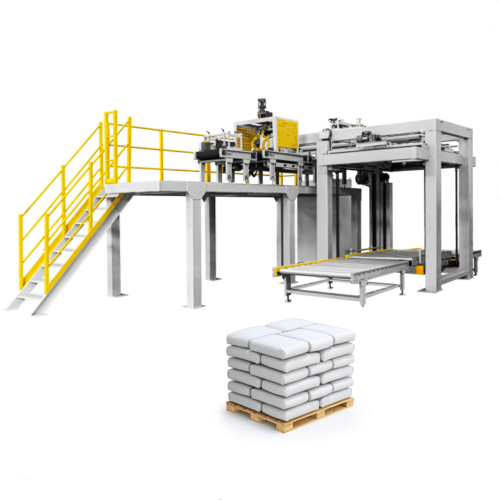
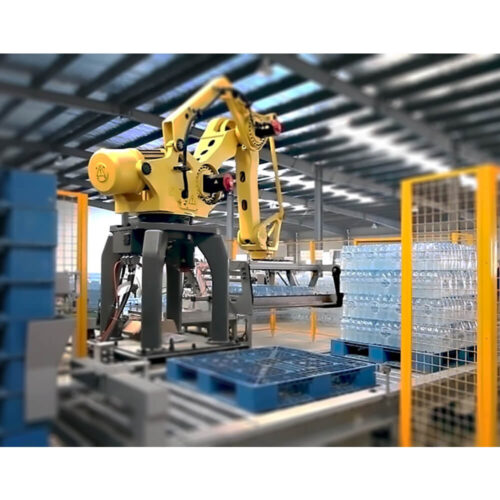
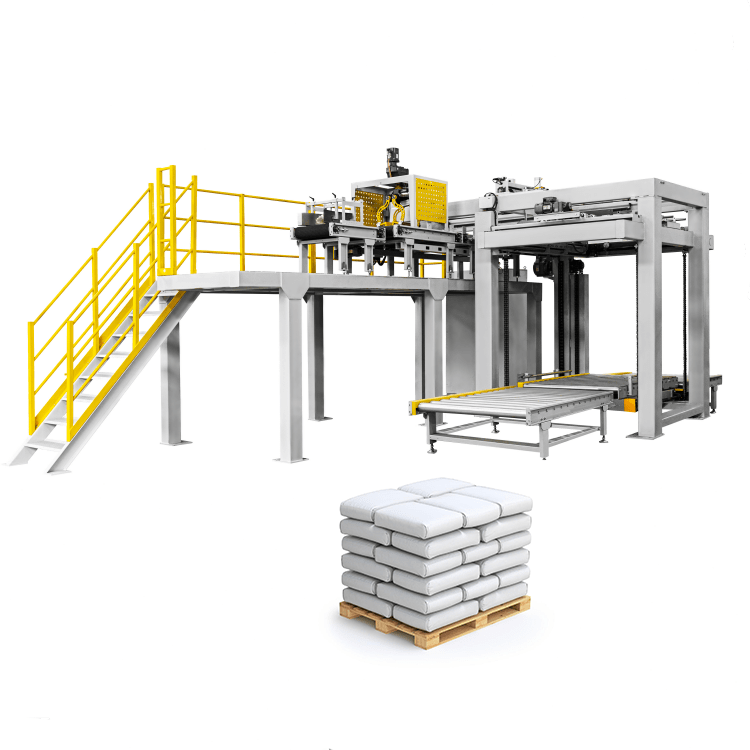
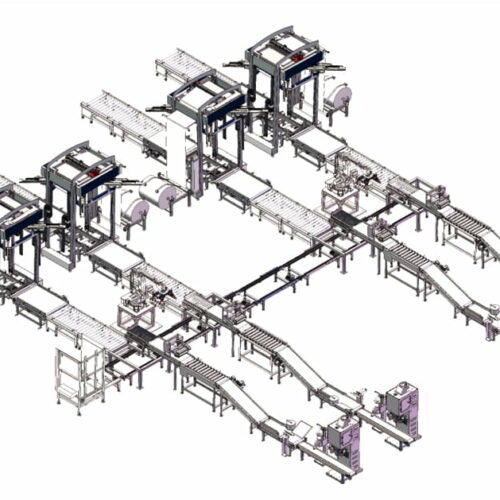
List Technical Parameters of "Palletizer System"
A palletizer system is a machine designed to automate the process of stacking and arranging goods onto pallets for storage or transportation. Here are the key technical parameters typically associated with a palletizer system:
1. Throughput Rate:
- Measures the number of items or cases per hour that the system can handle.
- Typical rates range from 10 to over 200 cases per minute depending on the system type and configuration.
2. Payload Capacity:
- Maximum weight that the system can handle per item and per pallet load.
- Can vary from a few kilograms per item to several tons per full pallet.
3. Pallet Size Compatibility:
- Dimensions of pallets the system can accommodate, usually specified in standard sizes like 48"x40" or 1200×1000 mm.
4. Stack Pattern Configurability:
- Ability of the system to arrange items in various stack patterns to optimize load stability and space utilization.
- Often programmable to handle different product sizes and shapes.
5. Operational Speed:
- Speed at which the system operates, influencing cycle time for palletizing tasks.
6. Footprint:
- Physical space required for installation and operation, including buffer zones for safety and maintenance.
7. Power Requirements:
- Electrical specifications, typically ranging from 220V to 480V AC, and power consumption in kilowatts.
8. Control System:
- Type and features of the control system, such as PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface).
- Often includes software for diagnostics, monitoring, and remote access.
9. Sensor and Safety Features:
- Types of sensors used (e.g., photoelectric, proximity) for item detection, positioning, and operation safety.
- Safety standards compliance, including emergency stops, safety fencing, and light curtains.
10. End Effector Types:
- Types of grippers or handlers used, such as vacuum, mechanical, or magnetic, suitable for different product types.
11. Integration Capability:
- Ability to integrate with upstream and downstream systems like conveyors, stretch wrappers, and warehouse management systems.
12. Maintenance and Downtime:
- Frequency and ease of maintenance tasks, with features for quick access to critical components.
These technical parameters are crucial for determining the suitability and efficiency of a palletizer system in specific industrial applications.
List Product features of "Palletizer System"
Palletizer Systems are pivotal in automating material handling processes across various industries. Below are the key features:
1. Automation: Fully automates the stacking and arranging of products on pallets, reducing labor costs and increasing operational efficiency.
2. Versatility: Capable of handling diverse product types and sizes, from boxes and cartons to bags and pails, ensuring flexibility.
3. Speed and Efficiency: High-speed operation with precision placement enhances productivity and minimizes downtime.
4. Robust Construction: Durable and sturdy build designed to withstand heavy-duty industrial environments, ensuring long-term reliability.
5. User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive control systems with easy-to-use touchscreens simplify operation and monitoring.
6. Customizability: Tailor-made configurations to suit specific workflow requirements and spatial constraints.
7. Safety Features: Equipped with advanced safety mechanisms, including guards, emergency stops, and sensors, to protect operators.
8. Compact Footprint: Space-efficient designs maximize facility usage without compromising functionality.
9. Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient components and systems reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
10. Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing production lines and warehouse management systems for holistic automation.
11. High Load Capacity: Capable of handling heavy weights, accommodating a broad range of product loads.
12. Maintenance-Friendly: Easy access for routine maintenance and minimal downtime ensure continuous operation.
13. Advanced Robotics: Incorporation of robotic arms and AI for precise placement and optimal stacking patterns.
14. Scalability: Modular design allows for future expansion and upgrades as operational needs grow.
15. Real-Time Monitoring: Built-in sensors and software provide real-time data tracking and diagnostics to ensure optimal performance.
16. Reduced Product Damage: Gentle handling mechanisms minimize damage to products during stacking and transportation.
17. Economic ROI: Cost-effective solution with a quick return on investment through increased efficiency and reduced labor costs.
These features collectively make Palletizer Systems indispensable for modern industrial operations, enhancing productivity and ensuring consistent performance.
List Application of "Palletizer System"
A Palletizer System automates the process of stacking products onto pallets, efficiently organizing goods for storage or transport. Here are some key applications:
1. Manufacturing: In FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) sectors, palletizers stack cases of products like beverages, canned food, and household items, optimizing space and ensuring stability during transit.
2. Warehouse and Distribution: Automated palletizers streamline order fulfillment by organizing products according to shipment requirements, significantly reducing labor costs and improving turnaround time.
3. Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, palletizers handle the bulk packaging of medications, medical devices, and supplies, ensuring they are stacked in a stable and contaminant-free manner.
4. Food and Beverage: Palletizers assist in the orderly stacking of packaged food and beverages, enhancing efficiency in handling and storage, crucial for maintaining the supply chain’s integrity.
5. E-commerce: With the rise of e-commerce, palletizer systems are integral in distribution centers, arranging various items efficiently for shipment, thus speeding up the order delivery process.
6. Agriculture: They are used for stacking sacks of grains, vegetables, and fruits, aiding in efficient storage and transport from farms to markets or processing plants.
7. Chemical Industry: For handling hazardous materials or heavy chemical containers, automated palletizers ensure safety and precision, minimizing human exposure to risks.
8. Textiles and Apparel: Palletizers assist in organizing large volumes of clothing and textile products, preparing them for distribution to retail outlets.
9. Construction Materials: They are used to stack heavy materials like cement bags, tiles, and bricks, facilitating transportation and inventory management.
10. Electronics: Automated systems handle delicate items such as TVs, computers, and other gadgets, ensuring they are safely stacked and ready for dispatch.
Overall, palletizer systems enhance efficiency, safety, and accuracy across diverse industries, driving operational cost savings and ensuring timely delivery of products.
List Various Types of "Palletizer System"
Palletizer systems are automation solutions designed for efficiently stacking and arranging products onto pallets for storage or shipping. The various types of palletizer systems include:
1. Conventional Palletizers:
– Low-Level Palletizers: Handle products at ground level; ideal for lower-speed applications.
– High-Level Palletizers: Handle products from an elevated position; suited for higher-speed applications.
2. Robotic Palletizers:
– Articulated Arm Palletizers: Equipped with multi-joint arms for versatile, high-precision stacking.
– Gantry Palletizers: Utilize a Cartesian coordinate system; typically more rigid and suited for uniform stacking tasks.
– Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Safe for human interaction; smaller and more flexible for mixed-production environments.
3. Hybrid Palletizers:
- Combine elements of conventional and robotic palletizers for optimized performance.
4. Inline Palletizers:
– Single-Line Palletizers: Stack products from a single production line.
– Multi-Line Palletizers: Accommodate multiple production lines, improving throughput and reducing floor space.
5. Compact Palletizers:
- Designed for small to medium-sized operations; prioritize space efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
6. Layer Depalletizers:
- Typically used for unloading pallets; systematically remove layers of products for further processing or repackaging.
7. Tray Palletizers:
- Specialized for handling trays, commonly used in bottling or canning industries.
8. Mixed Load Palletizers:
- Capable of assembling pallets with mixed product types; useful in distribution centers.
Each type of palletizer system has its own set of advantages based on factors like speed, flexibility, precision, and space requirements. Choosing the right system depends on the specific needs and goals of the operation.
Custom Manufacturing Options for Palletizer System
When considering custom manufacturing options for a palletizer system, it’s essential to address specific requirements that maximize efficiency, productivity, and adaptability. Here are key customizable features to consider:
1. Configuration Type: Choose from robotic, gantry, or layer palletizers based on space constraints and operational needs. Robotic palletizers offer flexibility, while layer palletizers are ideal for high-speed operations.
2. Product Handling: Customize end-effectors to handle diverse packaging types (cases, bags, drums, etc.) and materials (plastic, metal, cardboard). Adaptive grippers or vacuum systems can accommodate different shapes and weights.
3. Infeed Systems: Tailor the infeed system to synchronize with existing production lines. Options include roller conveyors, belt conveyors, or sorting systems to manage product flow efficiently.
4. Layer Patterns: Program custom stacking patterns to optimize pallet stability and maximize storage space, taking into account product dimensions and weight distribution.
5. Pallet Types: Cater to various pallet sizes and materials (wood, plastic, metal) by adjusting the palletizer’s base and securing mechanisms.
6. Safety Features: Incorporate advanced safety measures such as guarding, light curtains, and emergency stop functions to protect operators and streamline compliance with safety regulations.
7. Integration Capabilities: Ensure the palletizer system can communicate with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for seamless workflow integration.
8. Scalability: Design the system with future scalability in mind, allowing for easy upgrades or expansions as production demands grow.
9. Environmental Considerations: Adapt the palletizer to specific environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, cleanliness) to ensure reliable performance.
10. Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Implement user-friendly HMI controls for easy operation, real-time monitoring, and quick troubleshooting.
By customizing these aspects, manufacturers can create a palletizer system tailored to their unique operational needs, enhancing efficiency and throughput while reducing downtime and costs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "Palletizer System"
Quality Control for Palletizer System:
1. Initial Testing:
- Components like sensors, actuators, and conveyors undergo individual functional tests.
- Control systems software is tested in a simulated environment.
2. Inspection:
- Visual and dimensional inspection of parts to ensure compliance with design specifications.
- Verification of welds, machined surfaces, and assembly tolerances.
3. Assembly Validation:
- Sub-assemblies are checked for correct alignment and connectivity.
- Full system assembly is subjected to operational checks.
4. Performance Testing:
- The palletizer system is run through its full range of motions.
- Load testing with actual products to ensure reliability under operational conditions.
5. Safety Checks:
- Verification of safety interlocks, emergency stops, and guarding.
- Compliance with relevant safety and regulatory standards.
6. Final Qualification:
- End-to-end testing incorporating integration with other systems.
- Validation of efficiency and throughput as per user requirements.
Manufacturing Process of Palletizer System:
1. Design and Engineering:
- Develop detailed CAD models and drawings.
- Create software algorithms for control systems.
- Simulate system performance.
2. Procurement:
- Source high-quality materials and components.
- Engage reliable suppliers for custom parts.
3. Fabrication:
- Manufacture frames, conveyors, and structural components.
- Machine parts to precise tolerances.
- Produce electrical harnesses and control panels.
4. Assembly:
- Assemble mechanical and electrical sub-systems.
- Install software and configure control systems.
- Integrate sub-systems into the main frame.
5. Integration:
- Connect the system to other production line components.
- Set up interface with factory control networks.
6. Testing and Debugging:
- Run diagnostic tests to find and fix issues.
- Fine-tune software parameters for optimal performance.
7. Installation and Commissioning:
- Transport and install the palletizer at the client site.
- Conduct final testing and calibration.
- Provide operator training and support documentation.
Each stage in manufacturing and quality control ensures the palletizer system meets performance, safety, and reliability standards.
How to use "Palletizer System"
A palletizer system automates the stacking of products onto pallets for storage or shipment. Here’s a concise guide on how to use one:
1. Setup:
– Positioning: Place the palletizer in proximity to your production line.
– Integration: Connect it to the conveyor system feeding products into the palletizer.
– Pallet Supply: Ensure pallets are loaded into the pallet dispenser, if available.
2. Configuration:
– Program Settings: Use the control panel to set parameters like product dimensions, pallet pattern, and stack height.
– Safety Check: Make sure all safety guards and sensors are in place and operational.
3. Operation:
– Start-Up: Turn on the machine and start the conveyor.
– Product Alignment: The system will align products as they arrive.
– Stacking: The robotic arm or moving parts will place products onto the pallet according to the programmed pattern.
4. Monitoring:
– Continuous Observation: Monitor the process to ensure products are being stacked correctly.
– Error Handling: If the machine stops due to an error, follow on-screen prompts to resolve issues.
5. Maintenance:
– Regular Checks: Perform routine inspections and cleanings to ensure smooth operation.
– Software Updates: Keep the system’s software up-to-date for optimal performance.
6. Shutdown:
– Turn Off: Safely stop the machine using the control panel.
– Clear Products: Ensure all products are cleared from the conveyor and pallets are properly stored.
By following these steps, you can efficiently and safely use a palletizer system in your operations.
List Properties and Terms of "Palletizer System"
A palletizer system is a mechanized device designed to stack and organize products onto pallets strategically, enhancing storage, handling, and transportation efficiency. Below are the key properties and terms associated with palletizer systems:
Key Properties:
1. Automation Level:
– Manual: Requires human operation to place products.
– Semi-Automatic: Partial automation with human intervention.
– Fully Automatic: Complete automation without human aid.
2. Types of Palletizers:
– Conventional Palletizers:
– Low-Level Palletizers: Product is positioned at ground level.
– High-Level Palletizers: Product is positioned at an elevated level for stacking.
– Robotic Palletizers: Use robotic arms for flexibility and precision.
3. Throughput Capacity: Measures the number of units or pallets processed per hour.
4. Footprint: The physical space required for installation and operation.
5. Product Handling:
– Layering Patterns: Different stacking patterns like interlock, column, or overlapping.
– Product Types: Capability to handle various shapes and sizes such as boxes, bags, or cases.
6. End-of-Arm Tooling (EOAT): Customizable tools on robotic arms for picking and placing products accurately.
7. Controller System: Manages operations, including Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) for automated control.
8. Safety Features: Includes guards, emergency stops, and sensors for protection.
Key Terms:
1. Infeed Conveyor: Transports products to the palletizer.
2. Pallet Dispenser: Automatically feeds empty pallets into the system.
3. Slip Sheets/Layer Sheets: Thin sheets placed between layers to provide stability.
4. Turntable: Rotates products to the correct orientation for stacking.
5. Pallet Wrapping: Applies stretch film to secure stacked products.
6. Grippers/Clamps: Device attachments for grasping products securely during transfer.
7. Depalletizer: Reverse function to remove products from pallets.
In summary, the palletizer system streamlines the stacking process, increases operational efficiency, and ensures safe and stable transportation of goods. It comes in varying levels of automation, with specific tools and features designed to handle diverse industrial needs.
List The Evolution history of "Palletizer System"
The concept of palletizing, or the process of stacking goods onto pallets for shipping and storage, has evolved significantly since its inception.
1910s-1940s: Manual Palletizing
Initially, palletizing was a manual process where workers physically stacked products onto pallets. The primary aim was to streamline the handling and transportation of goods.
1950s: Mechanical Palletizers
The industrial boom post-World War II saw the advent of mechanical palletizers. These early machines utilized simple mechanical arms and conveyors to stack products, greatly improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
1970s: Robotic Palletizers
The integration of robotics into industrial processes marked a significant evolution. Robotic palletizers used programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robotic arms to enhance flexibility and precision in stacking goods. The robots could handle more variability and complexity in product types and stacking patterns.
1990s: Advanced Robotics and Vision Systems
As technology advanced, robotic palletizers incorporated vision systems and sensors. This allowed for real-time adjustments and better accuracy. Increased computational power also enabled more complex stacking algorithms and remote monitoring capabilities.
2000s: Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
The new millennium brought the development of collaborative robots, or cobots, designed to work alongside human operators. These machines featured advanced safety systems and were easy to program, making them suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises.
2010s: Smart Palletizers and IoT Integration
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 saw palletizer systems becoming "smart." These systems could collect and analyze data, provide predictive maintenance, and integrate seamlessly with other automated systems in a manufacturing or warehousing environment.
2020s: AI and Machine Learning
Today, AI and machine learning enable even greater efficiencies. Modern palletizer systems can optimize stacking patterns dynamically, predict product flows, and adapt to changing conditions through self-learning algorithms.
The ongoing advancements continue to push the boundaries in efficiency, safety, and flexibility, cementing the role of palletizer systems in modern logistics and manufacturing.
How to Select a Reliable Palletizer System
Selecting a reliable palletizer system requires careful consideration of several key factors:
1. Type of Palletizer:
– Conventional Palletizers: Suited for high-speed operations with uniform products.
– Robotic Palletizers: Offer flexibility for various product shapes and sizes.
2. Throughput Requirements:
- Assess your production speed demands and ensure the palletizer can handle peak loads without bottlenecks.
3. Product Compatibility:
- Evaluate the system’s ability to handle different product types, sizes, and weights to ensure versatility and future scalability.
4. Footprint:
- Consider the available space in your facility. Robotic systems often require less floor space compared to conventional palletizers.
5. Ease of Use and Maintenance:
- User-friendly interfaces and simple maintenance protocols reduce downtime and operational costs. Look for systems with good documentation and training support.
6. Supplier Reputation:
- Research the manufacturer’s track record for reliability, customer service, and support. Check for reviews, case studies, and references.
7. Integration Capabilities:
- Ensure the system can integrate seamlessly with existing conveyor systems, warehouse management systems (WMS), and other automation equipment.
8. Safety Features:
- Confirm the presence of safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and compliance with industry safety standards to protect personnel.
9. Cost:
- Balance initial investment with long-term savings from efficiency gains. Consider total cost of ownership, including installation, training, and maintenance.
10. Customization Options:
- Some systems offer customization to fit specific operational needs. Evaluate if custom features are necessary for your workflow.
A methodical approach considering these elements helps in choosing a reliable palletizer system that meets operational demands efficiently and sustainably.
List "Palletizer System" FAQ
Palletizer System FAQ
-
What is a palletizer system?
A palletizer system is an automated machine designed to stack products on a pallet in a uniform and stable manner, optimizing storage and transportation. -
How does a palletizer system work?
The system takes products from a conveyor, arranges them in a specific pattern, and then stacks them layer by layer onto a pallet using robotic arms or other mechanical means. -
What types of palletizers are available?
– Conventional Palletizers: Use a series of conveyors and grid systems.
– Robotic Palletizers: Utilize robotic arms for flexibility and precision.
– Mixed-Load Palletizers: Can handle different products and package types simultaneously. -
What are the benefits of using a palletizer system?
– Increased Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, reducing manual labor.
– Consistency: Ensures uniform stacking, reducing product damage.
– Cost Savings: Lowers labor costs and improves operational efficiency.
– Safety: Reduces workplace injuries associated with manual lifting. -
Can a palletizer handle different product sizes?
Yes, most modern palletizers can be programmed to handle a wide variety of product sizes and packaging types. -
Is it possible to integrate a palletizer with existing systems?
Yes, palletizers can be integrated with existing conveyor systems, warehouse management software, and other automation technologies. -
What are the maintenance requirements for a palletizer system?
Regular maintenance is required, including:
– Inspection: Routine checks for wear and tear.
– Lubrication: Regular lubrication of moving parts.
– Cleaning: Keeping sensor and mechanical areas clean to prevent malfunctions. -
How do I choose the right palletizer for my needs?
Consider factors such as:
– Product Type: Size, weight, and packaging.
– Production Speed: Required throughput.
– Space Constraints: Available installation space.
– Budget: Initial cost and maintenance expenses. -
What safety features are included in a palletizer system?
- Emergency Stop Buttons
- Safety Fencing and Light Curtains
- Collision Detection Systems
-
How long does it typically take to implement a palletizer system?
Implementation depends on system complexity, but it generally ranges from a few weeks to a few months.
This summary provides a concise overview of the essential aspects of palletizer systems, covering the common questions users may have.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about Palletizer System for Buyer Sourcing from China
Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) with answers regarding sourcing a Palletizer System from China:
-
What is a palletizer system?
A palletizer system automates the stacking of products onto pallets for efficient and safe transportation. -
Why source a palletizer from China?
China offers a robust manufacturing ecosystem, cost-effective solutions, and a variety of options tailored to different industry needs. -
How to ensure quality control?
Conduct factory audits, request ISO certifications, arrange third-party inspections, and consider trial run samples. -
What are the lead times for delivery?
Typical lead times range from 30 to 90 days, depending on customization, order size, and manufacturer capabilities. -
What costs are involved?
Costs include the palletizer unit price, shipping, import duties, and possibly installation and training fees. -
Is installation support provided?
Many Chinese suppliers provide remote or on-site installation support, user manuals, and training, often included in the purchase price. -
How do I handle maintenance and spare parts?
Verify that the supplier offers a comprehensive after-sales service, including spare parts availability and technical support. -
What customization options are available?
Customization options often include the design for different product types, pallet configurations, operational speed, and integration with other systems. -
How is performance ensured?
Suppliers typically perform factory tests and provide performance guarantees to ensure the system meets specified requirements. -
What are the payment terms?
Common terms are a 30% deposit upfront and the balance before shipment or upon delivery, though this can vary.
By addressing these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing palletizer systems from China.