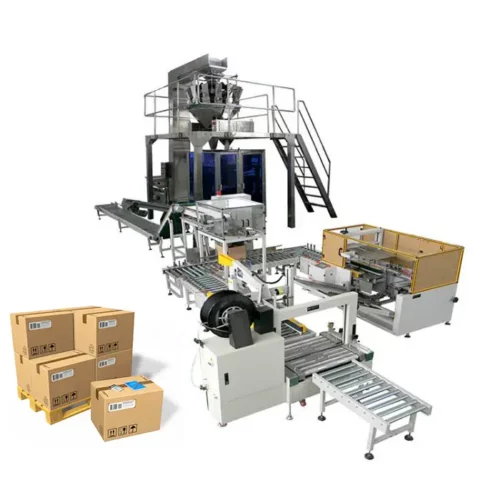
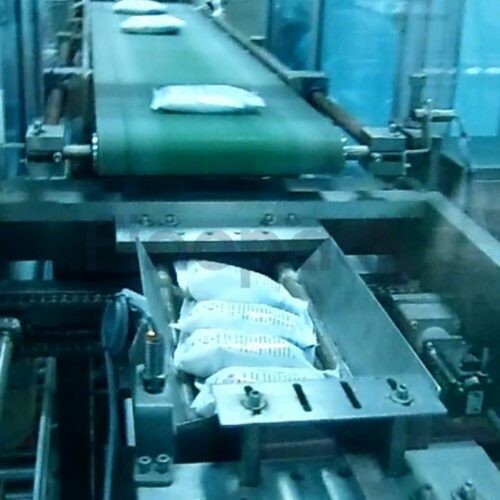
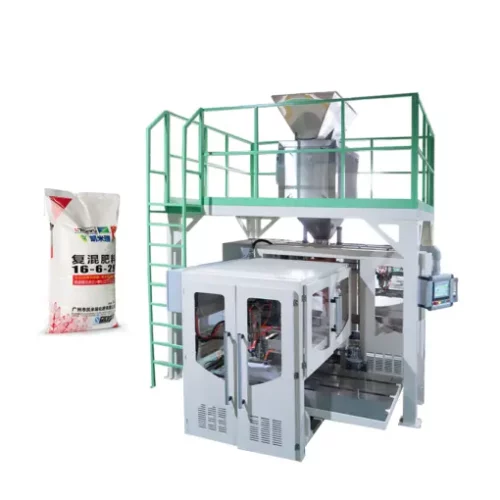
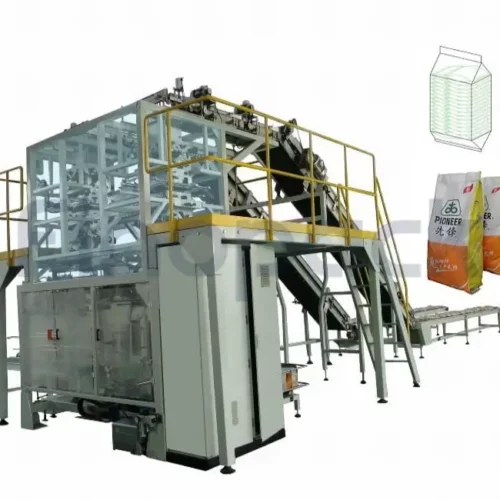
List Technical Parameters of "powder packaging machines"
Powder packaging machines are highly specialized equipment designed to pack powdered substances efficiently and accurately. Some of the critical technical parameters include:
1. Filling Capacity: The volume or weight range of powder the machine can handle per package. This can range from a few grams to several kilograms.
2. Speed: Measures the number of packages the machine can complete per minute. High-speed machines can process up to 120 packages per minute or more.
3. Accuracy: Precision in filling, often expressed as a percentage of the target weight. High-quality machines typically offer an accuracy of ±0.5% or better.
4. Packaging Material Compatibility: The types of materials the machine can work with, such as polyethylene, laminated films, and paper.
5. Bag Size Range: The range of bag dimensions the machine can accommodate, including width and length.
6. Sealing Type: Various sealing mechanisms like heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, and adhesive sealing, determining the integrity and shelf life of the packaged product.
7. Control System: Advanced machines use PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems with touch-screen interfaces for easier operation, monitoring, and maintenance.
8. Power Requirements: The electrical specifications, usually expressed in voltage (e.g., 220V, 380V) and power consumption (kW).
9. Material Handling Features: Options such as auger fillers, vacuum loaders, and vibratory feeders that cater to different powder characteristics.
10. Machine Dimensions and Weight: Physical size and weight, important for spatial planning in production facilities.
11. Material of Construction: Typically stainless steel or food-grade materials to ensure hygiene and durability, especially for food and pharmaceutical applications.
12. Dust Control Systems: Filters and enclosures to manage airborne particles during the packaging process.
13. Automation Level: Different levels from semi-automatic to fully automatic machines, impacting efficiency and labor requirements.
14. Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to standards such as FDA, CE, and GMP, depending on the intended application and region.
These parameters collectively determine the suitability, efficiency, and effectiveness of powder packaging machines in different industrial settings.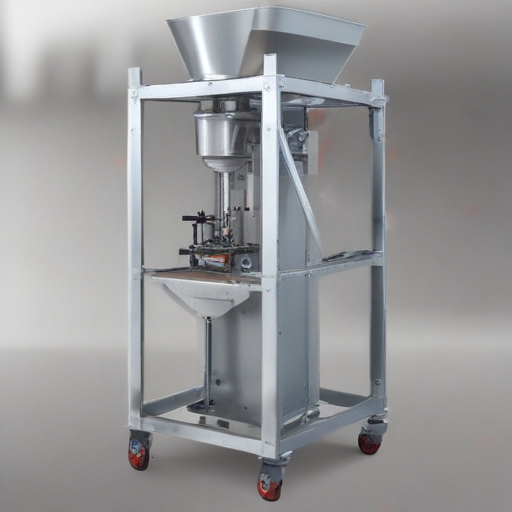
List Product features of "powder packaging machines"
1. Automated Operation and Control: These machines typically feature advanced automation for seamless operation, reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring consistent packaging quality.
2. High Accuracy and Precision: Powder packaging machines are designed with highly accurate weighing and filling systems to ensure precise quantity control and minimize material wastage.
3. Versatility in Packaging Types: They can handle various types of packaging, such as sachets, pouches, bottles, and cans, making them versatile for different product requirements.
4. Adjustable Speed: Many machines offer adjustable speed settings, allowing operators to control the packaging rate based on production demands and type of product being packaged.
5. Easy Changeover: Designed for quick and easy changeovers between different products, these machines minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
6. Efficient Sealing Mechanism: The sealing systems in these machines are robust, ensuring airtight and leak-proof packaging to maintain product freshness and shelf life.
7. User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with intuitive touch screen interfaces and control panels for easy operation and monitoring.
8. Hygienic Design: Made from stainless steel and other food-grade materials, ensuring easy cleaning and compliance with sanitary standards.
9. Dust Control Features: Integrated dust collection or emission control systems help maintain a clean work environment and reduce product loss.
10. Customization Options: Machines can be tailored to specific needs, accommodating various powder characteristics, packaging sizes, and desired production speeds.
11. Safety Mechanisms: Equipped with multiple safety features, including emergency stop buttons, sensors, and alarms to ensure operator safety and prevent damage to the machine.
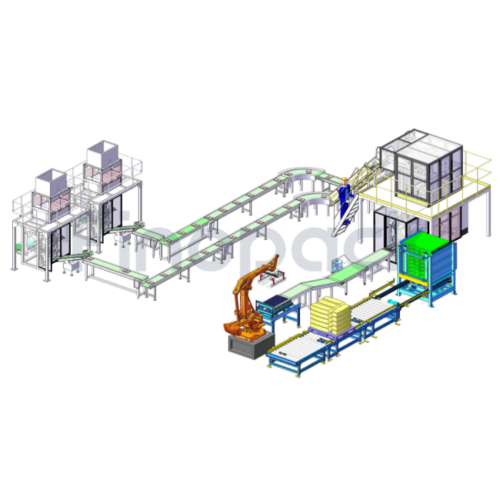
12. Integration Capabilities: Can be integrated with other production line equipment such as conveyors, labeling machines, and cartoners, providing a seamless production and packaging workflow.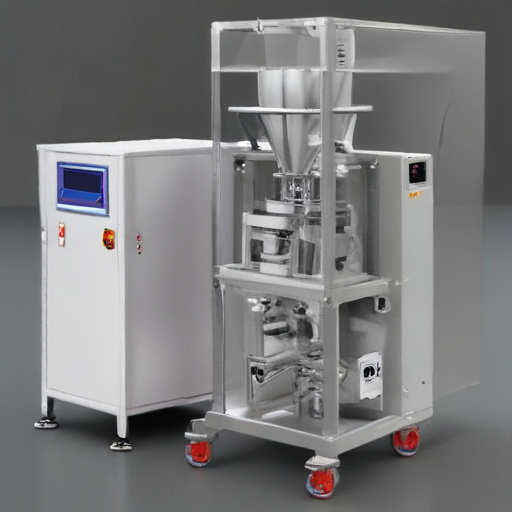
List Application of "powder packaging machines"
Powder packaging machines are specialized equipment used for packaging various types of powder products. These machines find applications across multiple industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and ability to maintain product integrity. Here are some prominent applications:
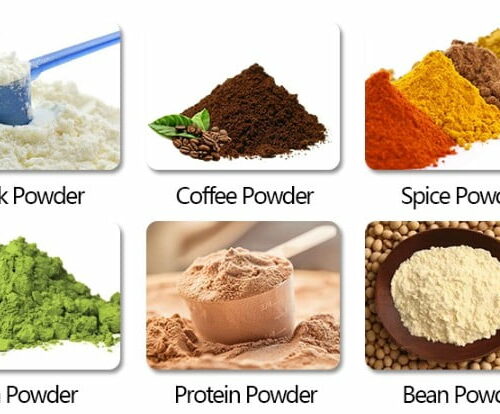
1. Food and Beverage Industry:
- Spices: Packaging spices like curry powder, chili powder, and pepper to preserve their aroma and extend shelf life.
- Baking Ingredients: Packaging baking powders, cocoa, and flour to prevent clumping and contamination.
- Instant Drinks: Packaging powdered coffee, tea, and drink mixes for convenience and easy consumption.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Medicinal Powders: Packaging powder forms of drugs, antibiotics, and dietary supplements to ensure precise dosages and maintain sterility.
- Protein Supplements: Packaging protein powders for athletes and fitness enthusiasts with specific labeling for dosage instructions.
3. Chemical Industry:
- Pesticides and Fertilizers: Packaging powdered pesticides and agricultural nutrients to facilitate easy application and safer handling.
- Cleaning Agents: Packaging powdered detergents and cleaning chemicals in various quantities for domestic and industrial use.
4. Cosmetic Industry:
- Beauty Products: Packaging powder-based cosmetics such as foundations, talcs, and dry shampoos to ensure product preservation and user convenience.
5. Construction Industry:
- Building Materials: Packaging powdered materials like cement, fillers, and joint compounds for easy transportation and accurate usage on construction sites.
6. Research and Development:
- Lab Chemicals: Packaging chemical and biological powders in precise quantities for laboratory research and testing to ensure experimental accuracy.
Powder packaging machines offer several benefits, including increased production speed, reduced labor costs, and high precision in packaging. They can handle a range of packaging materials like plastic, paper, and composite films, ensuring that product quality is maintained while meeting industry standards and consumer demands.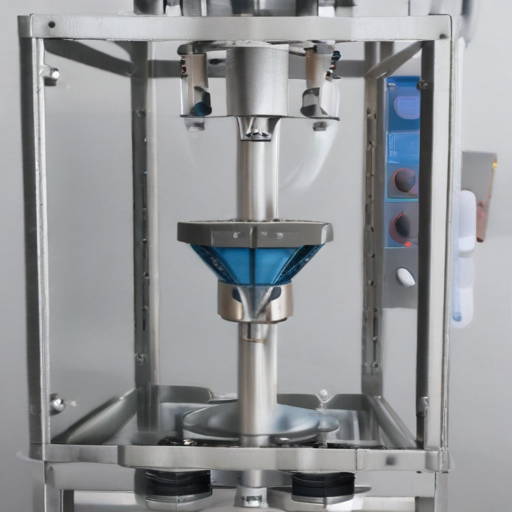
List Various Types of "powder packaging machines"
Powder packaging machines are essential in various industries for efficiently packing powdered products. These machines come in different types to accommodate various packaging needs:
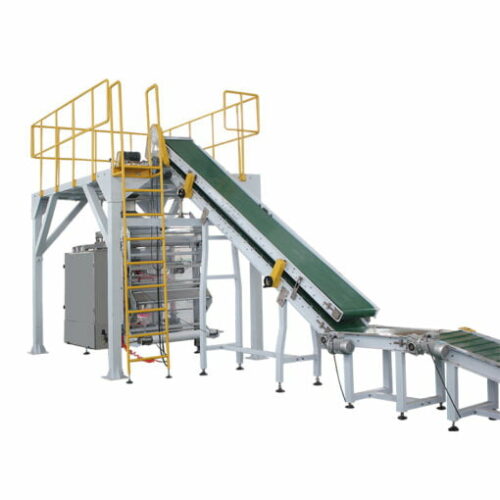
1. Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machines: These machines form pouches from a roll of packaging material, fill them with the product, and seal them. Ideal for high-speed operations and flexible packaging.
2. Horizontal Form Fill Seal (HFFS) Machines: Similar in function to VFFS but designed for horizontal packaging. Suitable for sachets and small packets, providing versatile and high-speed packaging.
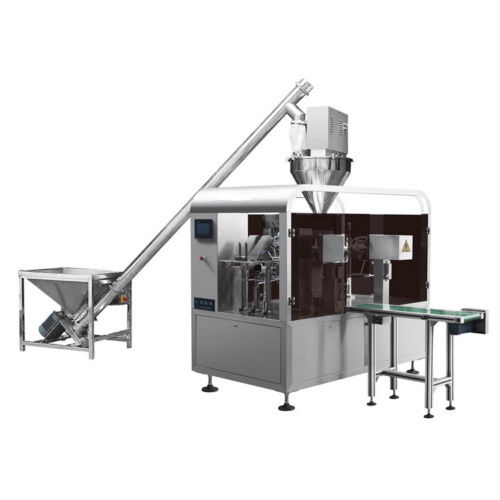
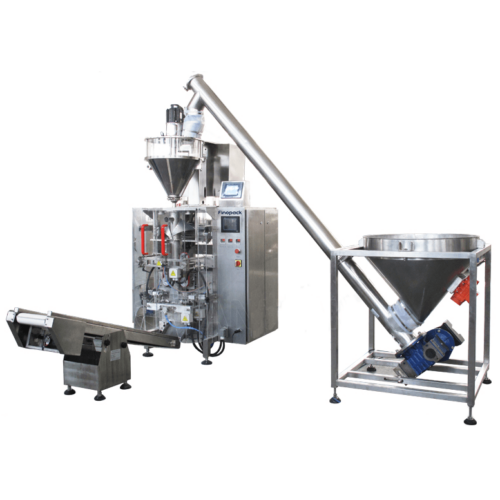
3. Auger Filling Machines: Utilizes a helical screw (auger) to measure and dispense the powder into bags, bottles, or other containers. Commonly used for consistent and accurate filling of free-flowing powders.
4. Cup Fillers: Uses a rotating cup system to measure and dispense powders. Less precise than auger fillers but effective for granular products and faster filling.
5. Stick Pack Machines: Designed specifically for small, single-serve stick packs. These machines are compact and suitable for pharmaceutical, food, and beverage industries.
6. Vacuum Packaging Machines: Removes air before sealing the package, extending the shelf life of the powdered product. Often used for high-value or sensitive powders.
7. Semi-Automatic Powder Filling Machines: Combine manual and automatic elements, requiring operator intervention for some steps. Suitable for small to medium-scale production.
8. Volumetric Fillers: Utilize a set volume to dispense product into packages. Useful for products where weight variation is acceptable.
9. Net Weight Fillers: Ensures precise weight of the product in each pack by measuring the net weight. Ideal for applications where exact weight is crucial.
10. Vacuum Auger Filling Machines: Combine the principles of auger and vacuum filling for more precise control over powder flow, particularly suited for fine powders.
Each type of powder packaging machine offers unique benefits, making them suitable for different product characteristics and production requirements.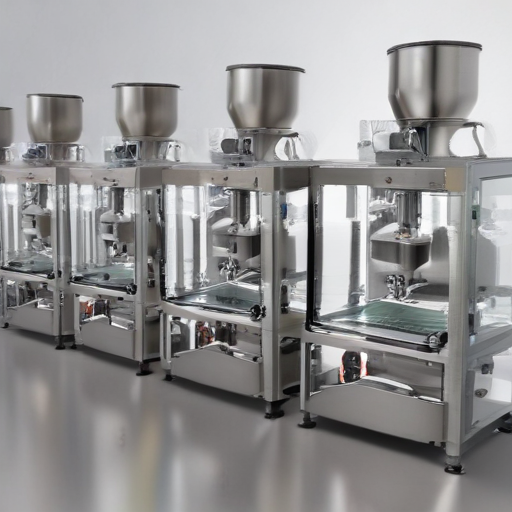
Custom Manufacturing Options for powder packaging machines
Custom manufacturing options for powder packaging machines offer numerous possibilities to cater to specific industry needs and product requirements. By tailoring your machine design, you can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Here are some customization options:
1. Filling Mechanisms: Choose from auger fillers, cup fillers, or volumetric fillers to match the product’s flow characteristics and required fill accuracy.
2. Packaging Formats: Customize for various packaging types such as sachets, stick packs, pouches, or jars. This includes adjustable sizes and configurations to fit different volumes and shapes.
3. Material Compatibility: Select construction materials like stainless steel for corrosive powders or food-grade plastics to meet industry standards like USDA or FDA regulations.
4. Automation Level: Options range from semi-automatic to fully automated systems, integrating features like automatic feeding, sealing, and labeling to streamline the operation.
5. Control Systems: Implement advanced PLC controls with touchscreen interfaces for ease of operation, real-time monitoring, and data logging to improve process control and traceability.
6. Speed and Capacity: Depending on production needs, machines can be customized to operate at various speeds and capacities, from small-scale to high-volume output.
7. Sealing Options: Different sealing mechanisms such as heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, or zipper closures can be incorporated based on the package type and desired hermeticity.
8. Additional Features: Integrate ancillary components like nitrogen flushing systems for shelf-life extension, anti-static devices for free-flowing powders, or cartoners for secondary packaging.
9. Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure compatibility with existing production lines, including conveyors, batching systems, and palletizers for a seamless manufacturing process.
10. Customization for Formulations: Adjustments tailored for hygroscopic, cohesive, or fine powders to ensure optimal handling and packaging without clumping or loss.
By customizing powder packaging machines to your specific needs, you enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and achieve higher precision, ultimately improving your product’s marketability.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "powder packaging machines"
Quality Control for Powder Packaging Machines:
1. Incoming Inspection:
- Raw materials and components are checked for compliance with specifications.
2. In-Process Inspection:
- Continuous monitoring during assembly to ensure adherence to design specifications.
- Measurement of parts to guarantee dimensional accuracy.
- Functional testing of sub-assemblies.
3. Final Inspection:
- Comprehensive evaluation of the completed machine.
- Performance tests to ensure accurate dosing and sealing.
- Verification of electrical and mechanical safety features.
4. Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT):
- Simulated production runs to test machine efficiency.
- Calibration checks for dosing accuracy and consistency.
5. Documentation and Traceability:
- Maintenance of detailed records of inspections, test results, and compliance certificates.
6. Customer Feedback and Iterative Improvements:
- Post-delivery performance monitoring.
- Incorporation of customer feedback into design refinements.
Manufacturing Process of Powder Packaging Machines:
1. Design and Prototyping:
- Detailed design blueprints and 3D models are developed.
- Prototyping for validation of design and functionality.
2. Procurement of Materials:
- Acquisition of high-grade steel, electronics, and components.
- Vendor quality assurance for standardized parts.
3. Machining and Fabrication:
- Precision machining of parts such as hoppers, augers, and frames.
- Welding and assembly of frames and structural components.
4. Assembly:
- Integration of mechanical components, including conveyors, filling systems, and sealing units.
- Installation of electrical components like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and sensors.
5. Quality Assurance Testing:
- Rigorous testing of assembled units for mechanical integrity, alignment, and operational functionality.
6. Final Assembly and Calibration:
- Final integration of sub-assemblies.
- Calibration of filling mechanisms to ensure dosing accuracy.
7. Packaging and Shipping:
- Preparation of machines for shipping with appropriate protective materials.
- Detailed user manuals and installation guidelines provided.
8. Installation and Training:
- On-site installation and operational training for end-users.
- Initial run testing and adjustments as necessary.

How to use "powder packaging machines"
Using powder packaging machines involves several key steps to ensure efficient and accurate packaging. Here’s a concise guide on how to use them:
1. Preparation:
- Select the Appropriate Machine: Choose a machine that suits the type and quantity of powder you are packaging (e.g., auger fillers, volumetric cup fillers).
- Check the Power Supply: Ensure the machine is connected to a stable power source.
- Clean the Machine: Make sure all parts in contact with the powder are clean to prevent contamination.
2. Setup:
- Fill the Hopper: Pour the powder material into the hopper or feeding unit of the machine.
- Program the Machine: Enter parameters such as weight, speed, and quantity using the control panel.
- Adjust Settings: Set up the packaging material by loading the film roll or placing the empty containers.
3. Operation:
- Start the Machine: Press the start button to initiate the packaging process.
- Monitor the Process: Keep an eye on the machine’s performance, ensuring it fills and seals packets correctly.
- Adjust as Needed: Make adjustments to settings if discrepancies arise (e.g., weight of the filled package).
4. Quality Check:
- Inspect Samples: Periodically check the packaged samples for accuracy in weight, sealing, and overall quality.
- Troubleshoot Issues: Address any problems immediately, such as misaligned seals or incorrect fill weights.
5. Shutdown and Maintenance:
- Turn Off the Machine: Follow the manufacturer’s procedures to power down the equipment safely.
- Clean the Machine: Ensure the machine is cleaned thoroughly after use to maintain hygiene.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance checks as recommended to prolong the machine’s lifespan.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use powder packaging machines to achieve consistent, high-quality packaging.
List Properties and Terms of "powder packaging machines"
Powder packaging machines play a crucial role in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. They ensure precise, efficient, and hygienic packaging of powdered products. Below are some of the key properties and terms associated with powder packaging machines:
Properties:
1. Automation Level: Ranges from semi-automatic to fully automatic, impacting speed and labor requirements.
2. Filling Accuracy: A crucial feature that ensures the right amount of product in each package, minimizing waste.
3. Speed: Measured in packs per minute (PPM), indicating the machine's efficiency.
4. Material Compatibility: Capability to handle various types of powders, including fine, granular, and free-flowing materials.
5. Hygienic Design: Features such as easy-to-clean parts and stainless-steel construction to meet sanitary standards.
6. Sealing Techniques: Methods like heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, or vacuum sealing to secure the packaging.
7. User Interface: Typically includes touch screens and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for easy operation and control.
8. Versatility: Ability to accommodate different packaging materials (such as bags, pouches, or bottles) and sizes.
9. Dust Control: Systems to minimize and manage dust release during packaging.
10. Durability: Built to withstand harsh operating environments and maintain performance over time.
Terms:
1. Auger Filler: A common technology for dispensing powder into packaging using a rotating auger screw.
2. Volumetric Filler: Measures product volume rather than weight, suitable for free-flowing powder.
3. Multi-head Weigher: Uses multiple weighing heads for high-precision filling.
4. Form-Fill-Seal (FFS): A machine that forms the package, fills the product, and seals it in one continuous process.
5. Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS): Specific FFS machine where the package is formed vertically.
6. Batch Coding: Printing production information on the package for traceability.
7. Hopper: A container that holds the powder before it is dispensed into the package.
8. Conveyor System: Transports packaging materials and filled packages through different stages of the packaging process.
9. Pneumatic Systems: Utilized to automate various aspects like sealing and material transport.
10. Servo Motors: Provide precise control over filling and sealing functions, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
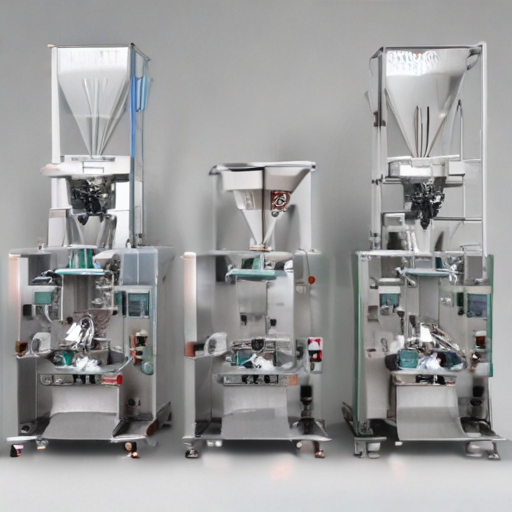

List The Evolution history of "powder packaging machines"
The evolution of powder packaging machines is marked by significant advancements that align with technological and industrial growth. Here’s a concise history:
Early 1900s: Manual Packaging
Packaging powders during the early 20th century was predominantly a manual task. Workers would scoop powders into paper bags or tins, and then seal them by hand. This method was labor-intensive and prone to inconsistencies in weight and contamination.
1930s: Basic Mechanization
The first mechanized packaging systems emerged, featuring simple conveyors and basic filling systems. These machines were limited in accuracy and speed but represented an essential shift away from manual labor.
1950s: Introduction of Form-Fill-Seal (FFS) Technology
The development of Form-Fill-Seal (FFS) machines revolutionized powder packaging. These machines automated the process by forming a package from a roll of film, filling it with the product, and sealing it. This innovation greatly improved efficiency, hygiene, and consistency in packaging.
1970s: Servo-Driven Systems
Servo motor technology introduced precise control over machine operations, elevating packaging accuracy and speed. Machines became capable of handling various packaging materials and configurations, from sachets to large bags, enhancing versatility in production lines.
1980s-1990s: Microprocessor and PLC Integration
The integration of microprocessors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) introduced automation into powder packaging machines. Operators could now control and fine-tune packaging processes with greater ease, enhancing productivity and reducing error rates.
2000s: Advanced Sensors and Robotics
The advent of advanced sensors and robotics further refined packaging precision and speed. Automated systems could now detect inconsistencies and make real-time adjustments, significantly reducing waste and downtime.
2010s-Present: Internet of Things (IoT) and AI
Modern powder packaging machines incorporate IoT and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. These smart machines offer predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data analytics, optimizing production efficiency and enabling seamless integration with smart factory environments.
Throughout its evolution, powder packaging technology has steadily moved towards increased automation, precision, and efficiency, driven by continual advancements in engineering and digital technology.
How to Select a Reliable powder packaging machines
Selecting a reliable powder packaging machine involves evaluating key factors to ensure efficiency and suitability for your needs. Here are essential steps to guide your decision:
1. Understand Your Requirements:
- Product Characteristics: Consider the type of powder (granular, fine, hygroscopic), flow properties, and the level of sensitivity to moisture or air.
- Packaging Style: Determine if you need bags, pouches, jars, or bottles.
- Production Volume: Assess your daily, monthly, or annual production requirements to select a machine with appropriate speed and capacity.
2. Machine Specifications:
- Accuracy: Look for machines with high precision for consistent and accurate dosing.
- Speed: Ensure the machine meets your production rate without compromising quality.
- Material Compatibility: Verify that the materials used in the machine are suitable for contact with your powder.
3. Quality and Reliability:
- Brand and Manufacturer: Opt for reputable manufacturers with positive reviews and a history of reliable machines.
- Build Quality: Choose machines with durable construction and high-quality components to minimize maintenance issues.
4. Technology and Features:
- Automation Level: Decide the level of automation required – fully automatic, semi-automatic, or manual.
- Control Systems: Modern machines with touchscreen interfaces, easy programming, and integrated control systems enhance usability and precision.
- Flexibility: Machines that can handle different packaging formats and sizes offer better adaptability for future needs.
5. Support and After-Sales Service:
- Technical Support: Ensure the manufacturer provides robust technical support and training.
- Spare Parts Availability: Confirm the availability of spare parts to avoid long downtimes.
- Warranty: A good warranty period reflects the manufacturer's confidence in their product.
6. Budget Considerations:
- Balance the cost of the machine with its features, reliability, and the expected return on investment.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a reliable powder packaging machine that meets your operational needs and ensures long-term productivity.
List "powder packaging machines" FAQ
Powder Packaging Machines FAQ
-
What types of powders can be packaged?
Powder packaging machines can handle a variety of powders including food powders (flour, spice, sugar), pharmaceutical powders, chemical powders, and cosmetic powders. -
What types of packaging are available?
Typical packaging includes sachets, pouches, bottles, jars, and larger bulk bags. Machine versatility allows for multiple packaging formats. -
How accurate is the packaging?
Most modern machines offer high precision through advanced weighing and filling systems, ensuring consistency and minimizing material wastage. -
What is the production speed?
Production speed varies by machine type and model, typically ranging from 20 to 120 packets per minute. Industrial models can achieve even higher speeds. -
Are the machines customizable?
Yes, machines are highly customizable to meet specific product requirements and production needs. Options include customized filling heads, sealing mechanisms, and integrated printing systems. -
What materials can be used for packaging?
Common materials include plastic films, laminated films, aluminum foils, and biodegradable materials, depending on the machine and product compatibility. -
How do I maintain the machine?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning to prevent contamination, checking for wear and tear on parts, and periodic calibration to maintain accuracy. -
What are the key features to look for in a powder packaging machine?
Key features include accuracy, speed, material compatibility, ease of use, automation capabilities, and after-sale support. -
Can the machine be integrated with existing production lines?
Yes, many machines are designed for seamless integration into existing production lines, featuring compatibility with upstream and downstream equipment. -
What safety features are included?
Safety features typically include emergency stop buttons, protective guards, automated shutdowns in case of malfunctions, and compliance with safety standards. -
How do I choose the right machine for my business?
Consider factors like production volume, type of powder, packaging material, budget, and the level of automation required. -
What is the cost range for powder packaging machines?
Costs vary widely based on capabilities and specifications, starting from a few thousand dollars for small-scale machines to over $100,000 for advanced industrial units.
These FAQs provide a basic understanding of powder packaging machines, helping you make informed decisions and ensuring efficient and precise packaging processes.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about powder packaging machines for Buyer Sourcing from China
Absolutely! Here's a concise FAQ about powder packaging machines for buyers sourcing from China:
-
What types of powder packaging machines are available?
- There are several types including vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) machines, auger filling machines, automatic pouch packing machines, and semi-automatic packing machines, each tailored to different powder packaging needs.
-
What materials are compatible with these machines?
- Most machines handle various packaging materials such as plastic films, laminates, paper-based materials, and aluminum foils, which can be in roll form or pre-made pouches.
-
Are Chinese powder packaging machines reliable?
- Yes, many manufacturers in China produce high-quality machines, often with international certifications like CE and ISO. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and possibly visit the factory or ask for sample testing.
-
What is the average lead time for these machines?
- Typically, it ranges from 30 to 60 days depending on the machine’s complexity and customization requirements. Confirming lead time with the manufacturer is crucial.
-
How do I ensure the machine meets my specific requirements?
- Provide detailed specifications of your product, including powder type, desired packaging weight, and packaging material. Request a customized solution if needed.
-
What kind of after-sales support is available?
- Reputable manufacturers offer comprehensive support including installation guidance, technical training, and maintenance services. Ensure that spare parts are readily available.
-
What is the typical warranty period?
- Warranties usually range from 12 to 24 months. It's advisable to clarify the terms, including coverage for parts and labor, with the supplier.
-
Do these machines comply with international safety standards?
- Many Chinese manufacturers adhere to international safety standards. Verify compliance by checking for CE, ISO, and other relevant certifications.
-
What factors affect the pricing of these machines?
- Pricing depends on machine type, functionality, automation level, capacity, and customization. Always compare quotes from multiple suppliers.
-
How do I address language barriers and communication challenges?
- Many suppliers employ English-speaking staff. Use clear, simple language and confirm details via formal documentation to avoid misunderstandings.
These FAQs should provide a solid foundation for buyers looking to source powder packaging machines from China.