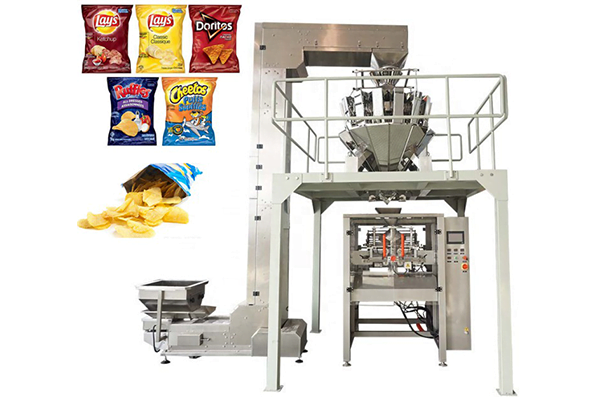
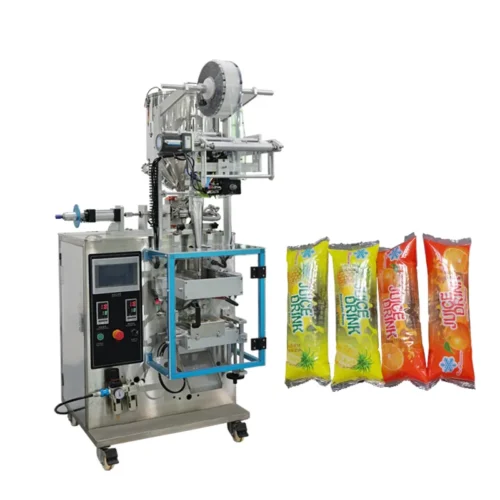
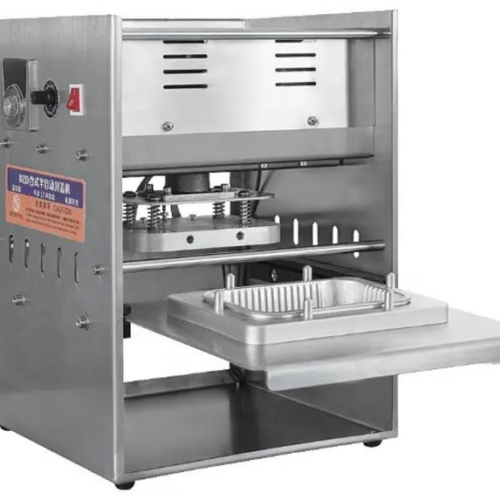
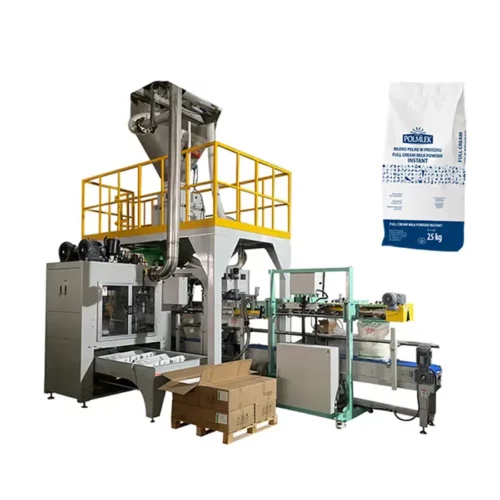
List Technical Parameters of "sealing machine"
Sealing machines are indispensable in various industries for packaging products efficiently and securely. Their technical parameters significantly influence their functionality and suitability for different applications. Below are some critical technical parameters of sealing machines:
1. Sealing Type:
– Impulse Sealing: Uses short, high-current electricity pulses.
– Constant Heat Sealing: Maintains a continuous temperature for sealing.
2. Sealing Width/Length:
- Determines the maximum sealing area the machine can manage, usually specified in millimeters or inches.
3. Sealing Temperature Range:
- The range of temperatures the machine can operate within, essential for handling various materials like plastics, laminates, or foils.
4. Power Supply:
- Voltage and frequency requirements, commonly 110V/220V and 50Hz/60Hz.
5. Sealing Speed:
- Measured in seals per minute or meters per minute, indicating the machine’s efficiency.
6. Maximum Seal Thickness:
- Specifies the maximum material thickness the machine can handle, usually mentioned in millimeters.
7. Pressure Control:
- Regulates the sealing pressure to ensure uniform seals, critical for different material types and thicknesses.
8. Control System:
– Manual: Basic machines with manual controls.
– Automatic: Advanced machines equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLC) for precision.
9. Cooling System:
- Ensures efficient operation by maintaining optimal machine temperature, either air-cooled or water-cooled.
10. Material Compatibility:
- Types of materials the machine can seal, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, or multi-layered films.
11. Machine Dimensions and Weight:
- Physical size and weight, crucial for space considerations in production environments.
12. Safety Features:
- Includes emergency stops, safety guards, and thermal overload protection to ensure operator safety.
13. Automation Level:
- Indicates whether the machine operates manually, semi-automatically, or fully automatically, impacting labor requirements and productivity.
By understanding these parameters, one can select the appropriate sealing machine tailored to specific industrial needs and applications.
List Product features of "sealing machine"
A sealing machine is an essential tool for packaging products securely and maintaining their freshness. Here are some key product features typically associated with a sealing machine:
1. Heat Sealing Technology: Utilizes heat to bond materials together, creating airtight and watertight seals for diverse packaging types.
2. Adjustable Temperature Control: Allows precise regulation of heat to suit various materials such as plastic, foil, or composite films, ensuring optimal sealing effectiveness.
3. Versatile Sealing Widths: Accommodates different bag or pouch widths, providing flexibility in packaging various product sizes.
4. Manual, Semi-Automatic, or Fully Automatic Operation: Options for different levels of automation based on production needs, from simple manual presses to advanced automated systems.
5. Digital Display: Provides real-time information on sealing parameters, such as temperature and sealing time, enhancing accuracy and ease of use.
6. Pressure Control: Ensures consistent pressure is applied during sealing, producing uniform and reliable seals.
7. Safety Features: Includes heat-resistant handles, emergency stop buttons, and protective shields, ensuring user safety during operation.
8. Durable Construction: Built from robust materials like stainless steel or aluminum for longevity and resistance to wear and tear.
9. Compact Design: Space-saving designs for easy integration into existing production lines or small workspaces.
10. Energy Efficiency: Designed to minimize power consumption, reducing operational costs.
11. Easy Maintenance: Features like accessible components and self-cleaning mechanisms simplify upkeep.
12. Compatibility: Works with various packaging formats including bags, pouches, tubes, and more.
13. Mobility Options: Some models include wheels or lightweight designs for easy movement and repositioning as needed.
14. Customizable Settings: Programmable settings for different packaging requirements, enhancing versatility across various products.
15. Quick Sealing Cycle: Fast operation speeds to boost productivity and streamline the packaging process.
These features collectively make sealing machines indispensable in industries ranging from food and pharmaceuticals to electronics and consumer goods.
List Application of "sealing machine"
Sealing machines are versatile devices used across various industries to ensure products are securely sealed for storage, transport, and sale. Here are some key applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Packaging Perishable Goods: Extends the shelf life of products like meat, poultry, dairy, and snacks by vacuum sealing or using modified atmosphere packaging.
– Sealing Bottles and Jars: Securely seals beverages, sauces, and condiments, preventing contamination and spillage.
2. Pharmaceuticals:
– Blister Packaging: Ensures individual doses of medications are protected from moisture and tampering.
– Strip Packaging: Encases tablets and capsules, maintaining their integrity.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care:
– Tube Sealing: Used for products like toothpaste, creams, and ointments.
– Jar Sealing: Ensures creams, lotions, and powders are protected from contamination.
4. Retail and Consumer Goods:
– Flexible Packaging: For items like clothing, electronics, and toys to protect from dust, moisture, and tampering.
– Clamshell Packaging: Often used for small electronics, batteries, and other retail products to prevent theft and damage.
5. Chemical and Industrial Products:
– Chemical Sealant Packages: Used for securing pesticides, fertilizers, and other industrial chemicals.
– Bulk Packaging: Ensures large quantities of raw materials are securely sealed for transport.
6. Medical Supplies:
– Sterilized Packaging: Ensures medical instruments and supplies remain sterile until use.
– Lab Sample Sealing: Prevents contamination of samples during transport and analysis.
7. Agricultural Products:
– Seed Packaging: Protects seeds from moisture and pests.
– Produce Packaging: Keeps fruits and vegetables fresh for longer periods during transit and storage.
8. E-commerce and Shipping:
– Tamper-evident Sealing: Ensures packages remain unopened and intact during shipping.
– Poly Bag Sealing: Protects items sold online, ensuring they arrive in pristine condition.
These applications highlight the critical role sealing machines play in maintaining product quality, safety, and shelf life across various sectors.
List Various Types of "sealing machine"
Sealing machines are essential in packaging to protect products from contamination and extend shelf life. Here are various types of sealing machines:
1. Impulse Sealer: Uses a brief pulse of electricity to generate heat. Ideal for sealing thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene.
2. Continuous Band Sealer: Employs a continuous loop to seal items quickly. Suitable for a high-volume sealing of bags and pouches.
3. Vacuum Sealer: Removes air before sealing. Commonly used for food packaging to extend freshness.
4. Heat Sealer: Uses constant heat to seal objects. Works well with thicker materials.
5. Automatic Sealer: Automated process ensures high efficiency and consistent seals. Often used in industrial settings.
6. Induction Sealer: Uses electromagnetic induction to create heat and seal foil liners. Common in bottling industries for tamper-evident seals.
7. L-Sealer: Creates an "L" shaped seal to encase products in shrink film before heat shrinking.
8. Shrink Wrap Sealer: Seals and then applies heat to shrink film around products for a tight fit.
9. Band Sealer with Gas Flush: Uses inert gas to displace oxygen before sealing. Utilized for packaging perishable items.
10. Foot Pedal Sealer: Operated by foot, freeing up both hands to handle products. Common for small-scale operations.
11. Bar Sealer: Seals using a bar that applies heat and pressure. Suitable for various materials and often used in laboratory settings.
12. Rotary Sealer: Uses rotating elements for sealing, ideal for continuous production lines.
13. Cup Sealer: Seals cups and containers commonly used in beverage and food industries.
These various types cater to different needs, materials, and volumes, making them integral to diverse industrial applications.
Custom Manufacturing Options for sealing machine
Custom manufacturing options for sealing machines allow businesses to tailor equipment to their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. These customizations can range from modifications in dimensions and power settings to advanced automation and integration capabilities. Here are some common custom manufacturing options for sealing machines:
1. Size and Design:
- Custom dimensions to fit unique production spaces.
- Ergonomic designs for ease of use.
2. Material Compatibility:
- Adaptation to seal various materials, such as plastics, metals, and composites.
- Specialized coatings or construction materials to prevent corrosion or wear.
3. Automation and Controls:
- Integration with existing production lines via PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems.
- Customizable user interfaces and touchscreen controls.
- Remote monitoring and control capabilities.
4. Sealing Technologies:
- Variety of sealing methods (heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, thermal impulse).
- Custom sealing bar configurations and temperatures.
- Multi-lane or multi-head systems for increased throughput.
5. Process Customization:
- Adjustable sealing times and pressures.
- Programmable cycles for different products.
6. Safety and Compliance:
- Compliance with industry-specific safety standards and regulations.
- Custom safety features, such as emergency stops and guarding.
7. Integration Features:
- Compatibility with other packaging machinery.
- Data logging and integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES).
8. Aesthetic and Branding:
- Custom paint colors and branding options.
9. Energy Efficiency:
- Energy-saving modes and customized power settings.
- Use of energy-efficient components.
By leveraging these custom options, businesses can ensure their sealing machines are perfectly aligned with their production requirements, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced product quality.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "sealing machine"
Quality Control in Sealing Machine Manufacturing:
1. Material Inspection:
– Raw Materials: Check for compliance with material specifications.
– Component Quality: Ensure all parts are within tolerance levels.
2. In-Process Testing:
– Dimensional Checks: Regular measurement during machining and assembly.
– Functional Testing: Validate each component’s function in the production line.
3. Assembly Verification:
– Sub-Assembly Testing: Ensure each sub-assembly meets design and performance criteria.
– Complete Assembly Audits: Whole machine inspection post-assembly for functional integrity.
4. Performance Testing:
– Operational Testing: Simulate working conditions to ensure reliable performance.
– Pressure and Seal Integrity: Test to ensure seal quality under various conditions.
5. Final Inspection:
– Aesthetic Check: Inspect for any cosmetic defects.
– Documentation Review: Ensure all records and certifications are complete.
Manufacturing Process of Sealing Machine:
1. Design and Prototyping:
– Concept Design: Develop initial models and layouts using CAD software.
– Prototype Creation: Build and test a working prototype for design validation.
2. Material Sourcing:
– Supplier Selection: Choose reliable suppliers for high-quality materials.
– Quality Verification: Inspect all incoming materials for compliance with specs.
3. Machining and Fabrication:
– Cutting and Shaping: Use CNC machines for precision cutting and forming.
– Welding and Assembly: Assemble components using welding, bolting, or soldering techniques.
4. Component Integration:
– Electrical Systems: Install circuits, sensors, and wiring.
– Mechanical Systems: Fit motors, gears, and other mechanical parts.
5. Software Installation:
– Programming: Load and test operating software for control systems.
– Calibration: Calibrate sensors and actuators for precise operation.
6. Testing and Debugging:
– Initial Testing: Conduct basic function and safety tests.
– Fine-Tuning: Adjust and refine settings for optimal performance.
7. Final Assembly and Packaging:
– Full Assembly: Complete the machine assembly following stringent protocols.
– Packaging: Securely package the machine for shipping, ensuring protection against damage.
8. Shipment and Installation:
– Logistics: Coordinate shipping to the customer.
How to use "sealing machine"
Using a sealing machine is relatively straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Preparation:
- Ensure the sealing machine is on a stable surface.
- Check that the device is plugged into a power source and turned on.
2. Material Setup:
- Select the appropriate sealing material, such as plastic bags or pouches, compatible with the machine.
- Place the item to be sealed inside the pouch or bag.
3. Positioning:
- Align the open edge of the bag with the sealing element (heating strip or bar) of the machine.
- Ensure the sealing area is clean and free from wrinkles for an even seal.
4. Operation:
- Close the machine’s lid or press the handle down, depending on the machine model.
- Set the required sealing time and temperature. Refer to the machine’s manual for guidelines based on the material you’re using.
- Engage the sealing process by pressing the appropriate button if needed.
5. Sealing:
- Wait for the machine to complete the sealing cycle. This usually involves heating to melt the material and then cooling to bond it.
- Some machines have an indicator light or sound to signal that sealing is complete.
6. Removal:
- Open the lid or release the handle.
- Carefully remove the sealed item, allowing time for the seal to cool and set properly.
7. Post-Sealing:
- Check the seal to ensure it’s secure and even.
- Store the sealed items as required.
Tips:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Regularly clean the sealing element to prevent residue build-up.
- Practice on a few test bags to get a feel for the timing and pressure needed.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a sealing machine for various applications, ensuring items are securely sealed.
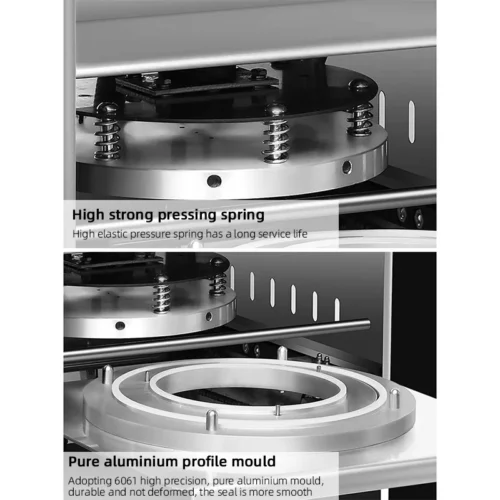
List Properties and Terms of "sealing machine"
A sealing machine is a device designed to close and seal various types of packaging, ensuring contents remain secure and uncontaminated. Here are some key properties and terms associated with sealing machines:
Properties:
1. Seal Type: Different methods such as heat seal, adhesive seal, ultrasonic seal, or induction seal.
2. Capacity: Refers to the volume or number of packages it can seal per minute or hour.
3. Material Compatibility: Types of materials it can seal, such as plastic, aluminum, paper, or composite packaging.
4. Seal Strength: The durability and integrity of the seal, critical for product preservation.
5. Size Range: The dimensions of the packages it can handle.
6. Automation Level: Manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic.
7. Temperature Control: Ability to control the temperature for heat sealing.
8. Pressure Control: Adjustable pressure settings for optimal sealing.
9. Speed: Adjustable speed settings for different production requirements.
10. Energy Efficiency: Power consumption rates.
11. User Interface: Ease of use, often featuring digital displays and controls.
12. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and ease of maintenance.
Terms:
1. Die: A tool used to shape or cut the sealing material.
2. Seam: The line where the two edges of the packaging meet and are sealed.
3. Thermocouple: A sensor for measuring temperature, critical in many heat-sealing machines.
4. Servo Motor: Used for precise control in automated sealing machines.
5. Conveyor: A belt or system to move products through the machine.
6. Nozzle: In adhesive sealing, the part that dispenses the adhesive.
7. Vacuum Sealing: A method of removing air before sealing to extend shelf life.
8. Cut-off Knife: A component that cuts the packaging material after sealing.
9. PID Control: Proportional-Integral-Derivative control used for maintaining consistent temperature.
10. Thermal Printer: Often integrated for printing dates or batch numbers on the package.
In summary, sealing machines are versatile tools essential for maintaining product integrity and efficient packaging. They come with diverse features tailored to specific production needs and material types.
List The Evolution history of "sealing machine"
The evolution of sealing machines spans several centuries and showcases significant technological advancements:
1. Early Beginnings (1700s-1800s): The concept of sealing started with simple wax seals used primarily for documents. The Industrial Revolution brought the invention of early packaging methods, including the use of tin cans sealed by hand.
2. Mechanical Advances (1830s-1900s): Bryan Donkin and John Hall patented the tin canister in 1810. By the mid-1800s, machines for sealing tin cans were developed, making the process more efficient. In 1858, Ezra Warner patented the first can opener, complementing the sealing process.
3. Early 20th Century: Automating the sealing process gained traction. Augustinson’s invention of the "Double Seam" technique in 1904 revolutionized canning by creating a hermetic seal. This period also saw the advent of heat-sealing pipes for food preservation.
4. Post-War Innovations (1940s-1960s): The rise of plastics brought new sealing technologies. The introduction of thermoplastics led to the development of heat-sealing machines for plastic bags and pouches, enhancing food and product packaging.
5. Late 20th Century: Continuous advancements led to the development of vacuum sealing machines, which further improved food preservation. The 1970s saw the rise of impulse sealers and automatic sealing systems, increasing efficiency in packaging lines.
6. Early 21st Century: Technological advancements resulted in the integration of computerized controls, enhancing precision and efficiency. The trend towards sustainability led to innovations in eco-friendly sealing materials and methods.
7. Recent Developments: The focus has shifted towards automation and smart technologies. Modern sealing machines incorporate AI and IoT for enhanced tracking, quality control, and operational efficiency. The move towards biodegradable and recyclable materials is also influencing sealing technology development.
These innovations have continuously refined the sealing process, catering to evolving industrial demands and environmental considerations.
How to Select a Reliable sealing machine
Selecting a reliable sealing machine is crucial for ensuring product integrity and operational efficiency. Here are key considerations:
1. Types of Sealing Machines: Understand the different types: impulse sealers, heat sealers, vacuum sealers, etc. Choose one that matches your packaging needs.
2. Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine is compatible with the materials you’re sealing, such as plastic, foil, or composites.
3. Sealing Speed and Efficiency: Evaluate the machine’s sealing speed and capacity. It should match your production requirements without compromising quality.
4. Ease of Use: A user-friendly machine reduces training time and errors. Look for features like digital controls and easy maintenance options.
5. Durability and Build Quality: Reliable machines are built with high-quality materials and components. Stainless steel housings and robust sealing bars are indicators of durability.
6. Versatility: A versatile machine can adapt to different sizes and types of packages, enhancing its utility across various applications.
7. Sealing Quality: Consistent and strong seals are paramount. Test the machine to ensure it delivers airtight and aesthetically pleasing seals every time.
8. Manufacturer Reputation: Choose machines from reputable manufacturers with positive reviews and reliable customer support.
9. Warranty and Support: A good warranty and accessible customer support are vital for maintenance and troubleshooting issues.
10. Compliance and Safety Standards: The machine should comply with industry standards and safety regulations for peace of mind and legal compliance.
11. Cost: While budgeting is important, prioritize quality and reliability over the initial cost to avoid frequent replacements and repairs.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a sealing machine that enhances productivity, ensures quality, and provides long-term value.
List "sealing machine" FAQ
Sure, here are some frequently asked questions (FAQ) about sealing machines, condensed to under 300 words:
-
What is a sealing machine?
A sealing machine is a device used to seal packaging materials to preserve and protect the contents. They are commonly used in food, pharmaceutical, and consumer goods industries. -
What types of sealing machines are there?
Sealing machines come in various types such as:
– Impulse Sealers: Use heat for a short period.
– Vacuum Sealers: Remove air before sealing.
– Continuous Band Sealers: Seal bags in a continuous process.
– Induction Sealers: Use electromagnetic induction for sealing. -
How does an impulse sealer work?
Impulse sealers generate heat only when the sealing arm is pressed down. This heat melts the edges of the plastic material, creating a seal when cooled. -
What materials can be sealed?
Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), aluminum foil bags, and laminated films. -
Is there any material-specific sealer?
Yes, some sealers are designed for specific materials. For example, induction sealers are often used for sealing foil. -
What’s the difference between manual and automatic sealers?
– Manual Sealers: Require user intervention for each seal.
– Automatic Sealers: Perform sealing automatically without continuous user interaction. -
Are sealing machines energy-efficient?
Modern sealing machines are designed to be energy-efficient, often incorporating features like programmable settings and energy-saving modes. -
How do I maintain a sealing machine?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning the sealing elements, checking for wear and tear, and following the manufacturer’s guidelines for servicing. -
Can sealing machines handle liquids?
Yes, but a vacuum sealer or a specialized liquid packaging machine is usually required to handle liquids effectively. -
What should I consider when choosing a sealing machine?
Factors to consider include the type of material, the volume of production, and the specific requirements of your product (e.g., shelf life, seal strength).
These FAQs cover the essentials, helping users understand the basics and operational aspects of sealing machines.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about sealing machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What types of sealing machines are available?
- Chinese manufacturers offer various types of sealing machines including heat sealers, vacuum sealers, induction sealers, ultrasonic sealers, and impulse sealers. Each type is suited for different materials and applications.
-
What is the typical lead time for sealing machine production and delivery?
- Lead times can vary but generally range from 20 to 45 days. Customizations and large orders may extend the timeline. Always confirm with the supplier.
-
Are Chinese sealing machines compliant with international quality standards?
- Many reputable Chinese manufacturers comply with ISO, CE, and other international standards. Always request certifications and conduct due diligence on the supplier’s credentials.
-
Can I request customization of the sealing machine to meet specific needs?
- Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization services for size, sealing modes, power specifications, and additional features. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier.
-
What is the shipping typically cost and what Incoterms are used?
- Shipping costs depend on the size, weight of the machine, and the shipping method (air, sea, or express). Commonly used Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight).
-
What after-sales services and warranty are provided?
- Warranties vary but generally range from 1 to 2 years. After-sales services may include remote troubleshooting, spare parts provisions, and on-site training. Verify specifics with the supplier.
-
How do I ensure the machines meet my quality expectations?
- Conduct factory audits, request pre-shipment inspections, and ask for test videos or samples. Hiring a third-party inspection company is also advisable.
-
What payment terms are generally accepted?
- Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes Escrow. Negotiation on terms is usually possible based on trust and order size.
-
Are there any language barriers when dealing with Chinese suppliers?
- Many Chinese suppliers have English-speaking sales teams. However, clear and concise communication is crucial. Use translated documents if needed and confirm understanding of all technical details.
-
How do I identify reliable Chinese sealing machine suppliers?
- Use platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, and Made-in-China. Look for verified suppliers with positive reviews and extensive transaction histories. Request references and visit trade fairs when possible.