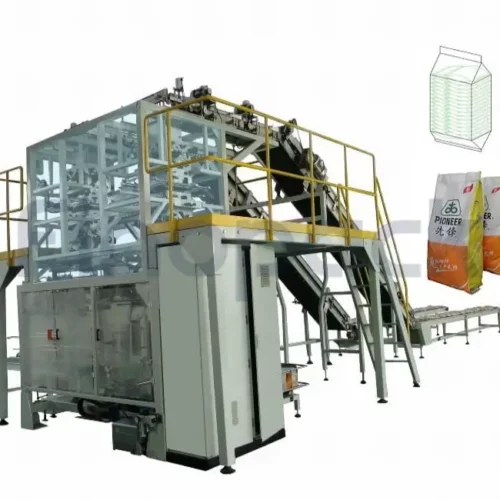
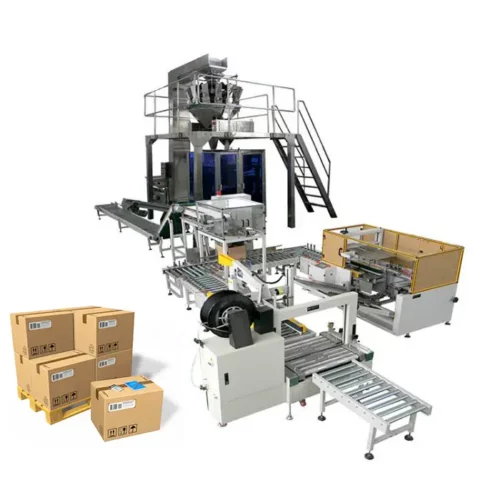
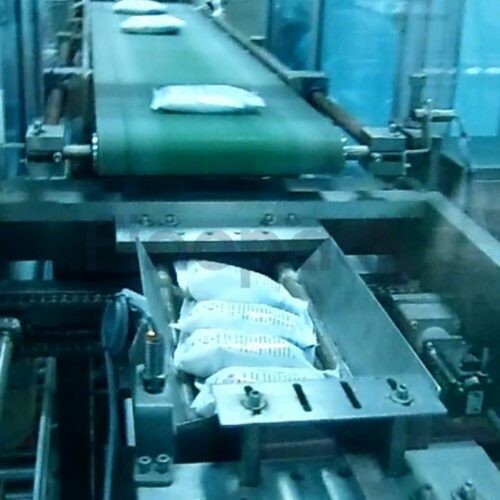
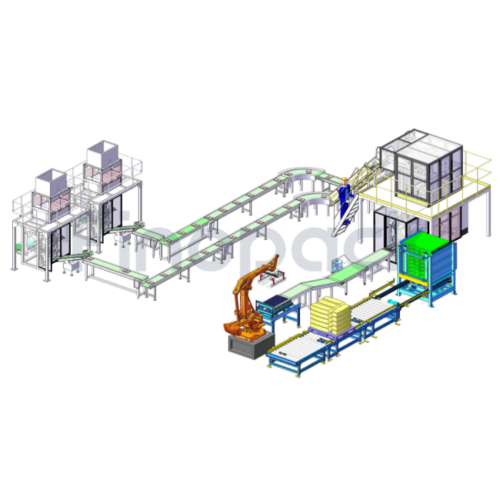
List Technical Parameters of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
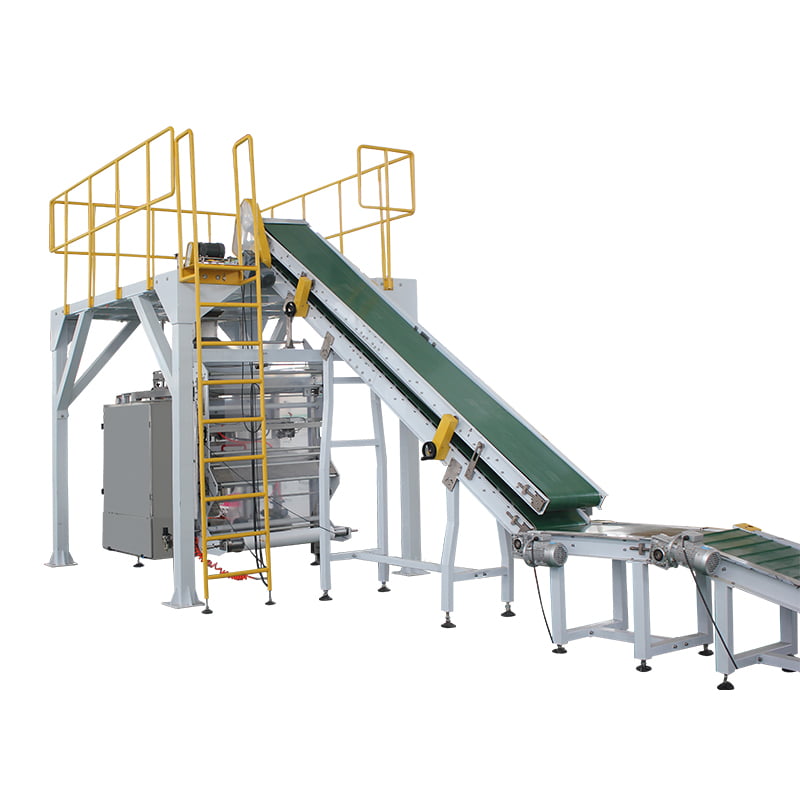
A Secondary Packaging Machine is designed to package primary packaged products into secondary containers like cartons, boxes, or bundles, preparing them for distribution or sale. Here are the critical technical parameters:
1. Throughput Capacity: Measured in units per minute (or hour), this defines how many products the machine can handle within a specific time frame.
2. Product Size Range: The minimum and maximum dimensions (length, width, height) of primary packages that the machine can process.
3. Carton Size Range: The range of carton dimensions the machine can handle, ensuring flexibility in packaging various products.
4. Material Compatibility: Types of materials the machine can accommodate, such as corrugated cardboard, paperboard, or plastic films.
5. Seal Type: Methods used to seal cartons, including hot-melt glue, tape, or locking tabs.
6. Changeover Time: The time required to switch the machine from processing one product size to another, crucial for operational efficiency.
7. Automation Level: Degree of automation—manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic operation—which impacts labor requirements and precision.
8. Control System: Type of control system (PLC, touchscreen interface) used for machine operation, settings adjustments, and diagnostics.
9. Power Requirements: Electrical specifications including voltage, phase, and frequency necessary for machine operation.
10. Footprint: Physical dimensions of the machine, which affects space planning and installation requirements.
11. Air Consumption: For pneumatic systems, the air pressure and volume required, usually measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
12. Load Capacity: Maximum load the machine can handle, ensuring it supports the total weight of products being processed.
13. Safety Features: Including emergency stops, interlock systems, and safeguarding measures to ensure operator safety.
14. Compliance: Adherence to industry standards and regulations like CE, UL, or ISO for quality assurance and legal compliance.
15. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and type of maintenance necessary to keep the machine functioning optimally.
Understanding these parameters will help in selecting the appropriate secondary packaging machine to meet specific production needs and ensure efficient operation.
List Product features of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
Secondary Packaging Machine: Key Product Features
1. Automated Operation: The machine offers efficient automated processes, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing throughput.
2. Versatile Packaging Options: Supports various types of secondary packaging formats, including cartons, trays, shrink wraps, and cases, ensuring adaptability for different products.
3. High-Speed Performance: Capable of handling high volumes of products at rapid speeds, optimizing production lines and minimizing downtime.
4. Precise Alignment and Placement: Advanced sensors and alignment systems ensure accurate placement of products, reducing error rates and improving package quality.
5. Integration Capabilities: Easily integrates with existing production line equipment such as primary packaging machines, conveyors, and palletizing systems for seamless operations.
6. User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with intuitive touch-screen controls and user interfaces, simplifying operation and monitoring for operators.
7. Adjustable Settings: Features adjustable components to cater to different product sizes and packaging requirements, enhancing flexibility.
8. Quality Assurance Systems: Incorporates inspection systems to detect defects and ensure the integrity of the packaging, maintaining high quality standards.
9. Compact Design: Space-saving design fits into various production environments without compromising functionality or accessibility.
10. Durability and Reliability: Constructed with robust materials and components, ensuring long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
11. Energy Efficiency: Implements energy-saving technologies to reduce power consumption, promoting sustainability and lowering operational costs.
12. Safety Features: Equipped with comprehensive safety mechanisms such as guards, emergency stops, and fail-safe systems to protect operators and the equipment.
13. Customizable Configurations: Available in various configurations to meet specific industry needs, offering tailored solutions for different sectors.
14. Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: Enabled with connectivity options for remote monitoring and diagnostics, allowing for proactive maintenance and swift issue resolution.
15. Compliance with Industry Standards: Adheres to relevant industry regulations and standards, ensuring compliance and quality assurance.
These comprehensive features of a secondary packaging machine drive efficiency, quality, and adaptability in packaging operations.
List Application of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
Secondary packaging machines play a pivotal role in ensuring that products are efficiently and safely packaged for distribution and sale. Here are key applications of secondary packaging machines:
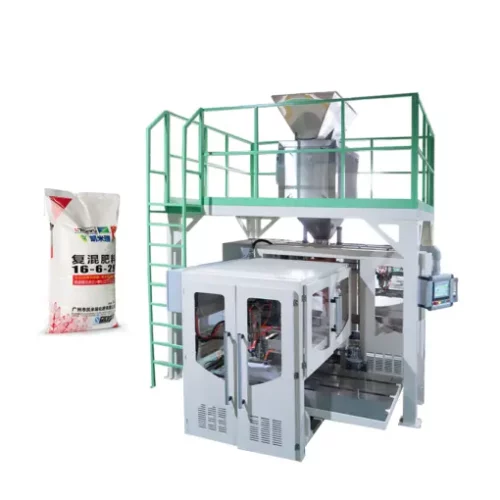
1. Cartoning: These machines automatically pack products into cartons, ideal for items like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food products, ensuring tamper-proof and clean packing.
2. Case Packing: Used extensively in industries like beverage, food, and consumer goods, case packers arrange and pack individual items into outer cases for bulk handling and transportation.
3. Shrink Wrapping: Applicable in retail, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, shrink wrapping machines wrap items in a polymer film, which is then shrunk to conform to the product shape for protection and visual appeal.
4. Tray Packing: Popular in the food and beverage industry, tray packers load products into trays, which can be easily stacked and transported.
5. Palletizing: Automation in palletizing helps industries like warehousing, logistics, and manufacturing stack products on pallets in a systematic manner, optimizing space and transportation efficiency.
6. Bundling: Frequently used in the beverage industry, bundling machines wrap multiple items together, such as bottles or cans, making them easier to handle and transport as a single unit.
7. Flow Wrapping: Employed in packaging various items like confectioneries, snacks, and small consumer goods by enclosing them in a protective film, enhancing shelf-life and presentation.
8. Overwrapping: Used in packaging high-end products like chocolates, perfumes, and high-value pharmaceuticals to enhance aesthetic appeal and provide an additional protective layer.
9. Labeling: Important for pharmaceuticals and food products, these machines ensure that each package is accurately labeled with essential information like ingredients, usage instructions, and expiration dates.
10. Strapping: Strapping machines are essential in the logistics and shipping industries to secure packages and prevent movement during transit, ensuring product integrity.
Secondary packaging machines amplify efficiency, enhance product protection, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, making them indispensable across various industries.
List Various Types of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
Secondary packaging machines play an essential role in preparing products for distribution and sale, offering an additional layer of protection and aiding in the product handling process. Here are various types of secondary packaging machines:
1. Cartoning Machines:
– Horizontal Cartoners: Insert products horizontally into cartons.
– Vertical Cartoners: Insert products vertically, suitable for granules or loose parts.
2. Case Packing Machines:
– Wrap-around Case Packers: Wrap cases around groups of products.
– Drop Packers: Drop products into cases from above.
3. Shrink Wrapping Machines:
– L-Bar Sealers: Create a loose shrink film around products.
– Side Sealers: Continuous sealing for longer products.
4. Palletizing Machines:
– Robotic Palletizers: Use robotic arms for precision stacking.
– Conventional Palletizers: Use mechanical systems for stacking.
5. Tray Packaging Machines:
– Form-Fill-Seal Tray Packers: Form trays, fill them with products, and seal.
– Wrap-around Tray Packers: Wrap product into a tray to ensure rigidity.
6. Bag-in-Box Packaging Machines:
– Semi-automatic bag inserters: Insert and seal bags manually within boxes.
– Automatic bag-in-box systems: Fully automated, including bag insertion, filling, and sealing.
7. Overwrapping Machines:
– Flow Wrappers: Wrap products individually.
– Fold Wrappers: Fold wrapping material around products for a neat finish.
8. Stretch Wrapping Machines:
– Turntable Stretch Wrappers: Rotate products on turntables while wrapping.
– Rotary Arm Stretch Wrappers: Stationary products with wrapping arms moving around them.
These machines enhance product integrity, streamline transportation, and facilitate easier handling and stocking, thereby supporting efficient supply chain management.
Custom Manufacturing Options for Secondary Packaging Machine
Custom manufacturing options for secondary packaging machines are essential to meet specific industry needs, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. Here are key customizable features:
1. Machine Size and Configuration:
– Footprint: Tailor the machine dimensions to fit in existing space constraints.
– Modules: Select modular designs for flexibility in production line reconfiguration.
2. Packaging Types:
– Cartoners: Custom size and shape to match the product.
– Case Packers: Options for wrap-around, side-load, or top-load cases.
– Tray Packers: Adaptability in tray size and material.
3. Speed and Throughput:
- Adjust machine speed to match production requirements.
- Incorporate high-speed options for demanding applications.
4. Material Handling:
– Conveyors: Custom lengths, widths, and materials to suit product handling.
– Grippers and Feeders: Designed for delicate products like pharmaceuticals or rigid items like bottles.
5. Integration Capabilities:
– ERP Systems: Seamless integration with existing ERP systems for real-time data tracking.
– Robotics: Integration of robotic arms for precise and automated packaging tasks.
6. User Interface:
– Touchscreen HMIs: Customizable interfaces for easy operation.
– Multi-language support: Essential for multinational operations.
7. Quality Control:
– Vision Systems: Tailored for specific defect detection and verification.
– Weight Checkers: Adjust for precision required, varying from grams to kilograms.
8. Material Specifications:
- Optimized for specific packaging materials, whether it’s cardboard, plastic, or biodegradable materials.
9. Industry Compliance:
- Custom designs to adhere to sector regulations, such as FDA requirements for food and pharmaceuticals.
10. Safety Features:
- Bespoke safety features, including guards, emergency stops, and interlocks.
11. Sustainability Features:
- Options for energy-efficient components and recyclable materials.
By opting for custom manufacturing, companies can ensure their secondary packaging machines are finely tuned to their unique operational needs, promoting efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
Quality Control in Secondary Packaging Machine Manufacturing
1. Incoming Material Inspection:
- Assess components like frames, motors, belts, and electronic parts upon receipt.
- Use precision tools (calipers, micrometers) for measurement accuracy.
2. In-Process Inspection:
- Conduct checks during various assembly stages.
- Functional testing of sub-assemblies (e.g., conveyor belts, sealing units).
3. Final Assembly Inspection:
- Ensure all components are correctly assembled and securely fastened.
- Perform operational tests to verify machine functionality.
4. Performance Testing:
- Run the machine with actual packaging materials.
- Monitor for consistency, speed, and accuracy in packaging processes.
5. Safety and Compliance Check:
- Verify alignment with industry standards (ISO, CE).
- Perform electrical safety tests and risk assessments.
6. Documentation:
- Maintain detailed records of inspections, tests, and certifications.
- Develop user manuals and maintenance guides.
Manufacturing Process of Secondary Packaging Machine
1. Design and Prototyping:
- Develop detailed CAD models.
- Create prototypes for initial functional assessment.
2. Material Procurement:
- Source high-quality metals, electronics, and plastics.
- Establish supply chain for consistent material quality.
3. Fabrication:
- Cut, weld, and machine metal components to precise specifications.
- Assemble frames, gears, and other main components.
4. Component Assembly:
- Integrate electrical and mechanical parts.
- Utilize specialized jigs and fixtures for accuracy.
5. Sub-Assemblies Integration:
- Combine various sub-assemblies into the main machine.
- Include conveyor systems, sealing units, and control panels.
6. Wiring and Control System Installation:
- Install electrical wiring and control systems.
- Program PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for operation.
7. Testing and Calibration:
- Conduct comprehensive testing (mechanical, electrical, software).
- Calibrate settings for optimal performance.
8. Finishing and Packaging:
- Apply protective coatings.
- Pack machines securely for shipment.
By maintaining stringent quality control and meticulously following each manufacturing step, a reliable and efficient secondary packaging machine can be produced.
How to use "Secondary Packaging Machine"
A Secondary Packaging Machine is designed to encase already primary-packaged products into an additional layer of packaging such as cartons, cases, or shrink wraps. Here’s a basic guide on how to use it:
1. Preparation: Ensure the machine is on a flat, stable surface. Verify that all components are clean and free of debris. Check that the machine is properly assembled and connected to a power source.
2. Loading the Machine:
– Material Handling: Load the secondary packaging material (e.g., cartons, wraps) into the designated feeder or magazine.
– Product Input: Place the primary-packaged products on the in-feed conveyor or hopper.
3. Settings and Adjustments:
- Adjust the machine settings to match the size and type of packaging and product.
- Set parameters on the control panel, which may include speed, temperature (for shrink wraps), and folding or sealing preferences.
4. Operation:
- Start the machine using the main control panel.
- The machine will automatically begin feeding the primary packages into the secondary packaging material, folding, sealing, and labeling as per the set parameters.
- Monitor the process through any available display panels to ensure smooth operation.
5. Quality Control:
- Regularly inspect the output to ensure quality standards are met.
- Make necessary adjustments on the machine if any inconsistencies or issues arise.
6. Maintenance and Safety:
- Turn off and unplug the machine before performing any maintenance.
- Regularly clean the machine to prevent buildup and blockages.
- Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines to keep the machine in optimal working condition.
- Observe all safety protocols to prevent accidents, including using protective gear and ensuring guards and shields are in place.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use a Secondary Packaging Machine to enhance your packaging process.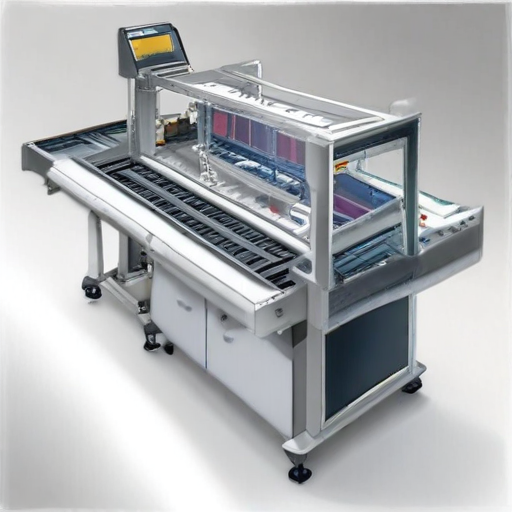
List Properties and Terms of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
Secondary Packaging Machine: Key Properties and Terms
Properties:
1. Automation: Highly automated for increased efficiency and consistency.
2. Versatility: Capable of handling various packaging materials and sizes; adaptable to different product types.
3. Speed: High throughput capabilities to match the production line speed.
4. Durability: Robust construction to withstand continuous operation under industrial conditions.
5. Precision: Ensures accurate packaging to prevent product damage and maintain presentation quality.
6. Ease of Maintenance: Designed for easy access to components for routine checks and repairs.
7. Flexibility: Configurable settings for different packaging formats, such as boxes, cartons, and trays.
8. Integration: Can be seamlessly integrated with upstream and downstream equipment, such as primary packaging machines and palletizers.
9. Safety Features: Equipped with safety guards and emergency stops to protect operators.
10. User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive controls, often with touchscreens and programmable settings.
Terms:
1. Cartoning: The process of placing products into cartons.
2. Case Packing: Placing cartons into larger tertiary packaging cases.
3. Tray Packing: Arranging products on trays, which might be wrapped or shrink-wrapped.
4. Shrink Wrapping: A secondary packaging method using plastic film that shrinks when heated to encase products.
5. Palletizing: Stacking and securing packaged products onto pallets for transport.
6. Batch Coding: Printing or marking codes onto packages for identification and traceability.
7. Collation: Gathering and arranging multiple products together into a secondary package.
8. Sleeving: Applying a sleeve or band around a group of products.
9. Manual Override: A control feature that allows operators to manually intervene in machine operations if needed.
10. Inspection Systems: Integrated technology to ensure quality control, such as checking for correct weight, presence, or orientation.
A secondary packaging machine is quintessential in modern manufacturing, ensuring products are securely packed and ready for distribution while maintaining efficiency and safety standards.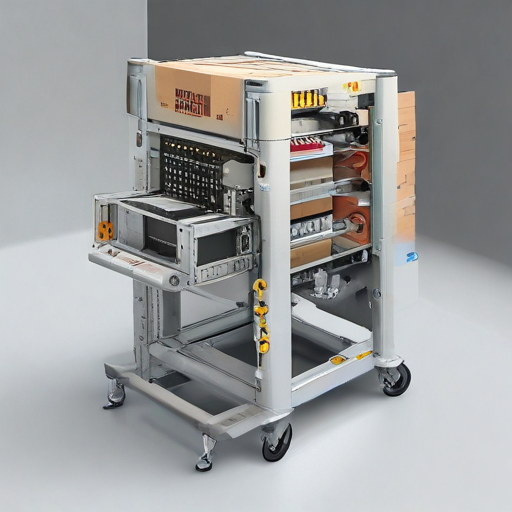
List The Evolution history of "Secondary Packaging Machine"
The history of secondary packaging machines, which work by automatically packaging already primary-packaged products into cartons, cases, or pallets, marks significant advancements in industrial automation and packaging technology.
Early 20th Century: Manual Assembly
Initially, secondary packaging was a manual process involving workers assembling products into boxes and securing them with adhesives or tape.
1940s-1950s: Mechanized Solutions
Mechanical aids such as semi-automatic case sealers and palletizers emerged, helping reduce labor intensity and increase throughput.
1960s-1970s: Integrated Systems
The integration of forming, filling, and sealing processes into one automated system took place, streamlining secondary packaging. Machines started to use simple electrical controls and pneumatics to automate repetitive tasks.
1980s-1990s: Microprocessor Controls
Advances in electronics led to the incorporation of microprocessors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This enhancement facilitated better precision, control, and efficiency. Machines became more adaptable to varying package types and sizes.
2000s: Advanced Robotics and Servo Technology
The advent of robotics and servo technology provided improved flexibility and reliability. Robots were integrated for tasks like palletizing, alongside advanced vision systems for quality control.
2010s: Intelligent Systems and IoT
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology allowed secondary packaging machines to connect with other systems for real-time data sharing. Smart sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) enhanced predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
Present Day: Sustainable and AI-Driven Solutions
Today’s focus is on sustainability, reducing material waste, and energy consumption. AI-driven systems enhance functionality, enabling more versatile, faster, and precise packaging processes tailored to a diverse range of products and packaging needs.
In summary, from manual assembly to highly intelligent and sustainable automation, the evolution of secondary packaging machines has been driven by technological innovations aimed at improving efficiency, precision, and adaptability.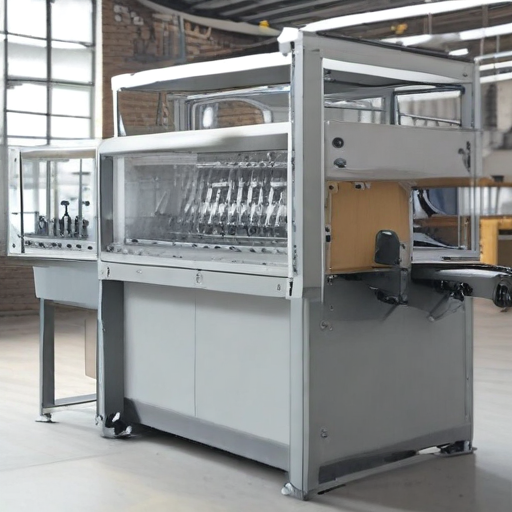
How to Select a Reliable Secondary Packaging Machine
Selecting a reliable secondary packaging machine is crucial for ensuring efficiency and protecting products in transit. Here are key guidelines to make an informed decision:
1. Assess Your Needs:
Analyze the specific packaging requirements of your products, including size, shape, and fragility. Consider production volume and speed, as these will influence machine capacity and efficiency.
2. Quality and Reliability:
Look for machines from reputable manufacturers known for durable equipment. Check for certifications and industry standards compliance. Read reviews and get references from existing users to gauge reliability.
3. Flexibility and Customization:
Choose a machine that can handle various packaging formats and materials. Flexibility to adapt to changing product lines is vital for long-term usability.
4. Ease of Operation and Maintenance:
Select equipment that is user-friendly with straightforward controls. Consider machines that offer easy maintenance, with accessible parts and support from the manufacturer.
5. Integration Capabilities:
Ensure the machine can seamlessly integrate with existing systems and other equipment on your production line to maintain a smooth workflow.
6. Cost and ROI:
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial investment, maintenance costs, and potential downtime. Compare this with the expected efficiency gains and quality improvements to determine the return on investment.
7. Support and Service:
Opt for suppliers who provide robust after-sales support, including training, maintenance services, and quick response to repairs. This minimizes potential downtime and ensures the machine runs reliably.
8. Trial and Testing:
Whenever possible, request a trial or demonstration to see the machine in action under conditions similar to your own production environment. This will give you a better understanding of its performance and reliability.
By focusing on these critical aspects, you can select a secondary packaging machine that meets your requirements, enhances productivity, and ensures long-term reliability.
List "Secondary Packaging Machine" FAQ
Certainly! Here’s a concise list of FAQs regarding Secondary Packaging Machines:
-
What is a Secondary Packaging Machine?
A Secondary Packaging Machine is a device used for packaging products that have already been primary packaged (e.g., boxed, bottled). Its primary function is to group these primary packages for easier transport, storage, and display. -
What types of secondary packaging can these machines handle?
They can handle a variety of packaging types, including cartons, cases, shrink wraps, trays, and pallets. -
What industries use Secondary Packaging Machines?
Industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer goods use these machines to efficiently manage their packaging processes. -
How does a Secondary Packaging Machine improve efficiency?
By automating the grouping and packaging process, these machines reduce manual labor, enhance speed, improve packing consistency, and minimize errors. -
Can a Secondary Packaging Machine be customized?
Yes, many machines can be customized to fit specific packaging needs, including size, shape, and type of secondary packaging material. -
What is the difference between primary and secondary packaging?
Primary packaging directly contains the product (e.g., a bottle for liquids), while secondary packaging groups primary packages together for easier handling (e.g., placing multiple bottles into a carton). -
How do I maintain a Secondary Packaging Machine?
Regular maintenance involves cleaning, checking for worn parts, lubricating moving components, and ensuring all mechanical and electronic parts function properly. -
What are the common features of Secondary Packaging Machines?
Common features include automated feeding systems, sensors for quality control, adjustable settings for different package sizes, and user-friendly interfaces. -
Are these machines compatible with other packaging machinery?
Yes, they are often designed to seamlessly integrate with primary packaging machines and other components within a packaging line. -
What are the costs associated with Secondary Packaging Machines?
Costs vary depending on the complexity, brand, customization needs, and capacity of the machine. Initial investment is balanced by long-term savings in labor and increased efficiency.
This list covers the essential FAQs about Secondary Packaging Machines, providing a basic understanding for those interested in utilizing them in their operations.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about Secondary Packaging Machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about sourcing Secondary Packaging Machines from China, with concise answers.
-
What is a Secondary Packaging Machine?
Secondary packaging machines handle the packaging of already-packed primary products, including tasks such as boxing, palletizing, and wrapping. -
Why should I source a Secondary Packaging Machine from China?
China offers a cost-effective solution with a variety of manufacturers providing high-quality machinery, advanced technology, and customizable options. -
How do I ensure the quality of the machine?
Look for manufacturers with ISO certification, positive customer reviews, and who offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales service. -
What types of Secondary Packaging Machines are available?
Options include cartoning machines, case packers, shrink wrappers, palletizers, and stretch wrappers, each suitable for different packaging needs. -
What should I consider when selecting a machine?
Consider factors like the type of products, packaging speed, level of automation, compatibility with existing systems, and available space. -
Is customization possible?
Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization to meet specific requirements such as product size, packaging material, and automation levels. -
What about the costs involved?
Costs vary widely based on the machine’s features and complexity. Be sure to consider additional costs such as shipping, taxes, and installation. -
How can I check the manufacturer’s credibility?
Verify the manufacturer’s credentials through third-party audits, request case studies, and ask for references from existing clients. -
What is the lead time for delivery?
Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the machine’s complexity and customization needs. Always consult with the manufacturer for a precise timeline. -
What after-sales support is provided?
Many manufacturers offer comprehensive after-sales services, including installation, training, maintenance, and readily available spare parts.
These FAQs and answers should help buyers make informed decisions when sourcing secondary packaging machines from China.