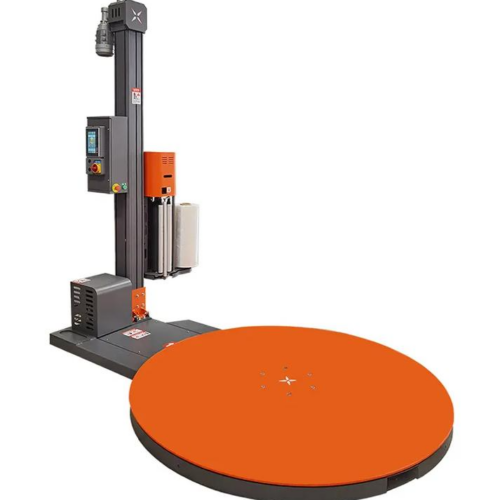
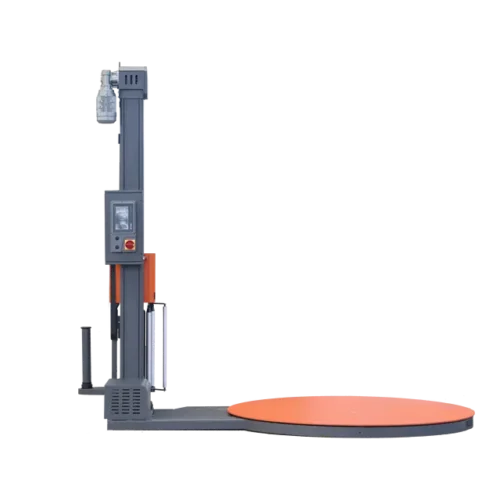
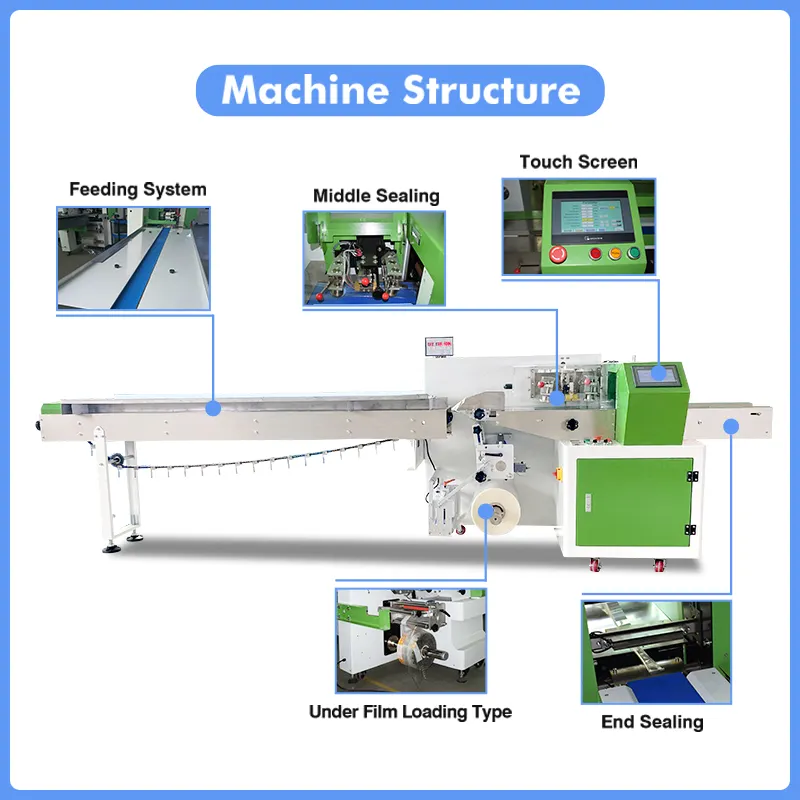
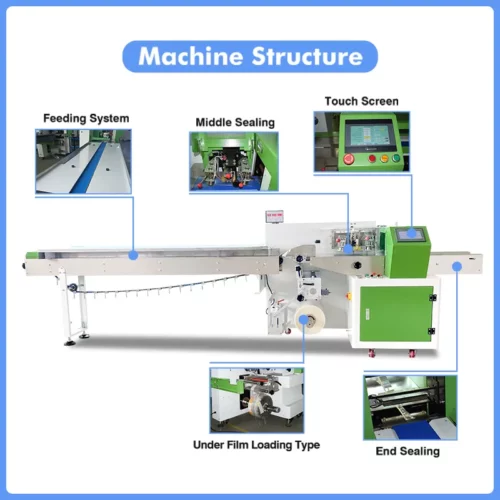
List Technical Parameters of "wrapping machine"
Technical Parameters of a Wrapping Machine
1. Speed: Measured in units per minute (UPM), this defines how many packages the machine can wrap within a minute.
2. Film Type: Specifies the type of wrapping film that can be used, such as polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polypropylene (PP).
3. Film Thickness: Indicates the range of film thickness the machine can handle, typically measured in micrometers (µm).
4. Package Size Range:
– Length: Minimum and maximum length of packages the machine can wrap.
– Width: Range of package widths accommodated.
– Height: Height limits for the packages.
5. Wrapping Material Width: The maximum width of the film material roll that can be installed in the machine.
6. Tension Control: Degree of tension applied to the film, often adjustable to cater to different types of products.
7. Power Consumption: Measured in kilowatts (kW), this indicates the amount of electrical power the machine requires for operation.
8. Voltage and Frequency: The electrical specifications, typically indicated in volts (V) and hertz (Hz), required for the machine to function.
9. Temperature Control: For machines that heat-seal the wrap, the temperature range and control accuracy.
10. Cycle Time: The time needed to complete one full wrapping cycle, affecting overall productivity.
11. Machine Dimensions:
– Length: Total length of the machine.
– Width: Total width of the machine.
– Height: Maximum height of the machine.
12. Weight: The overall weight of the machine, typically measured in kilograms (kg).
13. Automation Level: Degree of automation, such as semi-automatic or fully automatic, which affects the manpower needed.
14. Control System: Type of control interface, such as touchscreen, PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), or manual controls.
15. Safety Features: Include emergency stop buttons, safety guards, and sensors to prevent accidents.
16. Loading and Unloading Mechanism: Type and efficiency of systems for loading products onto and unloading them from the machine.
17. Expandability: Possibility for future upgrades, such as additional modules for different wrapping styles or enhanced speed.
These parameters help in selecting the right wrapping machine based on specific operational needs and constraints.
List Product features of "wrapping machine"
Certainly! Here are the key features of a wrapping machine:
1. Automatic Operation: Automated systems reduce the need for manual intervention, increasing efficiency and output.
2. Adjustable Settings: Customizable parameters for wrap tension, speed, and wrap cycles to suit various packaging requirements.
3. High-Speed Performance: Capable of wrapping a large number of packages per hour, optimizing productivity for high-volume operations.
4. Versatility: Suitable for different types of wraps including stretch film, shrink wrap, and bundling film, accommodating a variety of product sizes and shapes.
5. User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use control panels with touch screens for quick set-up, operation, and monitoring.
6. Robust Construction: Durable materials and sturdy design ensure longevity and reliable performance even under continuous usage.
7. Precision Wrapping: Advanced sensors and control mechanisms for consistent, quality wrapping with minimal waste.
8. Safety Features: Emergency stop functions, safety guards, and other safety protocols to protect operators during use.
9. Energy Efficiency: Designed for minimal power consumption, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
10. Integration Capability: Compatible with other line equipment like conveyors, labeling, and strapping machines, facilitating seamless production processes.
11. Minimal Maintenance: Designed for easy maintenance with accessible parts and straightforward troubleshooting.
12. Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces labor costs and product damage, providing a quick return on investment.
13. Space Efficiency: Compact designs available for operations with limited floor space.
14. Packaging Consistency: Ensures uniform wrapping, enhancing product presentation and protection.
15. Intelligent Controls: Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for precise and adaptive operations based on the specific needs of different packaging tasks.
By incorporating these features, wrapping machines significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure high-quality packaging.
List Application of "wrapping machine"
A wrapping machine is a versatile piece of equipment used in various industries to package products efficiently and securely. Below are several applications of wrapping machines:
1. Food Industry: Wrapping machines are widely used to package fresh produce, baked goods, meat, and confectionery items, preserving their freshness and extending shelf life. For example, cling film wrapping machines are commonly used to pack fresh fruits and vegetables.
2. Retail Packaging: In retail, wrapping machines help in packaging items like books, electronic gadgets, and household goods, providing an extra layer of protection during transport and enhancing product presentation.
3. Pharmaceuticals: These machines are essential for packaging medicines, medical devices, and other healthcare products, ensuring they remain sterile and uncontaminated.
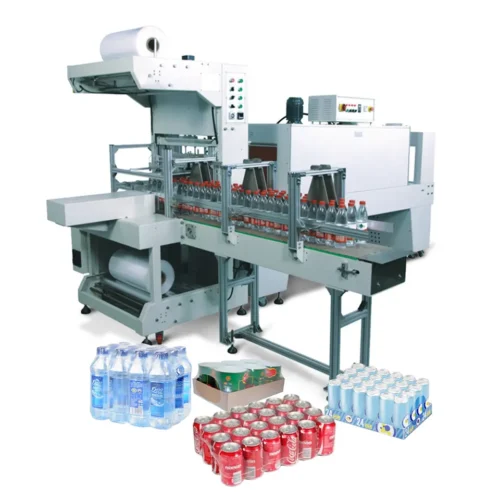
4. Beverages: Wrapping machines are employed to bundle cans and bottles, facilitating easier handling and transportation. Shrink-wrapping is a common method used in this sector.
5. Textile Industry: Textile manufacturers use wrapping machines to package clothing, fabric rolls, and linens, protecting them from dust and damage during storage and transport.
6. Automotive: In the automotive sector, wrapping machines are used to package spare parts, tires, and other components, ensuring they reach their destination in perfect condition.
7. Logistics and E-commerce: Wrapping machines are crucial in logistics and e-commerce for packaging parcels and pallets securely, enhancing protection during shipping and reducing the risk of tampering.
8. Consumer Goods: Many consumer products such as toys, cosmetics, and stationery are packaged using wrapping machines to improve their marketability and protection.
9. Agriculture: Wrapping machines are used to pack agricultural products like hay bales, ensuring they stay dry and retain their quality.
10. Industrial: In various manufacturing industries, wrapping machines are used for packaging machinery parts, equipment, and tools, safeguarding them against moisture, dust, and corrosion.
By automating the packaging process, wrapping machines improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance the overall quality and safety of the packaged products.
List Various Types of "wrapping machine"
Wrapping machines come in various types, each designed for specific packaging needs. Here are several prominent types:
1. Flow Wrappers: These machines wrap products in a continuous, horizontal motion. The product is placed on a film that is then sealed around it, commonly used for food items like chocolate bars and baked goods.
2. Shrink Wrappers: Shrink wrapping machines use heat to shrink a plastic film tightly around products. They are widely used for packaging multiple items together, such as bottled beverages or software boxes.
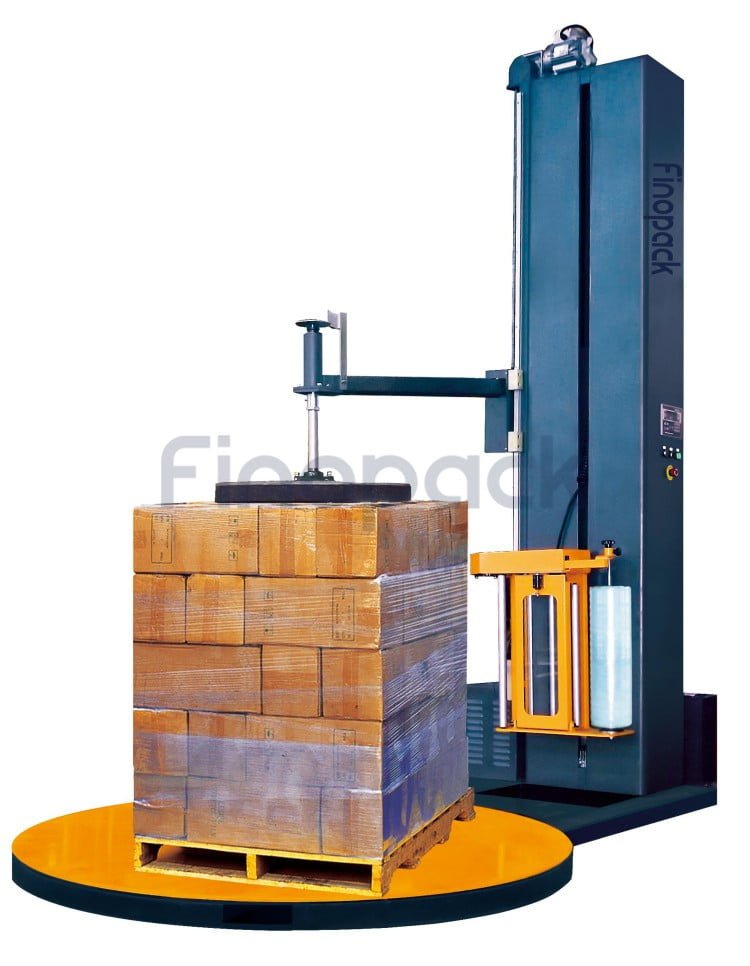
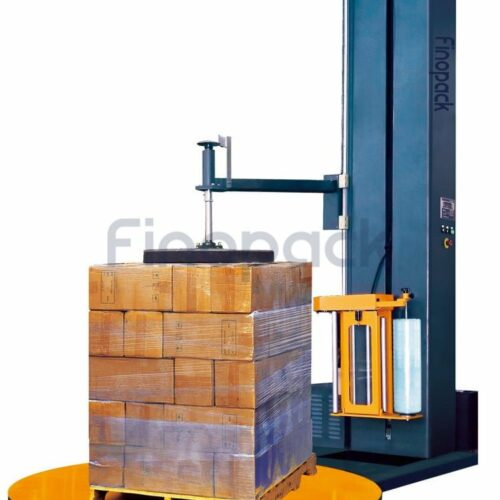
3. Stretch Wrappers: These are used for wrapping pallets with stretch film. Stretch wrappers apply a tight, stretchable film around the pallet to secure and stabilize products during transportation.
4. Bundling Machines: Designed to wrap multiple items together, often using a large plastic film. Bottled beverages and bulk items often use bundling machines for unitizing and securing products.
5. Overwrapping Machines: Overwrapping machines, also known as fold wrapping machines, wrap the product with a film or paper that is folded and sealed like a gift wrap. Commonly used for luxury items and cosmetic goods.
6. L-Bar Sealers: These machines use an L-shaped sealing bar to enclose products in shrink film before heat shrinking. Suitable for a variety of products, from books to food items.
7. Horizontal Wrappers: These are similar to flow wrappers but are used for larger items that require horizontal wrapping. Often utilized for industrial products and furniture.
8. Sleeve Wrappers: These machines wrap a sleeve of plastic around products, followed by a heat tunnel to shrink the film. Suitable for multipacks and bulkier items.
9. Bagging Machines: These machines are used to place products into preformed bags or create a bag from a film roll. They are common in the food industry for packaging snacks and other goods.
10. Rotary Wrappers: These machines encapsulate products using rotating wrapping mechanisms, ideal for heavy-duty and continuous wrapping.
Each type of wrapping machine caters to distinct packaging types, enhancing the protection, appearance, and transport efficiency of products.
Custom Manufacturing Options for wrapping machine
When considering custom manufacturing options for a wrapping machine, it’s essential to tailor the design to meet specific operational needs and packaging requirements. Here are key customizable aspects:
1. Machine Type:
– Horizontal or Vertical Wrappers: Choose between these based on product orientation and space constraints.
– Automatic or Semi-Automatic: Automation level affects speed and labor involvement.
2. Material Compatibility:
- Ensure the machine can handle various wrapping materials, such as shrink film, stretch film, or polyethylene.
3. Size and Capacity:
- Customizable dimensions to accommodate different product sizes.
- Adjustable throughput rates to match production demands.
4. Film Delivery System:
- Options for different film roll diameters and core sizes.
- Variable tension control to suit different film types and thicknesses.
5. Control Systems:
- Advanced PLCs for precise operation and diagnostics.
- Touchscreen interfaces for user-friendly operation and quick adjustments.
- Integration with existing ERP systems for seamless workflow management.
6. Sealing and Cutting Mechanisms:
- Different seal types (impulse, constant heat, ultrasonic, etc.).
- Custom cutting options to ensure clean edges and prevent film waste.
7. Safety Features:
- Custom guards and emergency stops tailored to the specific operational environment.
- Sensor systems for obstacle detection to prevent accidents.
8. Durability and Maintenance:
- Customizable materials and finishes to withstand specific operational conditions.
- Easy access and modular components to simplify maintenance and reduce downtime.
9. Additional Features:
- Integration with labeling or coding systems.
- Custom feeders or stackers to streamline packaging processes.
10. Energy Efficiency:
- Incorporation of energy-saving components and practices to reduce operational costs.
By focusing on these customizable options, you can optimize a wrapping machine for maximum efficiency, safety, and reliability, tailored precisely to your operational needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "wrapping machine"
Quality Control of Wrapping Machine
1. Incoming Material Inspection: Verify the quality of raw materials like metals, electronics, and plastic components.
2. In-Process Inspection: Regular checks during assembly to ensure parts meet design specifications, involving dimensional analysis and visual checks.
3. Functional Testing: Post-assembly, perform operational tests to ensure the machine wraps items correctly and reliably.
4. Electrical Safety Tests: Ensure compliance with electrical safety standards, checking for proper insulation and functioning circuits.
5. Software Validation: If applicable, test the software controlling the wrapping mechanism for reliability and user-friendliness.
6. Final Inspection: A thorough final check to ensure all parts are correctly assembled, smooth operation, and adherence to customer specifications.
7. Documentation and Certification: Keep detailed records of inspections and tests, providing clients with certifications of quality.
Manufacturing Process of Wrapping Machine
1. Design and Prototyping: Engineers create detailed designs and build prototypes for testing. The design undergoes several iterations based on test results.
2. Material Sourcing: Procure high-quality metals, motors, controls, and other components from trusted suppliers.
3. Component Fabrication: Produce parts like frames, covers, and mechanical elements using CNC machining, laser cutting, or molding.
4. Sub-Assembly: Assemble modules such as the electrical system, wrapping mechanism, and control panel in separate stages.
5. Main Assembly: Integrate all sub-assemblies into the main machine frame. Ensure all connections are secure and components are perfectly aligned.
6. Wiring and Cabling: Connect all electrical parts according to the schematic plans. Perform initial electrical safety checks.
7. Initial Testing: Conduct initial operational tests to identify any faults or misalignments.
8. Quality Control and Adjustment: Make necessary adjustments based on initial test results.
9. Final Testing: Perform extensive testing under real-world conditions to ensure reliability and performance.
10. Packaging and Shipping: Safely pack the machines, complete necessary documentation, and ship to customers.
Both quality control and efficient manufacturing processes are crucial for producing reliable and high-performing wrapping machines.
How to use "wrapping machine"
Using a wrapping machine is a straightforward process that can considerably increase productivity and consistency in packaging. Here’s a step-by-step guide to operating a typical wrapping machine:
1. Setup and Preparation:
– Position the Machine: Place the wrapping machine on a stable surface near the items to be wrapped.
– Load the Film: Install the wrapping film roll onto the machine. Ensure that the film is threaded correctly through the rollers and tensioners as per the machine’s manual.
– Power On: Plug in the machine and switch it on. Allow it to warm up if your machine uses heat for sealing.
2. Adjust Settings:
– Select Film Tension: Adjust the film tension setting to ensure the film wraps tightly around the items without tearing.
– Set Wrapping Preferences: Some machines allow settings for the number of wraps, speed, and film overlap. Adjust these settings based on your requirements.
3. Loading Items:
– Place Items on the Tray/Platform: Arrange the items neatly on the machine’s tray or conveyor belt.
– Ensure Stability: Make sure items are stable and won’t tip over during the wrapping process.
4. Wrapping Process:
– Automatic Operation: For automatic machines, press the start button. The machine will wrap the items with the film and cut it off once the cycle is complete.
– Manual Operation: For manual or semi-automatic machines, activate the wrapping cycle by pressing the relevant buttons or pedals and assist if needed.
5. Sealing and Finishing:
– Heat Seal (if applicable): Depending on the machine type, it may heat-seal the film to secure it.
– Check Wrap Quality: Inspect the wrapped items to ensure they are securely and neatly wrapped.
6. Maintenance:
– Clean the Machine: Regularly clean the rollers and other parts to prevent film buildup.
– Check Components: Periodically check for worn components and replace them as necessary.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use a wrapping machine, leading to better packaging quality and increased operational efficiency.
List Properties and Terms of "wrapping machine"
A wrapping machine is an automated device designed for wrapping products or items in protective material such as plastic, paper, or foil. These machines are widely used in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics to ensure products are securely packaged for transportation, storage, or retail display. Below are some key properties and terms related to wrapping machines:
Properties:
1. Automation: Wrapping machines operate with varying levels of automation, from semi-automatic to fully automatic systems.
2. Material Compatibility: They can handle different types of wrapping materials, including shrink film, stretch film, cellophane, and paper.
3. Speed: Machines can vary widely in their operational speeds, ranging from a few items per minute to hundreds, affecting throughput.
4. Size and Flexibility: Many machines are adjustable to accommodate different product sizes and shapes.
5. Efficiency: Modern wrapping machines are designed for minimal waste and operational downtime, thus enhancing productivity.
6. Durability: Built with robust materials to endure continuous use.
7. Safety Features: Equipped with safety mechanisms to protect operators.
8. Ease of Operation: User-friendly interfaces and programmable settings for quick setup and adjustments.
9. Customization: Options for customization to meet specific industry or product requirements.
Terms:
1. Film Roll: The roll of material used for wrapping items.
2. Heat Seal: A method that uses heat to bond the wrapping material around the product.
3. Shrink Wrapping: A technique where plastic film shrinks tightly around the product when heat is applied.
4. Stretch Wrapping: Wrapping that utilizes elastic film to apply tension around the product.
5. Conveyor: A mechanism for moving products into position for wrapping.
6. Turntable: A rotating platform used in some wrapping machines for even application of the material around the product.
7. Pallet Wrapping: Specialized machines designed to wrap goods stacked on pallets.
8. Load Capacity: The maximum weight or volume the machine can handle per wrap cycle.
9. Film Carriage: The part of the machine that holds and dispenses the wrapping film.
Conclusion:
Wrapping machines significantly improve packaging efficiency and product protection. Their properties, such as automation, material compatibility, and speed, along with specialized terms like shrink wrapping and heat seal, are crucial for understanding their functionality and applications across different industries.
List The Evolution history of "wrapping machine"
The evolution of the wrapping machine traces back to the late 19th century, driven by the burgeoning industrial revolution and the need for efficient packaging solutions.
1. Manual Wrapping (Pre-1880s): The earliest form of wrapping involved manual methods, where workers used paper, cloth, or other materials to wrap products by hand.
2. Automatic Wrappers (1890s): The first patent for an automatic wrapping machine was issued in the late 1890s. These early machines mechanized the process of wrapping candies and chocolates, significantly increasing speed and efficiency.
3. Twist Wrappers (1920s): The 1920s saw the introduction of twist wrapping machines, which became especially popular in the confectionery industry. These machines wrapped small items with a twist at each end, providing a secure and attractive package.
4. Shrink Wrapping (1940s-1950s): Post-World War II, the development of plastic films like polyethylene led to the advent of shrink wrapping. This involved wrapping a product in plastic film and then applying heat to shrink the film tightly around the item. It provided a clear, protective covering and became widely used for various goods.
5. Stretch Wrapping (1970s): The 1970s introduced stretch wrapping, primarily for palletizing. This method used stretchable plastic film to secure items on a pallet, revolutionizing logistics and warehousing by enhancing load stability and protection.
6. Flow Wrappers (1970s-1980s): Emerging in the late 20th century, flow wrapping machines became prevalent for packaging products in a continuous motion, facilitating the high-speed wrapping of food and other consumer goods.
7. Automated Systems (2000s-Present): The advent of computer-controlled machines has brought highly automated and precise wrapping solutions, integrating with production lines for seamless operation. These advanced systems optimize material usage, ensure consistent packaging quality, and improve productivity.
This continuous innovation reflects the growing demand for efficient, cost-effective, and protective packaging solutions across various industries.
How to Select a Reliable wrapping machine
Selecting a reliable wrapping machine requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure it meets your operational needs. Here are steps to guide your selection process:
1. Assess Your Needs: Determine the type and size of products you’ll wrap, the volume of output required, and the specific wrapping style (like shrink wrap, stretch wrap, or flow wrap).
2. Quality and Durability: Look for machines made with high-quality materials. Stainless steel components, for instance, offer rust resistance and long-term durability.
3. Brand Reputation: Research well-known brands that have a solid reputation in the industry. Established brands often provide better reliability, support, and a track record of performance.
4. Ease of Use and Maintenance: Select a machine that is user-friendly and easy to maintain. Machines with straightforward operating procedures and accessible components for cleaning and servicing can reduce downtime and operational costs.
5. Automation Level: Decide between manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic machines based on your production scale. Fully automatic machines offer higher efficiency and lower labor costs but come at a higher initial investment.
6. Customization and Flexibility: Choose a machine that can adapt to different product sizes and shapes if your product range is diverse. Customizable settings can enhance the machine’s versatility.
7. Energy Efficiency: Consider the machine’s energy consumption. Energy-efficient models can save operational costs over time and reduce your environmental footprint.
8. Safety Features: Ensure the machine has adequate safety features to protect operators from accidents and injuries.
9. After-Sales Support and Warranty: Reliable after-sales support, including training, technical support, and warranty, is crucial. A good warranty policy ensures protection against manufacturing defects and peace of mind.
10. Cost: Evaluate the total cost, including initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational expenses. Balance cost with the benefits provided.
By focusing on these factors, you can select a reliable wrapping machine that meets your specific requirements and provides long-term value.
List "wrapping machine" FAQ
Sure! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about wrapping machines:
-
What is a wrapping machine?
A wrapping machine is equipment used to apply a protective layer or film around a product for packaging, transportation, and storage purposes. -
What types of wrapping machines are available?
There are various types, including stretch wrappers, shrink wrappers, flow wrappers, and overwrappers. Each type of machine is designed for specific wrapping needs and materials. -
How does a stretch wrapper differ from a shrink wrapper?
Stretch wrappers use stretchable plastic film to tightly secure products, while shrink wrappers use heat to shrink a plastic film around the product. -
What materials can be used with wrapping machines?
Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polypropylene (PP) films. The choice depends on the product and the type of wrapping machine. -
Are wrapping machines suitable for all products?
Wrapping machines can handle a variety of products, from small items like chocolates to large items like palletized goods. However, the machine’s design and capabilities must match the product’s requirements. -
What are the benefits of using a wrapping machine?
Benefits include increased packaging speed, improved product protection, reduced labor costs, and enhanced product presentation. -
How do I maintain a wrapping machine?
Regular maintenance involves cleaning, lubrication, replacing worn parts, and ensuring proper alignment and tension of wrapping materials. -
What factors should I consider when choosing a wrapping machine?
Key factors include the type and size of products, production speed, machine flexibility, and budget constraints. -
Can wrapping machines be integrated into existing production lines?
Yes, many wrapping machines are designed to be compatible with existing production lines for seamless operation. -
Do wrapping machines require operator training?
Yes, proper training is essential for efficient and safe machine operation, as well as for performing routine maintenance.
This list covers the basics, but always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult with an expert for specific queries related to your needs.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about wrapping machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is a wrapping machine and why should I source it from China?
A wrapping machine automates packaging products with materials like plastic film or paper. Sourcing from China offers cost advantages, diverse options, and high-quality products from reputable manufacturers.
-
What types of wrapping machines are available?
Wrapping machines come in various types such as stretch wrap machines, shrink wrap machines, and flow pack machines. Each serves different packaging needs and product types. -
How do I verify the credibility of a Chinese supplier?
Check for certifications like ISO, review customer feedback, request product samples, and possibly visit the factory. Platforms like Alibaba and Made-in-China also have verification processes. -
What should I consider when choosing a wrapping machine?
Evaluate production speed, machine size, power requirements, compatibility with wrapping materials, and maintenance needs. Match these factors with your specific operational requirements. -
What are the common payment terms?
Suppliers typically accept T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and Western Union. It’s common to pay a 30%-50% deposit and the balance before shipment. -
How is shipping and logistics managed?
Depending on urgency and budget, choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Work with a reliable freight forwarder for smooth customs clearance and delivery. -
What kind of warranty and after-sales service is offered?
Most Chinese suppliers provide a 1-year warranty and comprehensive after-sales services, including remote troubleshooting, spare parts supply, and sometimes on-site support. -
Are there any hidden costs?
Beyond the machine’s cost, factor in shipping, customs duties, installation, and potential spare parts. Clarify all costs with the supplier to avoid surprises. -
How do I ensure quality control?
Insist on third-party inspection before shipment or hire a quality control agency. Checking the machine’s compliance with international standards is also crucial. -
What is the lead time for manufacturing and delivery?
Lead times can vary from a few weeks to several months, depending on the machine’s complexity and customization. Confirm timelines with your supplier to align with your project schedule.